An all-embracing guide to identity verification through CKYCR
-Kanakprabha Jethani | Executive
Updated as on January 19, 2022
Introduction
Central KYC Registry (CKYCR) is the central repository of KYC information of customers. This registry is a one stop collection of the information of customers whose KYC verification is done once. The Master Direction – Know Your Customer (KYC) Direction, 2016 (KYC Directions)[1] defines CKYCR as “an entity defined under Rule 2(1) of the Rules, to receive, store, safeguard and retrieve the KYC records in digital form of a customer.”
The KYC information of customers obtained by Reporting Entities (REs) (including banks) is uploaded on the registry. The information uploaded by an RE is used by another RE to verify the identity of such customer. Uncertainty as to validity of such verification prevails in the market. The following write-up intends to provide a basic understanding of CKYCR and gathers bits and pieces around identity verification through CKYCR.
Identity verification through CKYCR is done using the KYC identifier of the customer. To carry out such verification, an entity first needs to be registered with the CKYCR. Let us first understand the process of registration with the CKYCR.
Registration on CKYCR
The application for registration shall be made on CKYCR portal. Presently, Central Registry of Securitisation Asset Reconstruction and Security Interest (CERSAI) has been authorized by the Government of India to carry out the functions of CKYCR. Following are the steps to register on CERSAI:
- A board resolution should be passed for appointment of the authorised representative. The registering entity shall be required to identify nodal officer, admin and user.
- Thereafter, under the new entity registration tab in the live environment of CKYCR, details of the entity, nodal officers, admin and users shall be entered.
- Upon submission of the details, the system will generate a temporary reference number and mail will be sent to nodal officer informing the same along with test-bed registration link.
- Once registered on the live environment, the entity will have to register itself on the testbed and test the application. It shall have to test all the functionalities as per the checklist provided at https://www.ckycindia.in/ckyc/downloads.html. On completion of the testing, the duly signed checklist at helpdesk@ckycindia.in shall be e-mailed to the CERSAI.
- The duly signed registration form along with the supporting documents shall be sent to CERSAI at – 2nd Floor, Rear Block, Jeevan Vihar Building, 3, Parliament Street, New Delhi -110001.
- CERSAI will verify the entered details with physical form received. Correct details would mean the CERSAI will authorize and approve the registration application. In case of discrepancies, CERSAI will put the request on hold and the system will send email to the institution nodal officer (email ID provided in Fl registration form). To update the case hyperlink would be provided in the email.
- After completion of the testing and verification of documents by CERSAI, the admin and co-admin/user login and password details would be communicated by it.
Obligations in relation to CKYCR
The establishment of CKYCR came with added obligations on banks and REs. The KYC Directions require banks and REs to upload KYC information of their customers on the CKYCR portal. As per the KYC Directions – “REs shall capture the KYC information for sharing with the CKYCR in the manner mentioned in the Rules, as required by the revised KYC templates prepared for ‘individuals’ and ‘Legal Entities’ as the case may be. Government of India has authorised the Central Registry of Securitisation Asset Reconstruction and Security Interest of India (CERSAI), to act as, and to perform the functions of the CKYCR vide Gazette Notification No. S.O. 3183(E) dated November 26, 2015.
…Accordingly, REs shall take the following steps:
- Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) shall invariably upload the KYC data pertaining to all new individual accounts opened on or after January 1, 2017 with CERSAI in terms of the provisions of the Prevention of Money Laundering (Maintenance of Records) Rules, 2005.
- REs other than SCBs shall upload the KYC data pertaining to all new individual accounts opened on or after from April 1, 2017 with CERSAI in terms of the provisions of the Prevention of Money Laundering (Maintenance of Records) Rules, 2005.”
Further, para III and IV of the Operating Guidelines of CKYCR require reporting entities (including banks) to fulfill certain obligations. Accordingly, the reporting entities shall:
- Register themselves with CKYCR
- Carry out due diligence and verification KYC information of customer submitting the same.
- Upload KYC information of customers, in the KYC template provided on CKYCR portal along with scanned copy of Proof of Address (PoA) and Proof of Identity (PoI) after successful verification.
