Posts
MoF enables RBI to issue directions, circulars for FDI
/0 Comments/in Corporate Laws, FEMA /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsRBI amends mode of payment and remittance norms for units of Investment vehicles
/0 Comments/in Corporate Laws, FEMA /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsPermits FPIs and FVCIs to use Special Non-Resident Rupee (SNRR) account
CS Burhanuddin Dohadwala| Manager, Aanchal Kaur Nagpal| Executive
corplaw@vinodkothari.com
The Reserve Bank of India (‘RBI’) vide notification dated October 17, 2019 had notified the Foreign Exchange Management (Mode of Payment and Reporting of Non-Debt instrument) Regulations, 2019[1] (‘the Regulations’) governing the mode of payment and reporting of non-debt instruments consequent to the Foreign Exchange Management (Non-Debt Instrument) Rules, 2019[2] framed by the Ministry of Finance, Central Government.
RBI has recently vide its notification dated June 15, 2020 notified Foreign Exchange Management (Mode of Payment and Reporting of Non-Debt Instruments) (Amendment) Regulations, 2020[3] amending Reg. 3.1 dealing with Mode of Payment and Remittance of sale proceeds in case of investment in investment vehicles.
Let us discuss few terms to understand the recent amendments to the Regulations.
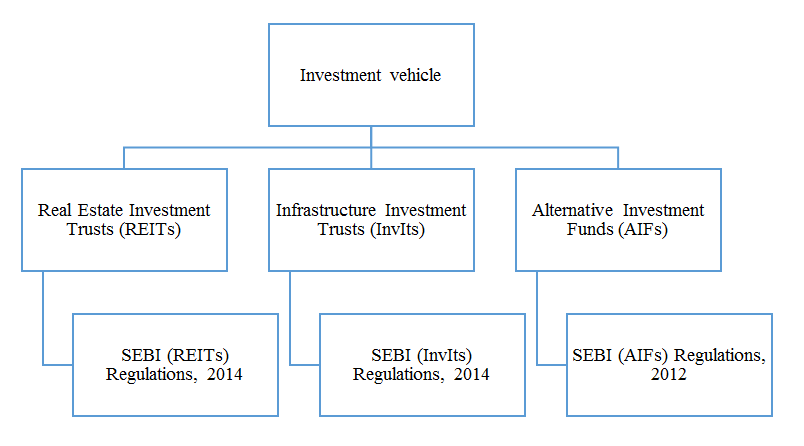
Investment Vehicles under FEMA:
According to FEMA (Non-Debt Instruments) Rules, 2019, investment vehicles mean:
Different types of account available under FEMA (Deposit) Regulations, 2016[1] (‘Deposit Regulations’)
The following are the major accounts that can be opened in India by a non-resident:
| Particulars | Eligible Person |
| Non-Resident (External) Rupee Account Scheme-NRE Account |
Non-resident Indians (NRIs) and Person of Indian Origin (PIOs) |
| Foreign currency (Non-Resident) account (Banks) scheme – FCNR (B) account | |
| Non-Resident ordinary rupee account scheme-NRO account |
Any person resident outside India. |
| Special Non-Resident Rupee Account – SNRR account |
Any person resident outside India. |
A significant advantage of SNRR over NRO is that the former is a repatriable account while the latter is non-repatriable.
What is Special Non-Resident Rupee (‘SNRR’) Account?
Any person resident outside India, having a business interest in India, may open SNRR account with an authorised dealer for the purpose of putting through bona fide transactions in rupees. The business interest, apart from generic business interest, shall include the following INR transactions, namely:-
- Investments made in India in accordance with Foreign Exchange Management (Non-debt Instruments) Rules, 2019 dated October 17, 2019 and Foreign Exchange Management (Debt Instruments)
- Import of goods and services in accordance with Section 5 of the Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999 Regulations, 2019;
- Export of goods and services in accordance with Section 7 of the Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999;
- Trade credit transactions and lending under External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) framework;
- Business related transactions outside International Financial Service Centre (IFSC) by IFSC units at GIFT city like administrative expenses in INR outside IFSC, INR amount from sale of scrap, government incentives in INR, etc;
Rationale behind the amendment:
Position under Master Direction – Foreign Investment in India by RBI
According to Annex 8 of Master Direction – Foreign Investment in India by RBI, investment made by a PROI was permitted with effect from 13th September, 2016. The provisions specify that the amount of consideration of the units of an investment vehicle should be paid out of funds held in NRE or FCNR(B) account maintained in accordance with the Deposit Regulations as one of the modes of payment.
