Single Corporate Group focused FPIs & Large value FPIs to disclose granular details of beneficial ownership
Prapti Kanakia | corplaw@vinodkothari.com
March 21, 2024 (original article dated October 31, 2023)
SEBI Circular, effective 1st November 2023, required FPIs to provide the details of their beneficial owners without applying any threshold in the shareholding or on layers of intermediate entities until all the natural persons are identified. An enabling provision to this effect had also been inserted as Reg. 22(6) in SEBI (Foreign Portfolio Investors) Regulations, 2019 effective from 10th August 2023. SEBI vide circular dated 27th July, 2023, had also mandated all non-individual FPIs to obtain Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) number by 23rd January 2024[1]. However, LEI could not address the requirement of additional disclosures as the LEI data stops at the parent entity level and does not provide the details of natural persons in control of the entity.
As to what could be the trigger for these regulatory changes may be anybody’s guess, but tacitly, the SEBI circular dated 24th August, 2023[2] (Circular) introducing some significant changes in beneficial ownership details by FPIs, made several admissions. It seemingly admitted that the disclosure of beneficial ownership by FPIs took advantage of technicalities by structuring the holding of natural persons to less than 10%. It also admitted that several FPIs had concentric investments in a single corporate group, making it apparent that these FPIs were used as conduits for investing in a single entity, and therefore, there may be affiliation between the FPIs and the controlling shareholders.
Briefly stated, the changed norms required FPIs, which have either (a) 50% or more of their Indian equity AUM in a single corporate group; or (b) hold along with investor group more than INR 25,000 Crore of equity AUM in Indian markets, to disclose their beneficial ownership, drilled down to the natural person level, irrespective of the percentage of holding, unless eligible for exemption.
These requirements, though effective from 1st November 2023, gave a time frame of 90 calendar days for existing FPIs to re-adjust their holdings. Meaning, FPIs had time till 29th January 2024 to realign their investment within the threshold prescribed in order to avoid providing the details of the beneficial owner as required under the Circular. Post 29th January 2024, FPIs whose investment continued to exceed the threshold as mentioned above were required to disclose the details of beneficial owners within 30 trading days ending on 12th March 2024, which if not provided led to cancellation of the FPI registration license and in the interim, blocking of account for further purchase of equity securities and restricted voting rights in investee companies.
Mandatory Beneficial Ownership (‘BO’) disclosure
The new norms differed from the erstwhile norms, where BO disclosure was required if a natural person’s beneficial holding exceeded the threshold as prescribed under PML (Maintenance of Records) Rules 2005, as indicated below:
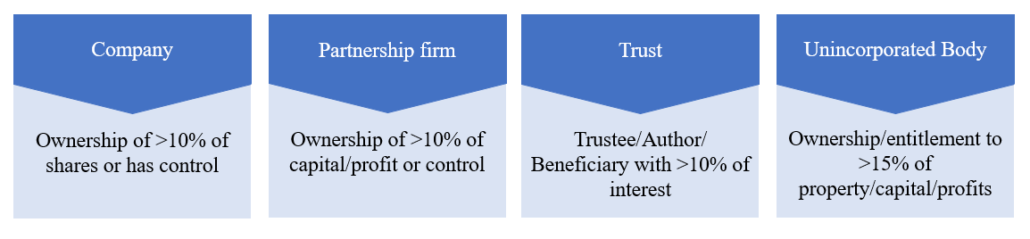
Figure 1: Threshold under PML (Maintenance of Records) Rules, 2005
The new norms required mandatory disclosure of BO, irrespective of the percentage of holding by the BO. No matter how many layers of entities covered the identity of the BO, FPIs had to identify the natural persons holding any ownership, economic interest, or exercising control, if the FPIs fall in either of the 2 categories discussed below, unless exempted.
FPIs covered under the Circular
(a) Single Corporate Group focused FPIs:
If, instead of investing in a diverse pool of assets, an FPI has concentrated into a single corporate group, there are apparent concerns that the FPI is being used as a facade for making investments into a single entity. Thus, if on an AUM basis, more than 50% of the AUM of an FPI is in a “single corporate group”, the FPI has to provide the BO disclosure unless exempted (refer discussion below).
Intent: As per SEBI BM Agenda, the intent is to ensure there is no circumvention of minimum public shareholding norms or disclosures under SAST Regulations or investing funds routed through land border sharing countries and therefore, the need to obtain granular information around the ownership of, economic interest in, and control of FPIs with concentrated equity holdings in single companies or corporate groups.
