Payal Agarwal, Vinod Kothari and Company ( payal@vinodkothari.com )
The recent cases of intervention by the stock market regulator and stock exchanges in preferential allotment of listed companies have brought to fore an important but fundamental point. That is, with a price band fixed under the SEBI (Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2018 (‘ICDR Regulations’), and considering th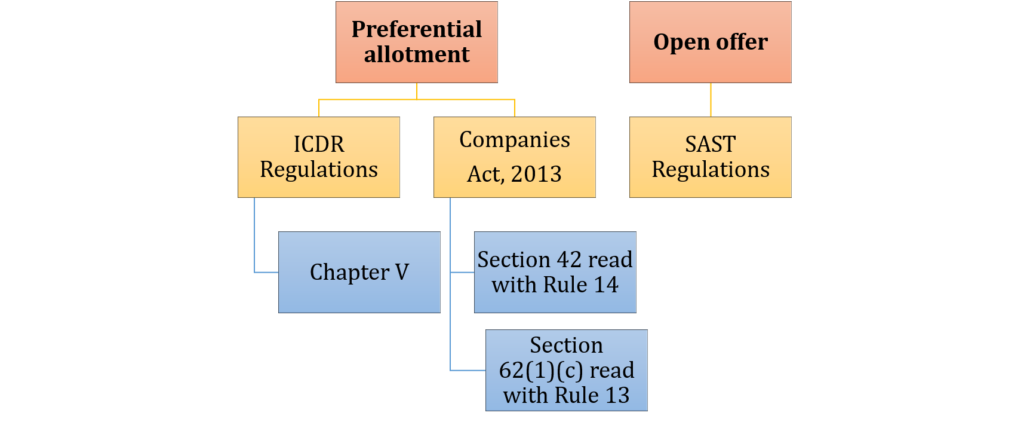 e liquidity in listed (and frequently traded) shares, whether there is a need for an independent valuation report, has become a question of great interest. Since the issue is currently under litigation will want to say that it will be interesting to see the evolution of jurisprudence on this important issue. While the issue is of relevance to minority shareholders, but it also touches a key issue in valuation as to whether there is a fair value beyond the quoted value of a company whose shares are not infrequently traded.
e liquidity in listed (and frequently traded) shares, whether there is a need for an independent valuation report, has become a question of great interest. Since the issue is currently under litigation will want to say that it will be interesting to see the evolution of jurisprudence on this important issue. While the issue is of relevance to minority shareholders, but it also touches a key issue in valuation as to whether there is a fair value beyond the quoted value of a company whose shares are not infrequently traded.
Further, there might be scenario, where a preferential allotment triggers an open offer under SEBI (Substantial Acquisition of Shares and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2011 (“SAST Regulations”). The SAST Regulations provides formula for determining offer price, which establish a clear nexus between the price of shares offered under preferential allotment and price of shares under open offer as per SAST Regulations. Given that the pricing of open offer is influenced by the pricing under preferential allotment, should the price under the ICDR Regulations be accepted or fair valuation of shares should be sought in order to ensure fair compensation to shareholders?
At this stage of discussion, it becomes important to look into the relevant provisions and the meaning of “fair value” and understand how fair it is to have a preferential allotment without ascertainment of such fair value by an independent valuer.
