RBI notifies Lending Restrictions on NBFCs
In pursuance of the Scale Based Regulatory Framework
-Anita Baid | Vice- President and Aanchal Kaur Nagpal | Assistant Manager
The Scale Based Regulatory Framework, introduced by the Reserve Bank of India (‘RBI’), among several other things, proposed to regulate loans extended by NBFCs to their directors, senior officers and relatives thereof.
In this regard, the RBI has, vide its notification on Loans and Advances – Regulatory Restrictions – NBFCs dated April 19, 2022, issued two sets of regulatory provisions – one for NBFC-UL and NBFC-ML and the other for NBFC-BL (‘Guidelines’).
- NBFC-BL are required to have a board approved policy on grant of loans to directors, senior officers and relatives of directors and to entities where directors or their relatives have major shareholding.
- NBFC-ML and NBFC-UL, on the other hand, have to abide by the restrictions prescribed by RBI, while extending loans to directors, senior officers and their relatives. The said restriction may have an adverse impact on the loans extended by the NBFC to its group companies with common directorship.
NBFC-BL have been given the liberty to decide the threshold limit of such connected lending above which internal approvals will be required, while NBFC-ML and NBFC-UL will be governed by the limits set by RBI.
Effective Date
The Guidelines will be effective from October 01, 2022.
NBFCs placed on similar footing with Banks
NBFCs have been put on a similar, if not equal footing with Banks. While Banks are completely prohibited from granting loans to their directors and connected entities, the Guidelines only restrict NBFCs from granting loans to its directors above a particular threshold with a pre-condition of Board approvals.
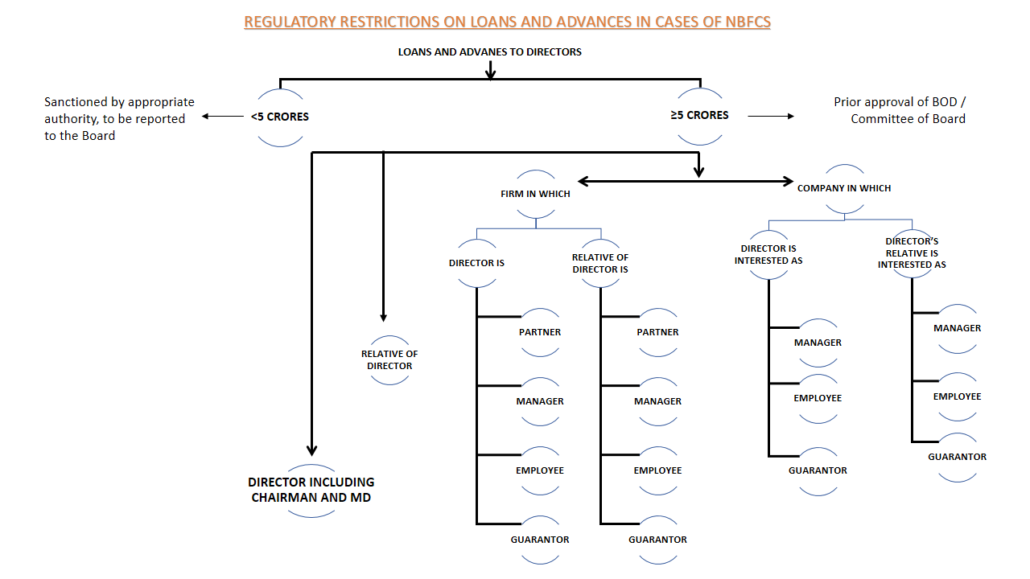
In case of relatives of directors and senior officers, similar conditions have been prescribed for NBFCs i.e. sanctioning of loans and advances above Rs. 5 crore will require prior Board approval.
Actionable for NBFCs
The immediate actionable for NBFCs will be as follows:

The requirement of having a policy in place has been made applicable only in case of NBFC-BL. However, it would be recommended that NBFC-ML and NBFC-UL should also incorporate relevant provisions of these Guidelines in their loan policies.
What kinds of facilities are covered?