Meaning of single corporate group: SEBI did not provide any clarity on single corporate group and left it to the stock exchanges/depositories. Rather than limiting to the existing law, BSE/NSE[3] identified a single corporate group more practically. Apart from entities having common control i.e. holding, subsidiary, associate, joint venture, and entities where promoters have major shareholding, entities which are mentioned on the website or in the annual report of the entity as a group company, have also been considered as a part of the group.
Basis this definition, BSE on its own identified the companies forming part of a single corporate group and asked the listed entities to confirm the name of the group as identified by BSE by sending communication in terms of Para 16 of the SEBI Circular that requires Stock exchanges/ Depositories to maintain a repository containing names of companies forming a part of each single corporate group and disseminate the same publicly on their websites[4].
(b) Large sized FPIs:
FPIs with an AUM of more than INR 25,000 crore, either individually or along with their investor group[5], may pose a systematic risk in the Indian markets. It will be more concerning if such FPIs are tacitly controlled by unfriendly nations, and therefore, SEBI mandated BO disclosure from such FPIs too.
Intent: As per SEBI BM Agenda, the intent was to examine from the perspective of DPIIT Press Note 3 of April 17, 2020 (although not applicable to FPI investments), if the FPI route could potentially be misused to circumvent the stipulations of the same and disrupt the orderly functioning of Indian securities markets by their actions by having a substantial number of investors from countries that share land borders with India. It is likely that the FPI with a large Indian equity portfolio may itself be situated out of a non–land bordering country, the first level/ intermediate investors in such FPIs may be based out of land–bordering countries. This reiterated the need to obtain granular information around the ownership of, economic interest in, and control of such FPIs.
Exemption from BO disclosure
- Single Corporate Group (‘SCG’) focused FPIs
- Investment in SCG is insignificant compared to global investment
There might be cases where the FPI has taken exposure over an SCG only, however, may have investments globally as well and the percentage of Indian investments might be quite less when compared with its overall global investment. In such a scenario, there are fewer chances of FPIs being used as a conduit for avoiding compliance or hiding the identity of the BO. Therefore, the FPIs which are holding more than 50% of their Indian AUM in an SCG and such investments are less than 25% of their global AUM, are exempt from providing the BO disclosure.
- No identified promoter in SCG
SEBI vide circular[6] dated 20th March, 2024, further exempted SCG focused FPIs meeting the following conditions:
- The apex company does not have identified promoter;
- Such FPI holds not more than 50% of its India equity AUM in the corporate group, after excluding its holding in the apex company with no identified promoter.
- The composite holdings of all such FPIs (having SCG exposure) in the apex company with no identified promoter, is less than 3% of its total equity share capital,
Intent: As per the Consultation Paper the intent is that if FPI has exposure in SCG with no identified promoter in the apex company, there is no risk of circumvention of minimum public shareholding provision and may be exempted from the disclosure requirement. Further, there is a possibility that even though the apex company itself has no identified promoter, the FPI might still hold a significant part of its portfolio in group companies that have an identified promoter and therefore if their holding in the group is not significant exemption can be granted.
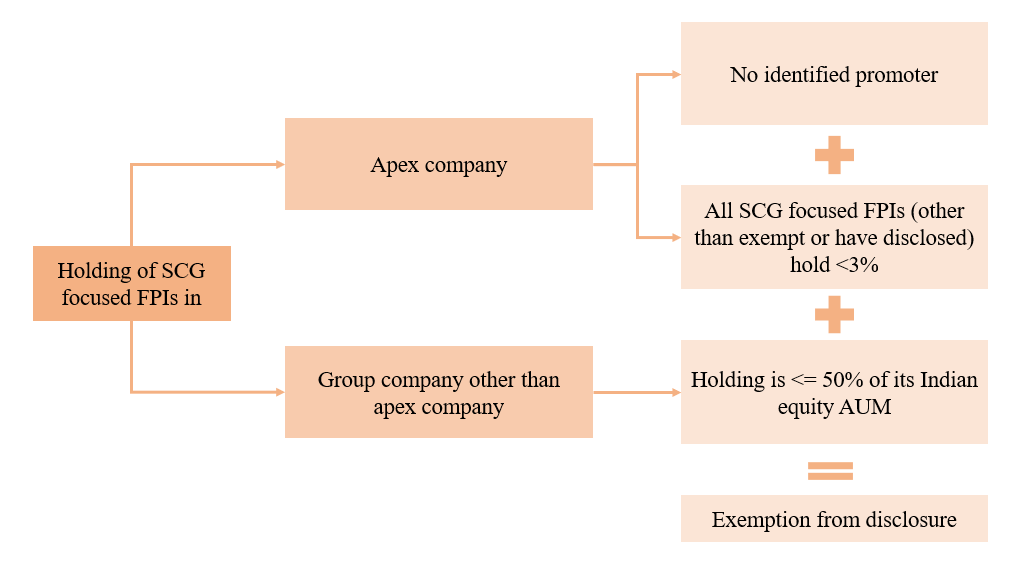
Figure 2: Exemption from disclosure requirement in case there is no promoter in SCG
- Large sized FPIs,
FPIs whose Indian AUM is more than INR 25,000 crore and their investments in India are less than 50% of their overall global investments are exempt from providing such disclosure since the probability of such FPIs being used as a facade to obtain control over Indian markets is quite less.
