Overview of sustainability-linked loans
-An emerging and promising financing substitute
Surabhi Chura | corplaw@vinodkothari.com
There has been a growing emphasis on sustainability across various sectors including finance, especially, with a growing mandatory requirement of disclosure of sustainability practices by companies around the world. Various sustainability-linked finance products are designed to promote the ESG objectives of the borrower while providing financial solutions.
Traditionally, loans have remained the most common way of raising finance, and sustainable finance is no exception to the same. These loans may be labelled as green loans, social loans, sustainable loans etc. Various organisations have issued voluntary guiding principles around the same[1]. A commonality in these loans is the restriction on the “use of proceeds” – that are directed towards the green, social or sustainable objectives of the borrower. Another form of sustainable finance through loans is Sustainability-linked Loans (SLLs), where the loan contains certain sustainability-linked terms. Contrary to typical green finance products, which allocate funds for designated green projects or assets, SLLs align the loan conditions with the sustainability performance of the borrower.
Other instruments of raising sustainable finance can be through the issuance of labelled bonds or GSS+ bonds. Read more about the same in our article – Sustainable finance and GSS+ bonds. One of the more recent innovative ways of financing sustainability objects of the borrower can be through Sustainability-linked derivatives.
Emergence of SLLs
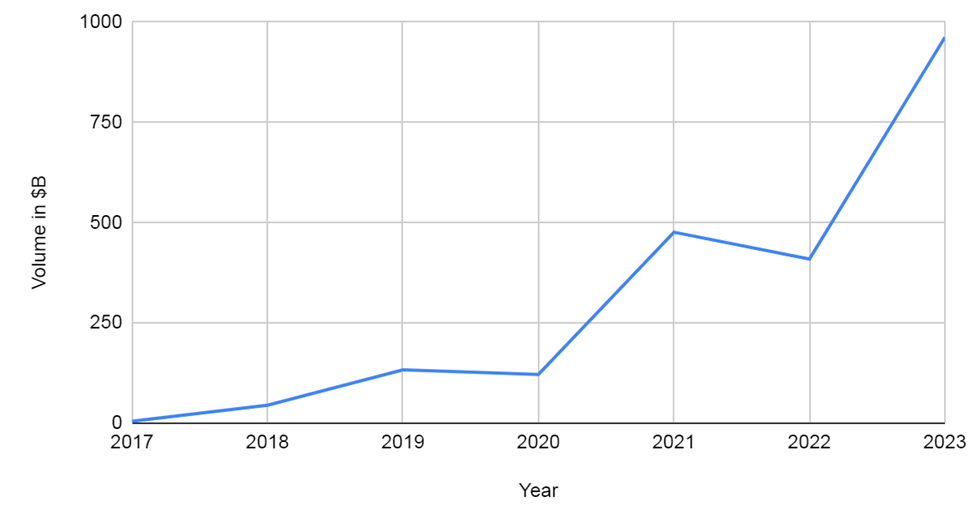
Being first issued in 2017, the market for SLLs has grown exponentially from $4.8 billion to $108 billion in the first eight months of 2023. Since the first issue, SLLs have experienced significant growth, with hundreds of companies worldwide adopting them in debt facilities totalling over $1 trillion.
Initially rooted in socially responsible investment philosophies, ESG investing has now evolved into a distinct responsible investment approach. As the demand for ESG investing is increasing, several prominent trends are emerging.
According to Forbes India, SLLs have emerged as a favoured option for sustainable financing, experiencing remarkable growth despite their relatively brief existence. From a modest $49 billion in 2018, SLLs surged to over $350 billion within the first half of 2021, marking a staggering 614% increase.