- Communicate KYC identifier obtained from CKYCR portal to respective customer.
- Download KYC information of customers from CKYCR, in case KYC identifier is submitted by the customer.
- Refrain from using information downloaded from CKYCR for purposes other than identity verification.
- In case of any change in the information, update the same on the CKYCR portal.
In and around verification
Registered entities may download the information from CKYCR portal and use the same for verification. Information can be retrieved using the KYC identifier of the customer. Before we delve into the process of verification and its validity, let us first understand what a KYC identifier is and how would a customer obtain it.
KYC identifier
A KYC Identifier is a 14 digit unique number generated when KYC verification of a customer is done for the first time and the information is uploaded on CKYCR portal. The RE uploading such KYC information on the CKYCR portal shall communicate such KYC Identifier to the customer after uploading his/her KYC information.
Obtaining KYC identifier
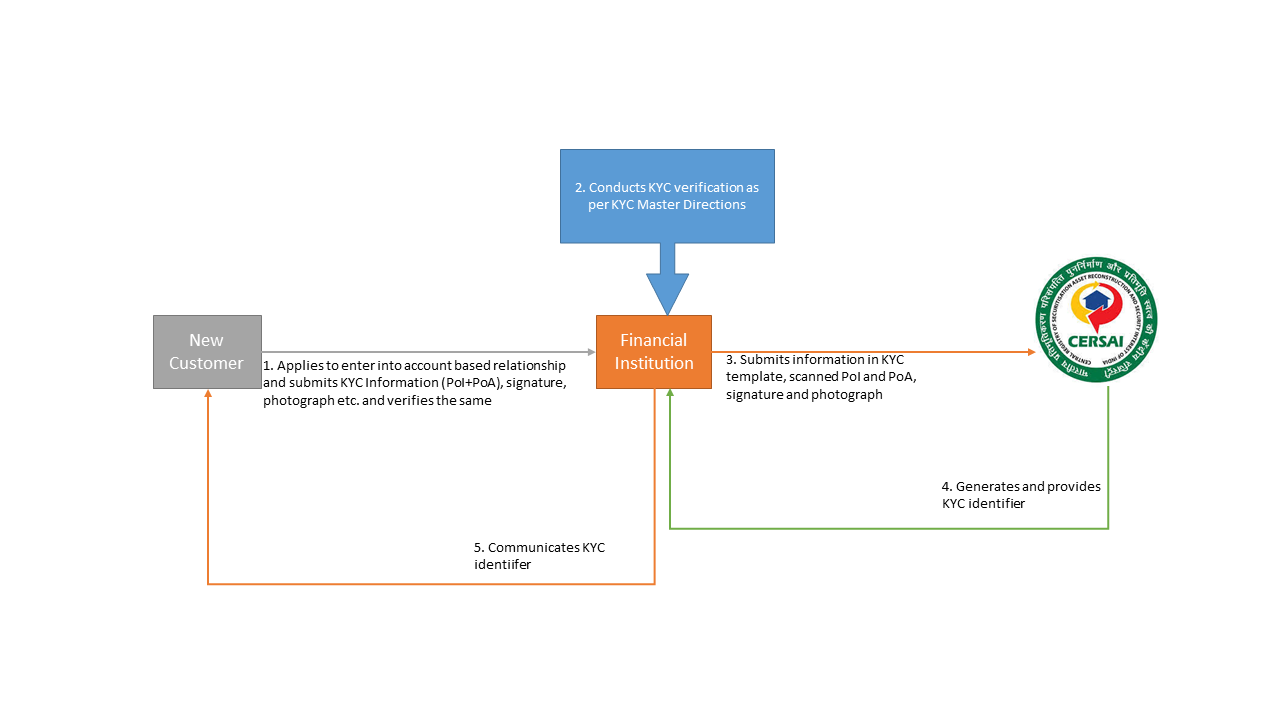
When a customer intends to enter into an account-based relationship with a financial institution for the very first time, such financial institution shall obtain KYC information including the Proof of Identity (PoI) and Proof of Address (PoA) of such customer and carry out verification process as provided in the KYC Master Directions. Upon completion of verification process, the financial institution will upload the KYC information required as per the common KYC template provided on the CKYCR portal, along with scanned PoI and PoA, signature and photograph of such customer within 3 days of completing the verification. Different templates are to be made available for individuals, and on the CKYCR portal. Presently, only template for individuals[2] has been made available.