Regulatory provisions with respect to preferential allotment
Preferential allotment in listed companies are governed by the following provisions –
- Section 42 of the Companies Act, 2013 [“Companies Act”], read with Rule 14 of Companies (Prospectus and Allotment of Securities) Rules, 2014
- Section 62(1)(c) of the Companies Act. read with Rule 13 of Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Rules, 2014
- Chapter V of ICDR (Regulation 164)
Preferential offers under section 62(1)(c) can be made to any person, if so authorised by a special resolution passed in general meeting if the price of such shares is determined by way of a valuation report of a registered valuer. However, if one goes through allied Rule 13 of SCD Rules, it becomes clear that the companies whose shares are listed on a stock exchange are not required to obtain a valuation report from a registered valuer. The said rules clearly bring out a distinction between preferential offers made by a listed company versus those made by unlisted companies. Sub-rule (2) specifically states that for companies whose shares are listed on a recognised stock exchange, the requirements under the relevant SEBI regulations (ICDR Regulations) will apply, while the unlisted companies will be governed by the provisions of the Companies Act; and sub-rule (3) states that the price under the preferential allotment shall not be less than the price determined on the basis of valuation report of registered valuer. Hence, it becomes clear that in case of a listed company, as per section 62 and rule 13, there is no requirement of a valuation report, per se. Instead, the legislature has left it to be regulated by SEBI regulations. Therefore, one will have to look for what ICDR says.
Reg. 164 of ICDR lays the floor limit of the price, which is to be calculated as the higher of average of weekly high and low of volume weighted average price of related equity shares quoted on a recognised stock exchange for –
- 26 weeks preceding the relevant date
- 2 weeks preceding the relevant date
The Regulation does not call for an independent valuation report. This must be read in contradistinction to regulation 165, which deals with pricing of infrequently traded shares. Reg. 165 rather specifically requires an independent valuation.
Requirement of independent valuation under regulatory provisions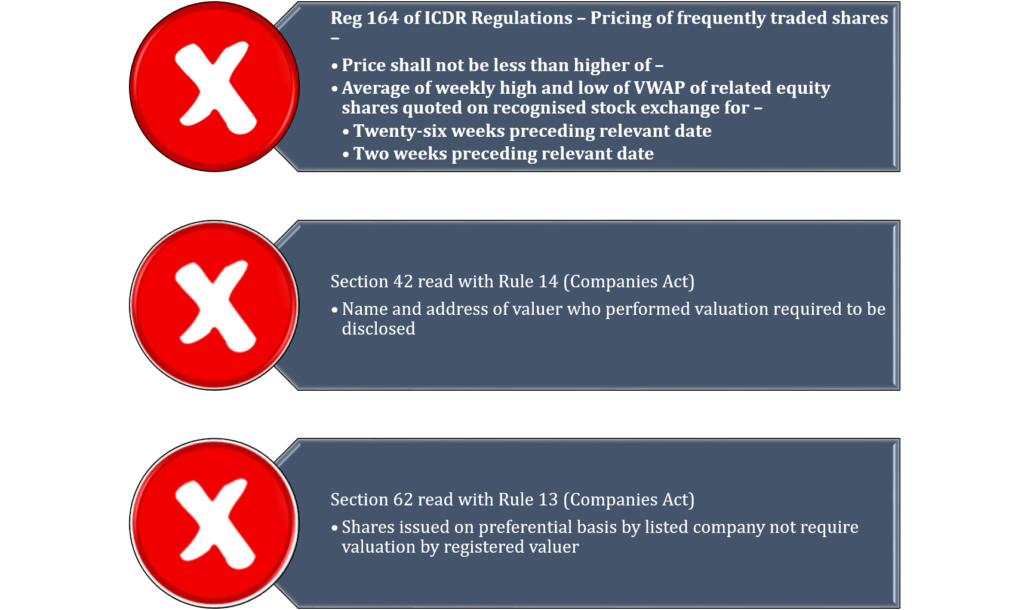
The above clearly demonstrates that the regulations have consciously exempted listed entities from seeking an independent valuation where listed shares are frequently traded. The regulations, in fact, draw a timeframe to extract weighted averages of the market prices to ensure that the fluctuations in prices, if any, are ironed out and the resultant price is the even price at which the market has transacted during that period. This, admittedly and reasonably too, is based on the assumption that ‘market’ is the best reflection of a fair price which a willing seller and a willing investor are ready to deal in. This view can also be substantiated with similar stipulations in other laws and valuation standards.