- Lending
- Advances
- Awarding of contracts. The requirement is similar to that of banks. However, the kinds of contracts that will be covered by the Guidelines, have not been specified by RBI. It seems that all sorts contract involving sale or purchase of good and rendering of any services, to or by the NBFC, shall be covered.
Exclusion List
As per the Guidelines, the term ‘loans and advances’ will not include loans or advances against:
- Government securities
- Life insurance policies
- Fixed deposits
- Stocks and shares
- Housing loans, car advances, etc. granted to an employee of the NBFC under any scheme applicable generally to employees. For instance, an HFC has also been extending housing loans to all its employees under a specific scheme- the loan to director or senior officer or their relatives would be covered under the provisions of the scheme and hence, the Guidelines shall not be applicable.
In the aforesaid cases, it must be ensured that NBFC’s interest/lien is appropriately marked with legal enforceability.
What all are the regulatory restrictions on loans and advances in case of NBFCs?
Meaning of important terminology
Major shareholder –
The term ‘major shareholder’ has been defined to mean a person holding 10% or more of the paid-up share capital or five crore rupees in paid-up shares, whichever is lower.
Here, paid-up share capital, in our view, shall include equity as well as preference share capital.
Further, the threshold limit of paid-up shares of Rs. 5 crore should be calculated on the basis of the face value of shares. The rationale, here, would be that in case the market value of the NBFC’s shares is volatile, shareholders with lesser number of shares may also touch the threshold of Rs. 5 crore of paid-up shares, which is not the intent of the regulator.
Guarantor –
Since no threshold amount has been set, guarantees granted for any amount to an entity by the directors or their relatives, may cause the directors or their relatives to be considered as ‘interested’ in such entity.
Control –
Control shall be as per the definition specified under section 2(27) of the Companies Act, 2013 i.e. the right to appoint majority of the directors or to control the management or policy decision exercisable by a person or persons acting individually or in concert, directly or indirectly, including by virtue of their shareholding or management rights or shareholder’s agreements or voting agreements or in any other manner.
The term control has only been used in the context of a holding or a subsidiary Company i.e. a director having control (or is a major shareholder) in a subsidiary or holding company, the holding company (of such subsidiary) or the subsidiary company (of such holding company) shall get included.
Employee –
Employees are those on the payroll of the company.
Senior officer –
As per section 178 of Companies Act, 2013, the expression ‘senior management’ shall mean personnel of the company who are members of its core management team excluding Board of Directors comprising all members of management one level below the executive directors, including the functional heads.
Loans prior to appointment as director/senior officer
In case of loans granted to an individual prior to becoming an employee/ director and such loans are still in existence at the time of their appointment, the same should ideally be reported to the Board at the time of appointment.
Loans to firms and entities where the directors, senior officers and their relatives are interested, should also be assessed at the time of appointment, and approvals/ reporting, as and where required as per these Guidelines should be undertaken.
Restrictions for NBFC-UL and NBFC-ML
Loans, advances and awarding of contracts to director, senior officer or their relative will be subjected to certain regulations in terms of the quantum and the approval requirements. Though there is not a complete restriction on extending such loans, however, the necessary approvals and disclosures have to be ensured.