Further it also specifies that the sale/ maturity proceeds of the units may be remitted outside India or credited to the NRE or FCNR(B) account of the person concerned.
Position under the erstwhile provisions of the Regulations
Schedule II of the Regulations (Investments by FPIs) stated earlier that of units of investment vehicles other than domestic mutual fund may be remitted outside India.
However, balances in SNRR account were permitted to be used for making investment only in units of domestic mutual fund and not in Investment Vehicles.
As discussed above, the NRO account is a non-repatriable account while the SNRR account is a repatriable account. Due to the above provisions, investment in Investment Vehicles could not be transferred to the SNRR account for repatriation resulting in ambiguity.
Owing to the above and to increase the inflow of foreign investment, the Government has amended the said provision and allowed FPIs & FVCI to invest in listed or to be listed units of Investment vehicle.
Brief comparison of the pre and post amendment is covered in our Annexure I.
Annexure-I
Comparison of the pre and post amendment
| Schedule | Post amendment | Prior to amendment | Remarks |
| Schedule II w.r.t Investments by Foreign Portfolio Investors | A. Mode of payment
1. The amount of consideration shall be paid as inward remittance from abroad through banking channels or out of funds held in a foreign currency account and/ or a Special Non-Resident Rupee (SNRR) account maintained in accordance with the Foreign Exchange Management (Deposit) Regulations, 2016.
2. Unless otherwise specified in these regulations or the relevant Schedules, the foreign currency account and SNRR account shall be used only and exclusively for transactions under this Schedule.
|
A. Mode of payment
1. The amount of consideration shall be paid as inward remittance from abroad through banking channels or out of funds held in a foreign currency account and/ or a Special Non-Resident Rupee (SNRR) account maintained in accordance with the Foreign Exchange Management (Deposit) Regulations, 2016. Provided balances in SNRR account shall not be used for making investment in units of Investment Vehicles other than the units of domestic mutual fund. 2. The foreign currency account and SNRR account shall be used only and exclusively for transactions under this Schedule.
|
The erstwhile provisions restricted use of SNRR account balance for making investments in investment vehicles other than mutual funds.
As a result FPIs could not use their SNRR account and had to resort to other types of accounts for investment in investment vehicles such as REITs, and InViTs. The recent amendment has removed this restriction. The amendment has been made to provide for the amendment made in Schedule VIII dealing with Investment by a person resident outside India in an Investment Vehicle. |
| B. Remittance of sale proceeds
The sale proceeds (net of taxes) of equity instruments and units of REITs, InViTs and domestic mutual fund may be remitted outside India or credited to the foreign currency account or a SNRR account of the FPI. |
B. Remittance of sale proceeds
The sale proceeds (net of taxes) of equity instruments and units of domestic mutual fund may be remitted outside India or credited to the foreign currency account or a SNRR account of the FPI. The sale proceeds (net of taxes) of units of investment vehicles other than domestic mutual fund may be remitted outside India. |
To align with the amendment made in Schedule VIII dealing with Investment by a person resident outside India in an Investment Vehicle. | |
| Schedule VII w.r.t Investment by a Foreign Venture Capital Investor (FVCI) | For Para A(2):
Unless otherwise specified in these regulations or the relevant Schedules, the foreign currency account and SNRR account shall be used only and exclusively for transactions under this Schedule. |
For Para A(2):
The foreign currency account and SNRR account shall be used only and exclusively for transactions under this Schedule. |
The insertion has been made to align with the amendments proposed in Schedule VIII dealing with Investment by a person resident outside India in an Investment Vehicle. |
| Schedule VIII w.r.t Investment by a person resident outside India in an Investment Vehicle | A. Mode of payment:
The amount of consideration shall be paid as inward remittance from abroad through banking channels or by way of swap of shares of a Special Purpose Vehicle or out of funds held in NRE or FCNR(B) account maintained in accordance with the Foreign Exchange Management (Deposit) Regulations, 2016. Further, for an FPI or FVCI, amount of consideration may be paid out of their SNRR account for trading in units of Investment Vehicle listed or to be listed (primary issuance) on the stock exchanges in India. |
A. Mode of payment:
The amount of consideration shall be paid as inward remittance from abroad through banking channels or by way of swap of shares of a Special Purpose Vehicle or out of funds held in NRE or FCNR(B) account maintained in accordance with the Foreign Exchange Management (Deposit) Regulations, 2016. |
Further, it is clarified that the SNRR account may be used for trading in units of listed as well as to be listed units of investment vehicles and the sale/ maturity proceeds can be credited to the said account. |
