Risk-based Internal Prescription for Audit Function
Qasim Saif | Executive (finserv@vinodkothari.com)
Updated as on June 11, 2021
Introduction
It is a well-known fact that an independent and effective internal audit function is of special importance to all corporates for mitigation of their risk. And it has increased importance for a financial sector entity as it provides for reasonable assurance to the board and its senior management regarding the quality and effectiveness of the entity’s internal control, risk management, and governance framework.
Given the current relatively uncertain economic environment which has put significant pressure on debt servicing capabilities of corporates and businesses, there is a need to critically examine the existing portfolio and take an account of the related risk management and accounting practices.
This on-going stressed situation coupled with the uncertain economic environment and the increased global regulatory watch requires financial institutions to critically evaluate the quality of their regulatory submissions, risk model, capital adequacy, and conduct in the financial markets.
In recent times, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) / Urban Co-operative Banks (UCBs) have grown in size and have become systemically important in the economy given their increased participation in the financial credit market. Just like banks, NBFCs and UCBs face similar risks by virtue of being engaged in financial intermediation activities, hence, it makes sense that their internal audit systems should also broadly align while keeping in mind the principle of proportionality.
Applicability
Earlier this year, RBI had issued RBIA Framework for Strengthening Governance Arrangements for commercial banks, local area banks, small finance banks, and payment banks on 7th January 2021[1].
To increase focus on the risk management function of NBFCs/UCBs, the RBI on 3rd February 2021[2] issued a circular prescribing the requirement for Risk-Based Internal Audit (RBIA Framework). The requirements prescribed under the circular are to be implemented by 31st March 2022.The said circular is applicable on-
The framework for NBFCs and UCBs draws largely from the framework for banks.
The circulars clearly indicates that RBI is now accepting a more stringent attitude towards risk management and audit, specifically given the challenges faced due to Covid -19. It seems like Covid-19 acted as a wake-up alarm to increase focus on risk management and its mitigation by financial sector entities.
Applicability on Housing Finance Companies (HFCs)
The RBI circular did not specifically state the applicability of RBIA Framework on HFCs. Hence the same was open for interpretation by the stakeholders and so there were 2 different school of thoughts on this. First is that since HFCs are also a class of NBFCs so the circular should also be applicable on HFCs. However, a counter interpretation was that the Master Direction for Housing Finance Company (which assembles all applicable regulations at one place) which was notified on February 17, 2021[3] (after the given 3rd February circular), did not include compliance with RBIA Framework. Accordingly, the coverage of the RBIA Framework did not seem to be applicable on HFCs. The interpretation by the stakeholders resultied in diverse practices in the market.
However, RBI on 11th June, 2021 has issued a circular stating “On a review, it has been decided that the provisions of the aforesaid circular (circular dated 3rd February, 2021) shall be applicable to all deposit taking HFCs, irrespective of their size and non-deposit taking HFCs with asset size of ₹5,000 crore and above.
Considering the above clarification from RBI, HFCs shall now be required to be undertake Risk Based Internal Audit and put in place RBIA framework by June 30, 2022.
Risk Based Internal Audit: A Sub-set of Risk Management Framework
An essential characteristic of an effective RBIA Framework would be that it should be a connecting link between various components of risk management framework and should provide for reasonable assurance that organisation’s internal controls, risk management, and governance related systems and processes are adequate to deal with risk faced by it.
The internal audit function should ideally be targeted towards contributing to the overall improvement of the organization’s governance, risk management, and control processes using a systematic and disciplined approach.