According to Bloomberg, with the wide-ranging appeal, SLL borrowers showcase the beauty of SLLs, which can benefit any company from any sector. Real estate firms dominate the SLL market with $97 billion in issuance as of May 2022, closely followed by utilities at $84 billion. However, sectors such as utilities, metals, mining, and chemicals are not far behind and contribute significantly to total issuance in the green loan market.Global issuance of SLLs, dropped nearly 70% to $108 billion in the first eight months of 2023, marking the steepest decline among all categories of ESG debt. Despite reaching over $500 billion in sales in 2021, SLLs remained the second-largest category of ESG debt by overall volume, with approximately $1.2 trillion outstanding as of mid-2023, primarily held by European investment-grade companies.[1]
Deciphering SLLs
Meaning
As per the Sustainability Linked Loan Principles[3]
“Sustainability-linked loans are any type of loan instruments and/or contingent facilities (such as bonding lines, guarantee lines or letters of credit) which incentivise the borrower’s achievement of ambitious, predetermined sustainability performance objectives.”
From the aforesaid definition, the following may be understood:
- Form of facility: SLLs are not limited to pure loans, but extend to other forms of financial instruments such as revolving credit facilities[4], guarantee lines, letters of credit etc.
- [5]Incentives linked with sustainability parameters – The facilities are linked with certain pre-determined sustainability performance objectives.
If the borrower achieves these targets successfully, they receive an incentive. These may include a haircut in the interest rates, or a decrease in the total value of security cover (in the case of secured facility). Conversely, failing to meet the targets may also result in disincentivization resulting in higher borrowing costs. According to the sample-based study report by the Harvard Business School in 2022, it was observed that the interest rates were based on borrowers meeting or missing sustainability targets. The range of sustainability spread adjustments in the tests was about 4.8 basis points to 8.5 basis points,
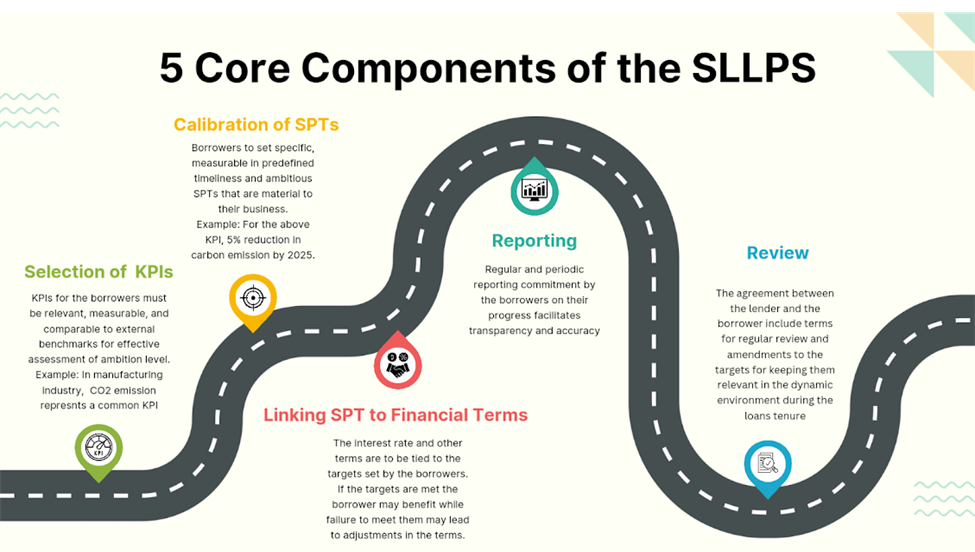
Principles of Sustainability-linked loans
While the earliest instance of raising SLL was in April of 2017, the Sustainability Linked Loan Principles (SLLPs) were published in March 2019 as a result of the collaboration between organizations like LMA, LSTA[6], and APLMA[7]] These principles acted as a catalyst for the subsequent expansion of SLLs in the loan market. The SLLPs (last revised in March 2022) aim to promote sustainable development.
Understanding KPIs and SPTs – key to structuring SLLs
SPTs are essential in SLLs, as they align financial incentives with environmental and social goals. These targets set measurable benchmarks for the borrower’s sustainability commitments and ensure transparency through regular reporting. Success in achieving SPTs triggers financial rewards, while failure may lead to penalties, incentivizing proactive sustainability efforts and embedding sustainability into strategic decision-making. A single SLL agreement can accommodate several SPTs. For instance, a borrower can aim to reduce their water consumption by 10% per year over the duration of financing or, improve its gas emission by 25% and increase the number of women on its board. Every year, the company would be required to show lenders how it performed against the predefined targets. If a borrower fails to meet their targets, it triggers an escalation in the interest rate. Meeting those targets results in a relaxation in interest rates. This creates an effective reward-punishment mechanism by offering rewards for success and penalties for non-compliance.