| B. Remittance of Sale/maturity proceeds:
The sale/ maturity proceeds (net of taxes) of the units may be remitted outside India or may be credited to the NRE or FCNR(B) or SNRR account, as applicable of the person concerned. |
B. Remittance of sale/maturity proceeds
The sale/maturity proceeds (net of taxes) of the units may be remitted outside India or may be credited to the NRE or FCNR(B) account of the person concerned. |
Link to our other articles:
Introduction to FEMA (NDI) Rules, 2019 and recent amendments:
http://vinodkothari.com/2020/04/introduction-to-fema-ndi-rules-2019-and-recent-amendments/
RBI rationalises operation of Special Non-Resident Rupee A/c:
http://vinodkothari.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/RBI-rationalises-operation-of-SNRR-Account.pdf
[1] http://vinodkothari.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/RBI-rationalises-operation-of-SNRR-Account.pdf
[1] http://egazette.nic.in/WriteReadData/2019/213318.pdf
RBI grants additional 3 months to FPIs under Voluntary Retention Route
/0 Comments/in Corporate Laws, FEMA, RBI /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsShaifali Sharma | Vinod Kothari and Company
In March, 2019, the RBI with an objective to attract long-term and stable FPI investments into debt markets in India introduced a scheme called the ‘Voluntary Retention Route’ (VRR)[1]. Investments through this route are in addition to the FPI General Investment limits, provided FPIs voluntarily commit to retain a minimum of 75% of its allocated investments (called the Committed Portfolio Size or CPS) for a minimum period of 3 years (retention period).However, such 75% of CPS shall be invested within 3 months from the date of allotment of investment limits. Recognizing the disruption posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, RBI vide circular dated May 22, 2020[2], has granted additional 3-months relaxation to FPIs for making the required investments. The circular further addresses the questions as to which all FPIs are covered under this relaxation and how the retention period will be determined.
This article intends to discuss the features of the VRR scheme and the implications of RBI’s circular in brief.
What is ‘Voluntary Retention Route’?
RBI, to motivate long term investments in Indian debt markets, launched a new channel of investment for FPIs on March 01, 2019[3] (subsequently the scheme was amended on May 24, 2019[4]), free from the macro-prudential and other regulatory norms applicable to FPI investment in debt markets and providing operational flexibility to manage investments by FPIs. Under this route, FPIs voluntarily commit to retain a required minimum percentage of their investments for a period of at least 3 years.
The VRR scheme was further amended on January 23, 2020[5], widening its scope and provides certain relaxations to FPIs.
Key features of the VRR Scheme:
- The FPI is required to retain a minimum of 75% of its Committed Portfolio Size for a minimum period of 3 years.
- The allotment of the investment amount would be through tap or auctions. FPIs (including its related FPIs) shall be allotted an investment limit maximum upto 50% of the amount offered for each allotment, in case there is a demand for more than 100% of amount offered.
- FPIs may, at their discretion, transfer their investments made under the General Investment Limit, if any, to the VRR scheme.
- FPIs may apply for investment limits online to Clearing Corporation of India Ltd. (CCIL) through their respective custodians.
- Investment under this route shall be capped at Rs. 1,50,000/- crores (erstwhile 75,000 crores) or higher, which shall be allocated among the following types of securities, as may be decided by the RBI from time to time.
- ‘VRR-Corp’: Voluntary Retention Route for FPI investment in Corporate Debt Instruments.
- ‘VRR-Govt’: Voluntary Retention Route for FPI investment in Government Securities.
- ‘VRR-Combined’: Voluntary Retention Route for FPI investment in instruments eligible under both VRR-Govt and VRR-Corp.
- Relaxation from (a) minimum residual maturity requirement, (b) Concentration limit, (c) Single/Group investor-wise limits in corporate bonds as stipulated in RBI Circular dated June 15, 2018[6] where exposure limit of not more than 20% of corporate bond portfolio to a single corporate (including entities related to the corporate) have been dispensed with. However, limit on investments by any FPI, including investments by related FPIs, shall not exceed 50% of any issue of a corporate bond except for investments by Multilateral Financial Institutions and investments by FPIs in Exempted Securities.
- FPIs shall open one or more separate Special Non-Resident Rupee (SNRR) account for investment through the Route. All fund flows relating to investment through the VRR shall reflect in such account(s).
What are the eligible instruments for investments?
- Any Government Securities i.e., Central Government dated Securities (G-Secs), Treasury Bills (T-bills) as well as State Development Loans (SDLs);
- Any instrument listed under Schedule 1 to Foreign Exchange Management (Debt Instruments) Regulations, 2019 other than those specified at 1A(a) and 1A(d) of that schedule; However, pursuant to the recent amendments, investments in Exchange Traded Funds investing only in debt instruments is permitted.