- General Exemption
FPIs that have a wide investor base or are backed by the government or government related investors do not pose any risk to Indian markets or the probability is quite low, and therefore the following categories of FPIs are exempt from providing BO disclosure. Also, if the investors in FPI fall under the below mentioned categories, then identification of BO for such investors will not be required. In case the constituents of Large sized FPIs fall under below mentioned category, their holding will also not be aggregated with their investor group to calculate the limit of Rs. 25,000 Crore.
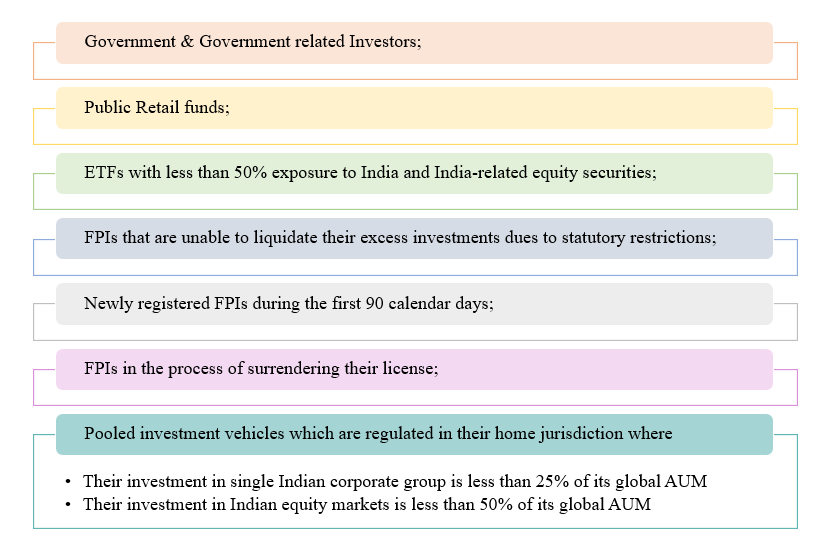
Figure 3: List of exempted FPI
The below figures provide a gist of the scenarios where FPIs are required to provide the disclosure
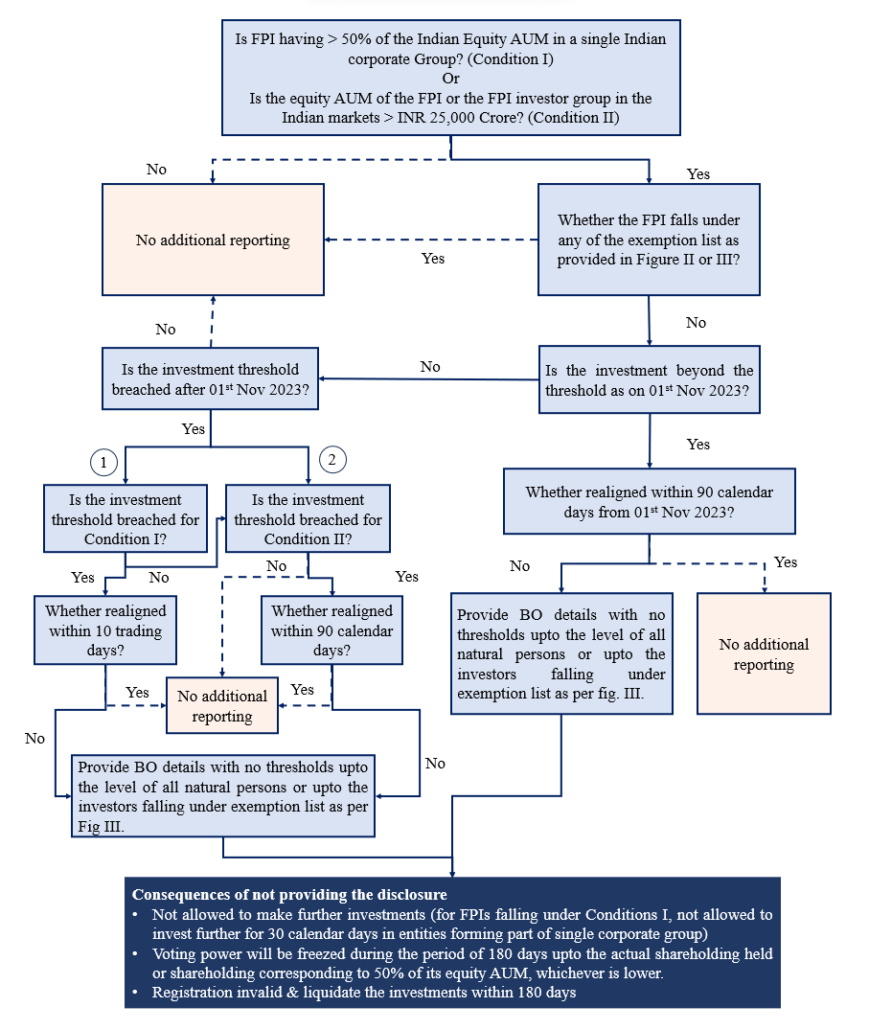
Figure 4: Flowchart depicting the scenarios that would warrant additional disclosures
Responsibility of DDPs/Depository
The FPIs are put under the obligation to ensure compliance with the SEBI Circular, i.e. providing the BO disclosure and monitoring the concentration limit in a single corporate group and the equity investments in India. Additionally, DDPs are also required to monitor the same and intimate the FPIs wherever they breach the criteria and once the registration of FPI is invalidated as a result of non-disclosure, the Depository will intimate the investee listed company to freeze the voting rights of such FPIs to the extent of actual shareholding or shareholding corresponding to 50% of its equity AUM on the date its FPI registration is rendered invalid, whichever is lower (refer the example below).
To ensure that there is no regulatory arbitrage amongst DDPs, a standard operating procedure (SOP)[7] has been framed & followed by all the DDPs to independently validate the conformance of FPIs with the conditions and exemptions prescribed. The SOP is based on the application of the core principles of minimising Type II errors i.e. where legitimate FPIs and their investors face challenges of onerous regulatory requirements) without adding to Type I errors i.e., where FPIs that may be breaching regulations, circumvent the need to make disclosures that would bring such breaches to light, through the ‘trust – but verify’ route.
Responsibility of a Listed Entity
The FPIs whose registration is rendered invalid as a result of non-disclosure are restricted from casting their vote and it is the responsibility of investee listed company to ensure that the voting rights of such FPIs are freezed to the extent of actual shareholding or shareholding corresponding to 50% of equity AUM on the date its FPI registration is rendered invalid, whichever is lower. The said information will be provided by the depository to the investee listed entity/its RTA. The following example clarifies calculation of extent of shareholding to be freezed.