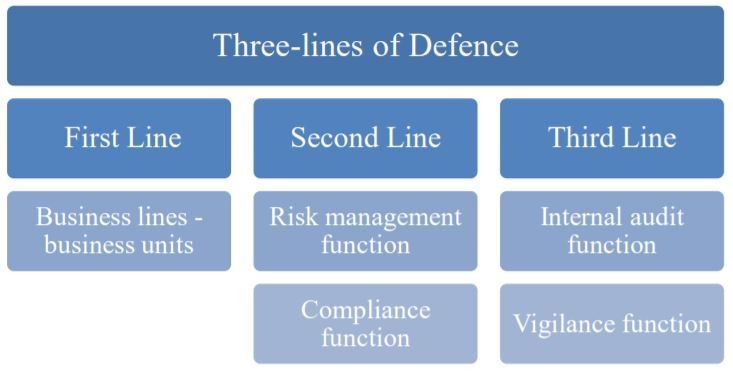
The circular provides that internal audit function is an integral part of sound corporate governance and is considered as the third line of defence. The inference for different lines of defence for risk management may be drawn from the RBIA circular for Banks, which provides as follows-
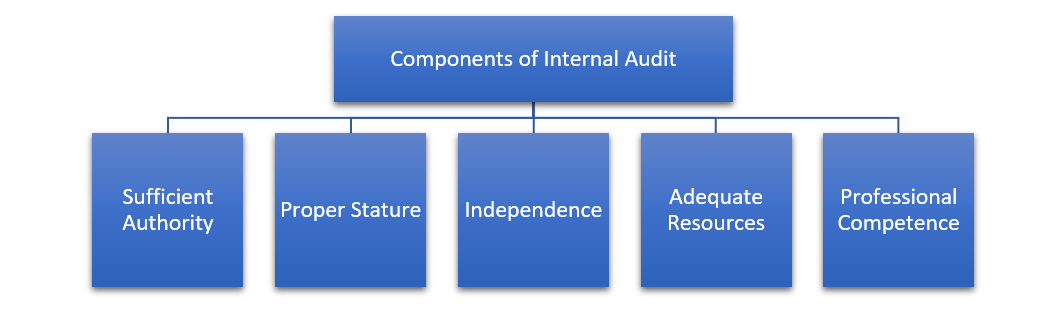
Based on the recent developments and emerging trends, the focus areas for robust internal audit should ideally inter-alia the following components-
The internal audit function in NBFCs/UCBs has generally been concentrated on accounting requirements and regulatory compliance etc. However, considering the market developments, testing limited to these factors may not be sufficient. Therefore, the current framework includes, above aspects along with, an evaluation of the risk management systems and control procedures in various areas of operations. This will help in anticipating areas of potential risks and mitigating such risks.
The RBIA should be conducted based on a RBIA plan which is required to be formulated after considering the elements of risk management framework of the entity.
Actionable
As mentioned above, reasonable amount of time is provided to NBFCs/UCBs to prepare for effective implementation of the RBIA Framework, that is, by 31st March 2022. However, though the requirements are to be complied by the end of next financial year, the preparedness for the same must be initiated immediately. A list of actionable on the part of NBFCs/UCBs has been provided below for reference:
Role and responsibilities of functionaries
It is a well understood notion that to get a particular task done, a fixed responsibility centre should be set-up, this enables proper implementation and also increases the efficiency of the implementation. Considering the same RBI has prescribed for responsibilities of senior management, Board and Audit committee to ensure proper implementation of RBIA Framework. The allotted role and responsibilities shall be as follows-
Board of Directors / Audit Committee of Board
The Board of Directors (the Board) / Audit Committee of Board (ACB) of NBFCs/UCBs shall have the primary responsibility of overseeing the internal audit function in the organization. The major responsibility of the Board and ACB would be to establish and further review the RBIA systems.
The RBIA policy is to be formulated with the approval of the Board and would be disseminated widely within the organization. The policy should be consistent with the size and nature of the business undertaken, the complexity of operations and should factor in the elements of internal audit. The ACB and Board would further review the performance of RBIA and shall also formulate and maintain a quality assurance and improvement program that covers all aspects of the internal audit function.
Senior Management
The senior management shall be responsible for implementation of the systems established by the board and ACB.
The senior management shall ensure adherence to the internal audit policy guidelines as approved by the Board and development of an effective internal control function that identifies, measures, monitors, and reports all risks faced. The senior management shall ensure audit reports is placed before the ACB/Board. Further, a consolidated position of major risks faced by the organization shall be presented at least annually to the ACB/Board, based on inputs from all forms of audit.
The senior management shall also be responsible for establishing a comprehensive and independent internal audit function that should promote accountability and transparency. It shall ensure that the RBIA Function is adequately staffed with skilled personnel of right aptitude and attitude who are periodically trained to update their knowledge, skill, and competencies.