- Repo transactions, and reverse repo transactions.
What are the options available to FPIs on the expiry of retention period?
| Option 1
|
Continue investments for an additional identical retention period |
|
Option 2
|
Liquidate its portfolio and exit; or
|
| Shift its investments to the ‘General Investment Limit’, subject to availability of limit under the same; or
|
|
| Hold its investments until its date of maturity or until it is sold, whichever is earlier. |
Any FPI wishing to exit its investments, fully or partly, prior to the end of the retention period may do so by selling their investments to another FPI or FPIs.
3-months investment deadline extended in view of COVID-19 disruption
As discussed above, once the allotment of the investment limit has been made, the successful allottees shall invest at least 75% of their CPS within 3 months from the date of allotment. While announcing various measures to ease the financial stress caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, RBI Governor acknowledged the fact that VRR scheme has evinced strong investor participation, with investments exceeding 90% of the limits allotted under the scheme.
Considering the difficulties in investing 75% of allotted limits, it has been decided that an additional 3 months will be allowed to FPIs to fulfill this requirement.
Which all FPIs shall be considered eligible to claim the relaxation?
FPIs that have been allotted investment limits, between January 24, 2020 (the date of reopening of allotment of investment limits) and April 30, 2020 are eligible to claim the relaxation of additional 3 months.
When does the retention period commence? What will be the implication of extension on retention period?
The retention period of 3 years commence from the date of allotment of investment limit and not from date of investments by FPIs. However, post above relaxation granted, the retention period shall be determined as follows:
| FPIS
|
RETENTION PERIOD |
| *Unqualified FPIs | Retention period commence from the date of allotment of investment limit
|
| **Qualified FPIs opting relaxation
|
Retention period commence from the date that the FPI invests 75% of CPS |
| Qualified FPIs not opting relaxation
|
Retention period commence from the date of allotment of investment limit |
*Unqualified FPIs – whose investments limits are not allotted b/w 24.01.2020 and 30.04.2020
**Qualified FPIs to relaxation – whose investments limits not allotted b/w 24.01.2020 and 30.04.2020
What will be the consequences if the required investment is not made within extended period of 3 months?
Since no separate penal provisions are prescribed under the circular, in terms of VRR Scheme, any violation by FPIs shall be subjected to regulatory action as determined by SEBI. FPIs are permitted, with the approval of the custodian, to regularize minor violations immediately upon notice, and in any case, within 5 working days of the violation. Custodians shall report all non-minor violations as well as minor violations that have not been regularised to SEBI
Concluding Remarks
The COVID-19 disruption has adversely impacted the Indian markets where investors are dealing with the market volatility. Given this, FPIs are pulling out their investments from the Indian markets (both equity and debt). Thus, relaxing investments rules of VRR Scheme during such financial distress, will help the foreign investors manage their investments appropriately.
You may also read our write ups on following topics:
Relaxations to FPIs ahead of Budget, 2020, click here
Recommendations to further liberalise FPI Regulations, click here
RBI removes cap on investment in corporate bonds by FPIs, click here
SEBI brings in liberalised framework for Foreign Portfolio Investors, click here
For more write ups, kindly visit our website at: http://vinodkothari.com/category/corporate-laws/
To access various web-lectures, webinars and other useful resources useful for the Corporate and Financial sector, visit and subscribe to our Youtube channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCgzB-ZviIMcuA_1uv6jATbg
[1]https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/NotificationUser.aspx?Id=11561&Mode=0
[2]https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/NotificationUser.aspx?Id=11896&Mode=0
[3]https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/NotificationUser.aspx?Id=11492&Mode=0
[4]https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/BS_CircularIndexDisplay.aspx?Id=11561
[5]https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/notification/PDFs/APDIR19FABE1903188142B9B669952C85D3DCEE.PDF
[6] https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/notification/PDFs/NT199035211F142484DEBA657412BFCB17999.PDF
Introduction to FEMA (NDI) Rules, 2019 and recent amendments
/0 Comments/in Corporate Laws, FEMA /by Vinod Kothari Consultants
For relevant questions discussed during the webinar, click here.
India seals its borders to corporate acquisitions
/1 Comment/in Corporate Laws, FEMA /by Vinod Kothari Consultants– Moves FDI from countries sharing land border with India under approval route
ODI Compliances, Contraventions and Compounding under FEMA
/3 Comments/in Corporate Laws, FEMA, RBI /by Vinod Kothari Consultants