Eg. FPI XYZ has 60 shares of Company A and 40 shares of Company B as on May 13, 2024, and the FPI fails to make the additional disclosures, thereby rendering its FPI registration invalid from May 13, 2024. Thereafter, FPI’s voting rights shall be restricted to shareholding corresponding to 30 shares of Company A and 20 shares of Company B.
Suppose as on July 01, 2024, the FPI has liquidated some shares and holds 15 shares of Company A and 30 shares of Company B. As on this date, the FPI will be able to exercise voting rights corresponding to 15 shares of Company A but only 20 shares of Company B (maximum permissible voting rights in Company A).[8]
The listed entities were required to intimate the details of their corporate group to the stock exchanges and any change is to be intimated within 2 working days of the effective date of such change[9].
The non-compliant FPIs are also restricted from purchasing further equity shares, however, the responsibility is not upon the listed entity to not issue equity shares to such FPIs. The DDPs/Custodian will block the account of FPIs for further purchases and they cannot participate in any corporate action which increases the equity shareholding such as rights issue, FPOs, etc. However, credit as a result of any involuntary corporate actions such as bonus issue, scheme of arrangement, etc will be allowed.
Conclusion
SEBI had stated that there cannot be sustained capital formation without transparency and trust. The Circular is a move to foster trust and increase transparency in the Indian Capital markets. The Circular does not seem to be a hindrance to genuine FPIs, though operational challenges might be faced by the FPIs in identifying the BOs.
[1] 180 days from the date of issue of the SEBI Circular.
[2] The said circular was approved in the SEBI Board meeting dated 28th June, 2023
[3] Circular dated 30th November 2023
[4] NSE – https://www.nseindia.com/regulations/listing-compliance
BSE – https://www.bseindia.com/static/about/corporate_group_repository.aspx
[5] Investor group means FPIs which, directly or indirectly, have common ownership of more than 50% or common control.
[6] The said exemption was approved in the SEBI Board meeting dated March 15, 2024
[7] https://av.sc.com/in/content/docs/in-sop-for-granular-reporting.pdf
[8] Calculation manner as provided in SOP
[9] BSE Circular dated 09th February, 2024