Upon successful uploading of KYC information of the customer on the CKYCR portal, a unique 14 digit number, which is the KYC identifier of the customer, is generated by the portal and communicated to the financial institution uploading the customer information. The financial institution is required to communicate the KYC identifier to respective customer so that the same maybe used by the customer for KYC verification with some other financial institution.
Verification through CKYCR
When a customer submits KYC identifier, the RE, registered with CKYCR portal, enters the same on the CKYCR portal. The KYC documents and other information of the customer available on the CKYCR portal are downloaded. The RE matches the photograph and other details of customer as mentioned in the application form by the customer with that of the CKYCR portal. If both sets of information match, the verification is said to be successful.
Identity Verification through CKYCR- is it valid?
The process of CKYCR is not a complete process in itself and is merely a means to obtain documents from the central registry. In the very essence, the registry acts as a storehouse of the documents to facilitate the verification process without having the customer to produce the KYC documents every time he interacts with a regulated entity. Para 56(j) provides that Regulated entities are not required to ask the customer to submit KYC documents, if he/she has submitted KYC Identifier, unless:
(i) there is a change in the information of the customer as existing in the records of CKYCR;
(ii) the current address of the customer is required to be verified;
(iii) the RE considers it necessary in order to verify the identity or address of the customer, or to perform enhanced due diligence or to build an appropriate risk profile of the client.
The above specification is for obtaining the documents from the customer and not for verification of the same. Verification can be done only through physical, digital or V-CIP modes of CDD.
Furthermore, V-CIP as a manner of CDD was introduced through an amendment to KYC Directions introduced on 9th January, 2019[5]. Para 18(b) of the KYC Directions prescribes that documents for V-CIP procedure may be obtained from the CKYCR portal. Logically, if the CKYCR procedure was to be complete in itself, the same would not have been indicated in conjunction with the V-CIP mode of due diligence.
Benefits from CKYCR
While imposing various obligations on REs, the CKYCR portal also benefits REs by providing them with an easy way out for KYC verification of their customers. By carrying out verification through KYC Identifier, the requirement of physical interface with the borrower (as required under KYC Master Directions)[4] may be done away with. This might serve as a measure of huge cost savings for lenders, especially in the digital lending era.
Further, CKYCR portals also have de-duplication facility under which KYC information uploaded will go through de-duplication process on the basis of the demographics (i.e. customer name, maiden name, gender, date of birth, mother’s name, father/spouse name, addresses, mobile number, email id etc.) and identity details submitted. The de-dupe process uses normaliser algorithm and custom Indian language phonetics.
- Where an exact match exists for the KYC data uploaded, the RE will be provided with the KYC identifier for downloading the KYC record.
- Where a probable match exists for the KYC data uploaded, the record will be flagged for reconciliation by the RE.
Conclusion
Identity verification using the KYC identifier is a cost-effective way of verification and also results into huge cost saving. This method does away with the requirement of physical interface with the customer. Logic being- when the customer would have made the application for entering into account-based relationship, the entity would have obtained the KYC documents and carried out a valid verification process as per the provisions of KYC Master Directions. So, the information based on valid verification is bound to be reliable.
However, despite these benefits, only a handful of entities are principally using this method of verification presently. Lenders, especially FinTech based, should use this method to achieve pace in their flow of transactions.
[1] https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/BS_ViewMasDirections.aspx?id=11566
[2] https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/content/pdfs/KYCIND261115_A1.pdf
[3] https://testbed.ckycindia.in/ckyc/assets/doc/Operating-Guidelines-version-1.1.pdf
[4] Our detailed write-up on the same can also be referred- http://vinodkothari.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/KYC-goes-live-1.pdf
[5] https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/NotificationUser.aspx?Id=11783&Mode=0
Our FAQs on CKYCR may also be referred here- http://vinodkothari.com/2016/09/ckyc-registry-uploading-of-kyc-data/
Our other write-ups on KYC:

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!