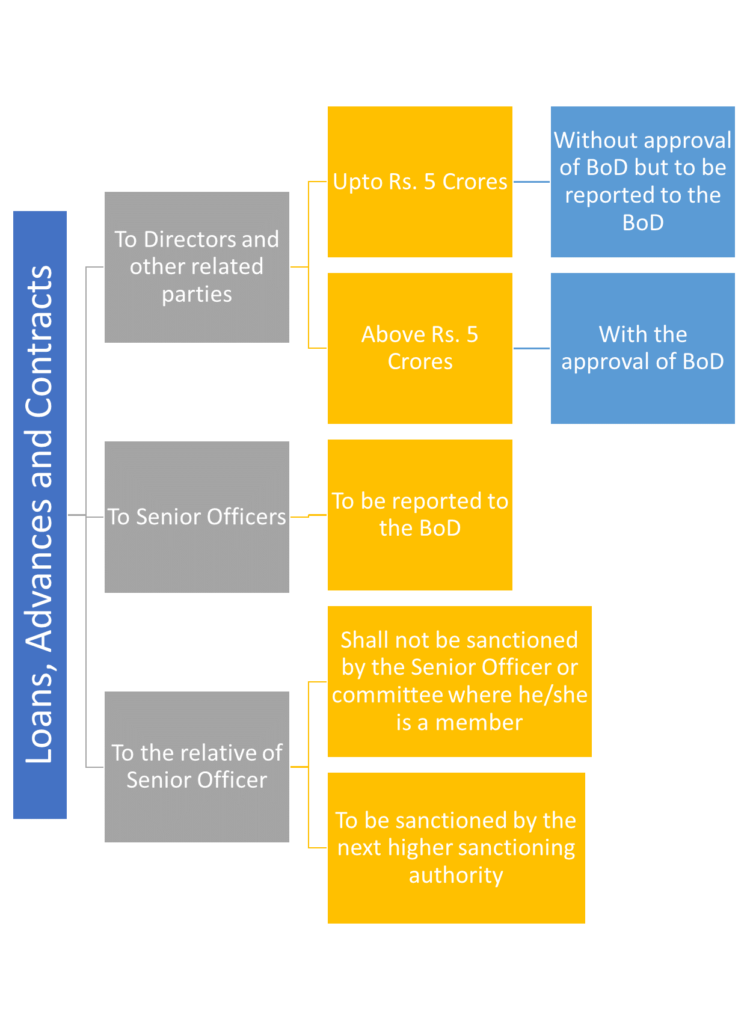
The proposals for credit facilities of an amount less than Rs. 5 crores to these borrowers may be sanctioned by the appropriate authority in the NBFC under powers vested to such authority, but the matter should be reported to the Board. While no periodicity has been specified, it is suggested that information of such lending should ideally be placed in the next Board meeting.
Real Estate Exposure
In case an NBFC-ML or NBFC-UL is appraising loan proposals involving real estate, it will have to ensure that prior permission from government/ local government/ other statutory authorities for the project is obtained before disbursement. Even if the approval is not there at the time of sanctioning or credit appraisal, the same must be ensured before the actual disbursement.
Policy on loan to directors and Senior Officers
As discussed, a policy for such loans has been made mandatory for NBFC-BL. However, it is suggested that NBFC-ML and NBFC-UL should also include relevant clauses in their existing loan policies.
The contents of the Policy may be as follows:
- Coverage
- Director and their relatives
- Entities where directors or their relatives have major shareholding
- Senior Officers
- Loan Sanction Process
- Declaration may be obtained from borrowers to determine if they are covered under the Policy
- Declaration by Director and Senior Officer
- Reporting to the Board
- Threshold to be prescribed of each of the aforesaid category
- Disclosure Requirements
- As per the template prescribed
Declaration by borrower
Every loan agreement should contain a declaration by the borrower that such borrower is not related to the director or senior officer (in case of individuals) or that the directors/ senior officers/ relatives are not interested in the borrower (in case of entities). The declaration should appropriately and adequately specify the definition of a relative, senior officer, major shareholder etc. for the clear understanding of the borrower providing the declaration. Obtaining the declaration is necessarily required in case of borrowers of NBFC-ML and NBFC-UL, however, we strongly suggest that the same should be obtained by NBFC-BL as well toi determine the applicability of the Guidelines.
Provisions of Companies Act, 2013
The Guidelines by RBI only prescribe a threshold limit for connected lending for NBFCs (or the requirement to have a policy in case of NBFC-BL). The terms of such lending shall be at the discretion of the NBFC. However, section 185(3)(b) of the Companies Act, 2013 exempt an NBFC from the restrictions under the section only if the NBFC is providing such loans in its ordinary course of its business and that the interest is charged at a rate not less than the rate of prevailing yield of one year, three years, five years or ten years Government security closest to the tenor of the loan.
Further, transactions being classified as related party transactions under the Companies Act or the Listing Regulations should duly comply with applicable RPT provisions.
Our presentation on the scale based regulatory framework can be read here.
Our write up summarising the scale based regulatory framework can be read here.
Our lecture on the scale based regulatory framework can be accessed here.

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!