One of the companies[8] fixed the SPTs as “Reduce carbon emissions by 25% by 2030, 100% of packaging recyclable, and return 100%+ of water used in drinks through water stewardship.” It has been observed that while now many companies have established ambitious sustainability goals, however, the same was not a priority for a very long time for several manufacturing companies. In what ways can these companies optimize their manufacturing processes, logistics, and daily operations to improve energy efficiency while maintaining high product quality and quantity? While feasible, achieving this goal often requires substantial capital investment, one avenue for securing funds for sustainability projects is by linking loans to sustainability performance. Indeed, companies are demonstrating their commitment to sustainability by investing in initiatives that align with their environmental goals.
SPTs play a significant role in raising SLL by ensuring that suppliers adhere to the sustainability criteria set. These criteria may include environmental performance metrics, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions or increasing energy efficiency. By participating in the SPT program, corporates demonstrate their commitment to sustainability, which can positively impact their ability to secure favourable terms for SLLs.
In the context of SLLs, greenwashing could occur if a company takes out a loan with SPTs that are easily achievable, loosely defined, or not truly representative of the company’s overall environmental impact.
For SLLs to be effective in promoting sustainability, it’s crucial to have clear, measurable, and ambitious sustainability targets. Independent verification of the company’s progress on these targets is also essential to prevent greenwashing. Social auditors can play a vital role in ensuring the credibility of SLLs by providing independent verification of a borrower’s performance against their sustainability targets. This helps to mitigate the risk of greenwashing, where a company might make misleading claims about their sustainability efforts.
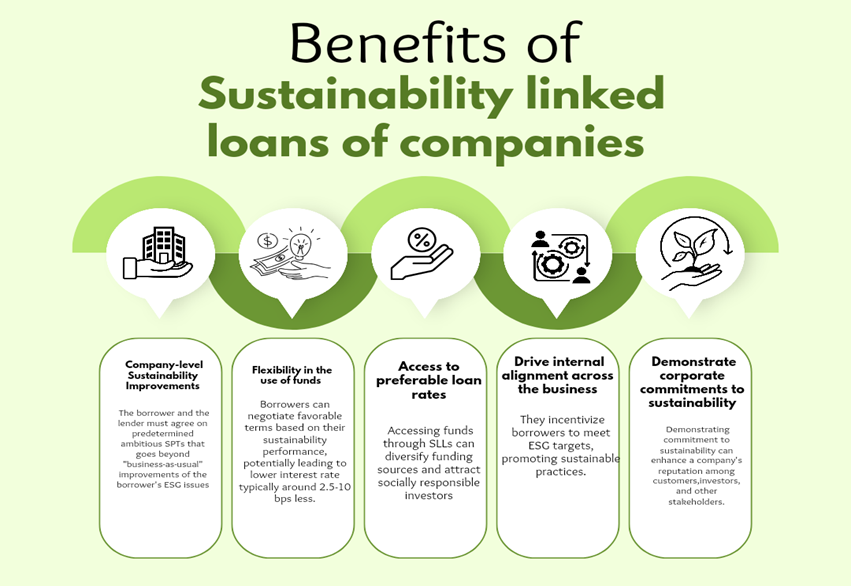
Benefits of raising funds through SLL
Fundraising through SLL offers companies a chance to showcase their dedication to sustainability to various stakeholders, such as customers, employees, and investors.
By linking financial benefits to sustainable objectives, SLLs encourage businesses to adopt sustainable practices, driving positive environmental and social impact while enhancing long-term value creation. For borrowers, SLLs offer several benefits, including access to capital at favourable terms, improved reputation and stakeholder relations, and enhanced resilience to ESG-related risks.
There are several benefits for lenders who participate in the SLL market:
- Attract new clients and diversification of portfolios: SLLs may be a way for lenders to attract companies with strong sustainability practices. This can help diversify a lender’s portfolio and reach a new customer base.