Internal Audit Function: Major Elements
The RBIA Framework broadly provides for a comprehensive internal audit function the major elements and their requirements are summarised as follows-
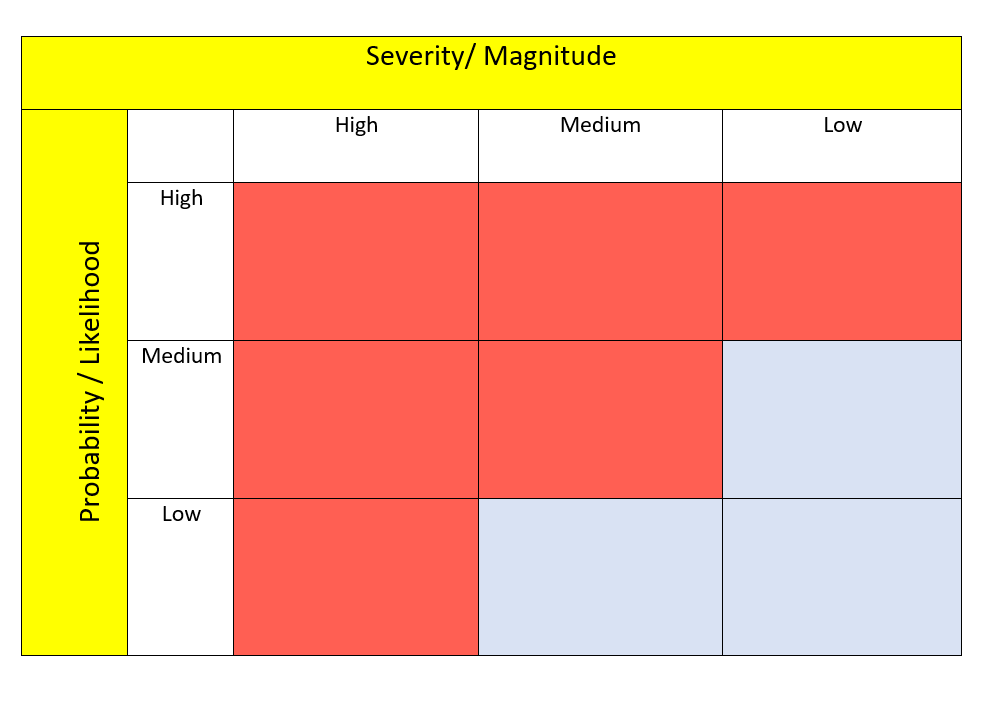
Risk Matrix
A risk matrix is a matrix that is used during risk assessment to define the level of risk by considering the category of probability or likelihood as against the category of consequence severity. This is a simple mechanism to increase visibility of risks and assist in management decision making.
The circular requires that the RBIA function should consider risk matrix while setting up action plan. Further, certain risk mentioned shall be given enhanced attention during the RBIA, the matrix and areas of focus are marked red in graph below-
Outsourcing of the Internal Audit Function
The internal audit function cannot be outsourced. However, where required, experts including former employees can be hired on a contractual basis subject to the ACB/Board being assured that such expertise does not exist within the audit function of the NBFC/UCB. Any conflict of interest in such matters shall be recognised and effectively addressed.
Monitoring and follow up
Monitoring and follow-up actions form an integral part of entire internal control system to ensure effective functioning of the procedures. Accordingly, the process as well as findings under the RBIA Framework should be regularly monitored. The said responsibility lies with the Board and Senior Management, as discussed above.
[1] https://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/NotificationUser.aspx?Id=12011&Mode=0
[2] https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/PressRelease/PDFs/PR10365F8B4F9BF8FE4A209F3BD7FD1D62B7D9.PDF
[3] Our write up on the topic “RBI consolidates directions for Housing Finance Companies http://vinodkothari.com/2021/02/rbi-consolidates-directions-for-housing-finance-companies/”
[4] Our write up on the top “Risk management policy” https://vinodkothari.com/2021/10/risk-management-policy-a-tool-of-risk-management/




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!