Meaning of fair valuation under various applicable laws
 Meaning of fair value under applicable accounting standards –
Meaning of fair value under applicable accounting standards –
Ind AS 113 deals with the fair valuation of equity shares. This Ind AS defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date, and thus considers fair value to be “a market based measurement and not an entity specific measurement.”
Clause 18 of the Ind AS 113 provides, “If there is a principal market for the asset or liability, the fair value measurement shall represent the price in that market.”
Meaning of fair value under the Income Tax Rules
Rule 11UA (1)(c) of the Income Tax Rules provides for the fair value of shares listed in a stock exchange.
It renders the transaction value of such shares to be the fair value in case the transaction has been done through stock exchange. Otherwise, the fair market value of such shares are taken to be –
“(a)the lowest price of such shares and securities quoted on any recognized stock exchange on the valuation date, and
(b)the lowest price of such shares and securities on any recognized stock exchange on a date immediately preceding the valuation date when such shares and securities were traded on such stock exchange, in cases where on the valuation date there is no trading in such shares and securities on any recognized stock exchange”
Meaning of fair value under the Valuation Standards
Rule 18 of the Companies (Registered Valuers and Valuation) Rules, 2017 requires the registered valuer to follow such valuation standards as prescribed by the Central Government. For valuation with effect from 01st July, 2018, all registered valuers are mandatorily required to apply the ICAI Valuation Standards in their valuation assignments for the purposes of the Companies Act, 2013.
The definition of ‘fair value’ under ICAI Valuation Standard (101) is the same as that in IndAS 113, that is, fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the valuation date. IVS 101 further states that fair value assumes that the price is negotiated in a free market. The ICAI Valuation Standards recognises three approaches for valuation, being – market approach, income approach, and cost approach.
Where the assets to be valued are traded in active market, the market approach is followed for valuation purposes.
Paragraphs 18-20 gives guidance over the valuation as follows –
“18. A valuer shall consider the traded price observed over a reasonable period while valuing assets which are traded in the active market.
- A valuer shall also consider the market where the trading volume of asset is the highest when such asset is traded in more than one active market.
- A valuer shall use average price of the asset over a reasonable period. The valuer should consider using weighted average or volume weighted average to reduce the impact of volatility or any one time event in the asset.”
The stipulations as above clearly reflect that for quoted shares, fair valuation is based on quoted prices only. Given that IVS too refers to ‘traded prices’, a registered valuer would rely on such traded prices to arrive at a fair value. It may be reiterated that ICDR uses a ‘range’ of time so as to spread out the fluctuations in prices, which has been similarly captured in the IVS.
One may argue that the price of a company’s shares can be tampered with, by the company as per its whims and wishes. However, for a listed company, whose every information is readily available on public domain, does such an argument hold good? In view of the strict regulatory surveillance constantly placed by SEBI and stock exchanges on listed companies, this does not seem to be a possible scenario.
Valuation in respect of infrequently traded shares
The aforesaid logic and arguments may not hold good in case of shares that are infrequently traded or are unlisted. As indicated above, the applicable rules/regulations and standards prescribe a different methodology to arrive at fair values of such shares. For instance, regulation 165 of ICDR requires the minimum price in case of infrequently traded shares to be determined on the basis of valuation as per applicable parameters. Also, the SAST Regulations requires the offer price in case of infrequently traded shares to be determined by way of valuation taking into account various valuation parameters such as comparable trading multiples, book value and such others.
To reiterate, such distinction made out between frequently traded and infrequently traded shares clearly buttresses the views here.
Conclusion
The chances of a listed company acquiring a fair deal without falling into the formalities of fair valuation does not seem to be a scarce event. Listed companies are well governed under the provisions of ICDR Regulations as regards pricing of shares under preferential allotment. To ensure shareholder protection, ICDR already prescribes a minimum threshold based on average quoted prices. The prices depend on the market price of related equity shares quoted and traded on stock exchanges. Further, fair value of equity shares depend on market value of such shares and there does not seem to be chances of much disparity among the price under ICDR versus that as determined by way of fair valuation.