- Enhance reputation: By offering SLLs, lenders can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability too, which can improve the brand reputation.
- Leadership in this space: The SLL market is still growing, and lenders who participate early can establish themselves as leaders in this space. This can be a competitive advantage when attracting new clients.
- Meet sustainability goals: Many lenders have their sustainability targets to meet. SLLs can contribute to achieving these goals by encouraging sustainable practices within the companies they lend to.
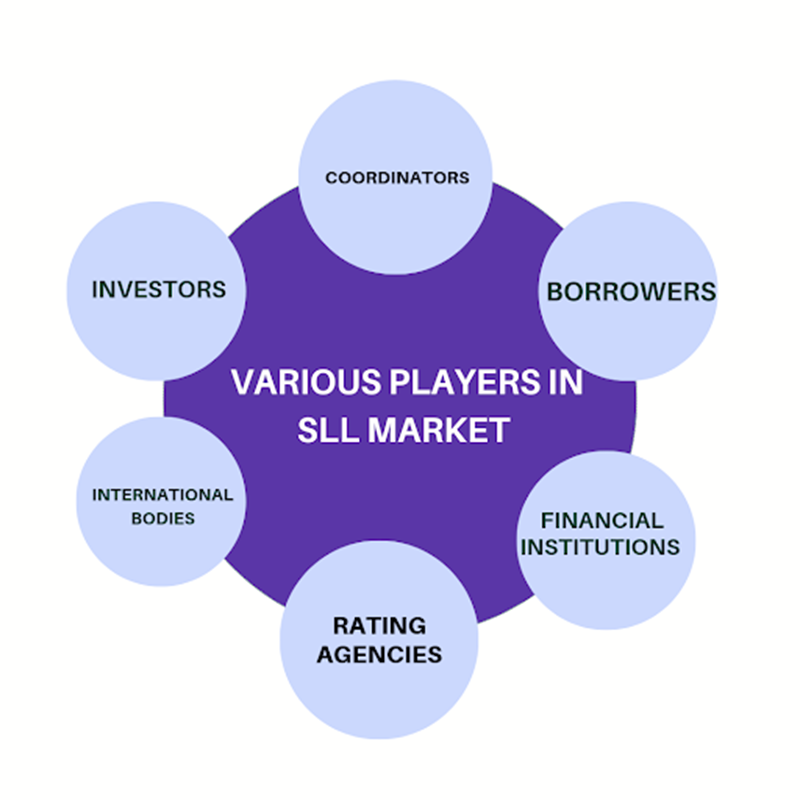
Key stakeholders in the market:
The collective efforts of the stakeholders propel the SLL market forward, enabling the integration of sustainability into mainstream finance and driving positive environmental and social outcomes.
- Banks and financial institutions(FIs): Banks and financial institutions serve as key enablers of sustainable finance by facilitating the development and implementation of SLLs, driving positive environmental and social impact while meeting the financial objectives of borrowers and investors. Several Banks have been propelling SLLs[9]. Banks and FIs have catalyzed the adoption of SLLs among corporates and financial institutions, fostering positive environmental and social impact.
- Corporate borrowers: Corporations and businesses across different industries seek SLLs to finance projects aligned with their sustainability objectives. These borrowers may range from renewable energy companies to manufacturing firms committed to reducing their environmental footprint.
- Sustainability coordinator: According to a survey by the Harvard Business School, a significant portion of the structure for a SLL features a designated sustainability coordinator. This individual or entity plays a crucial role in setting and monitoring the sustainability performance targets outlined in the loan agreement. Their responsibilities often extend to ensuring compliance with ESG criteria throughout the tenure.,
- Rating agencies: Rating agencies assess and rate the environmental and social performance of companies and projects involved in these loans. Their evaluations help investors, lenders, and other stakeholders gauge the sustainability credentials of borrowers and their initiatives. Thereby influencing investment decisions and promoting transparency and accountability in sustainable financing.
Why SLLs over SLBs?
One of the modes of sustainable finance is through the issuance of sustainability-linked bonds or SLBs, read at Moving towards sustainable finance through sustainable bonds.
SLLs and SLBs are valuable tools that offer companies and investors innovative ways to promote sustainability. SLBs are more commonly associated with capital markets and provide broader investor access, while SLLs offer flexibility and customization in loan agreements.
| BASIS | SLBs | SLLs |
| Nature | SLBs are debt securities where the issuer commits to using the funds towards the SPTs. | SLLs are loans where the interest rate is linked to the borrower’s sustainability performance. |
| Market Availability | SLBs are typically available in the capital markets, but less accessible to small businesses. | SLLs are negotiated directly between borrowers and lenders, often banks or financial institutions. More accessible to smaller companies. |
| Market Development | SLBs have seen significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing investor demand for sustainable investment opportunities. | SLLs have gained traction as companies seek financing instruments aligned with their sustainability goals, but the market is still evolving. |
| Maturity | SLBs are debt securities with fixed terms and maturities, limiting investors’ ability to adjust their investment strategy | SLLs are flexible in terms of investment duration and exit options compared to SLBs |
Impact of SLL on Global Finance
As ESG investing gains prominence, numerous companies are seeking to fund their sustainability initiatives in a manner that aligns with their corporate objectives. Several companies including Mercedes-Benz, Coca-Cola, Amazon, Anheuser-Busch, L&T Finance, and JSW Cement have employed SLLs in their businesses.
SLLs in India have been gaining momentum as companies seek financing that aligns with their ESG goals. The SLL market in India is still at the nascent stage compared to other regions like Europe and North America. However, there is growing interest and awareness among Indian businesses about the importance of integrating sustainability into financing strategies.
The sustainability-linked objectives are reviewed and the progress is reported in the annual report. The progress of the company with respect to the objectives shall lead to either a reduction or increase in interest rates on the credit facility availed.
As sustainability continues to gain prominence in the global financial landscape, Indian businesses are likely to increasingly embrace SLLs as a tool for advancing their sustainability objectives while accessing capital.
Conclusion
The growing popularity of SLL reflects a paradigm shift towards sustainable finance products. SLLs embody an innovative strategy to integrate environmental objectives into financial markets, providing a mutually beneficial solution for borrowers, investors, and society as a whole. By incentivizing sustainable behaviour and driving positive impact, these innovative financial instruments have the potential to act as a catalyst for progress towards a resilient future. As businesses increasingly recognize the value of SLL in driving long-term value creation, the momentum for sustainable finance is poised to continue growing, paving the way for a more sustainable and inclusive global economy. With the right frameworks in place, SLLs can serve to empower businesses to thrive in a rapidly evolving landscape while safeguarding the planet for future generations.
Our resource centre on SG and sustainability can be accessed here.
[1] Green loan Principles, Social Loan Principles, Sustainability Linked Loans Principles
[2] Data collated from various sources.
[3] LMA or the Loan Market Association is an international trade association, based in London, that represents the European syndicated loan market. It engages with its members, market participants and various stakeholders to tackle industry-wide issues and concerns and works with tax authorities, government bodies and a variety of national, European and US regulators and plays a crucial role in promoting transparency, efficiency, and integrity in the loan market.
[4] The first ever SLL was issued in April of 2017 was in the form of revolving credit facility is credit facility where the borrower withdraws money for using it to fund general corporate purposes of the business. After the repayment, it can then be withdrawn again when required.
[5] Bank guarantee and letter of credit are both non fund based credit facilities which are promises from a financial institution that a borrower shall be able to repay a debt.
[6] LSTA or the Loan Syndications and Trading Association is a financial services trade group which exists to enhance the development and running of the North American syndicated loan market.
[7] APLMA or the Asia Pacific Loan Market Association, established in 1998, aims to foster growth, enhance liquidity, and promote best practices within the syndicated loan markets across the Asia Pacific region. It facilitates access to regional and national insights for governments and political leaders while offering visibility into innovative approaches and tools crucial for combating malaria.
[8] SPTs of Coca Cola as per their Sustainability Report
[9] Several financial institutions, internationally have been engaged in driving SLLs.

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!