Corporate Law Updates – July, 2020
/0 Comments/in Corporate Law Updates, Corporate Laws, Publications, UPDATES /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsSEBI extends deadline for June quarter results amid COVID-19
/0 Comments/in Corporate Laws, SEBI, SEBI and listing-related compliances - Covid-19 /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsCompanies to manage the dual requirement of holding board meetings and submission of financial results
Shaifali Sharma
Vinod Kothari & Company
corplaw@vinodkothari.com
In the wake of the continuing impact of COVID-19 pandemic, SEBI vide circular[1] dated June 24, 2020, granted relaxation to listed entities and extended the timeline for submission of financial results for quarter / half year / financial year ended March 31, 2020 to July 31, 2020.
Since, now the first quarter of the FY 2020-21 has come to an end, companies are expected to finalize, approve and submit their financials to the respective stock exchange(s) within 45 days from the quarter ended June 30, 2020 as per Regulation 33 of the SEBI (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015 (‘Listing Regulations’) i.e. on or before August 14, 2020.
Considering the shortened time gap of 14 days between the two due dates stated above i.e. July 31 and August 14, SEBI vide its circular[2] dated July 29, 2020, has extended the deadline to submit financial results for the first quarter from August 14 to September 15, 2020 thereby allowing additional 32 days to the listed companies which will in turn provide extra time to companies and its auditors working on reporting the quarterly financial results.
It is pertinent to note here that the board of directors, as per Regulation 17(2) of the Listing Regulations, must meet at least four times a year, with a maximum time gap of 120 days between any two meetings. In this regard, the SEBI vide circular[3] date June 26, 2020 had exempted the listed entities from observing the stipulated time gap between two board meetings for the meetings held/proposed to be held between the period December 01, 2019 and July 31, 2020.
Considering no further extension has been granted by SEBI yet, the board meeting for approving the financial results should be scheduled keeping in mind the maximum time gap of 120 days prescribed under the Listing Regulations. For example, if we take a case of a listed company which held its last board meeting on May 02, 2020, the next board meeting shall be scheduled on or before August 31, 2020 instead of the extended due date of September 14, 2020.
As regards for unlisted companies, the maximum time gap for conducting board meetings had been relaxed vide MCA circular[4] dated March 24, 2020 to 180 days from present 120 days for the first two quarters of FY 2020-2021.
[1] https://www.sebi.gov.in/legal/circulars/jun-2020/further-extension-of-time-for-submission-of-financial-results-for-the-quarter-half-year-financial-year-ending-31st-march-2020-due-to-the-continuing-impact-of-the-covid-19-pandemic_46924.html
[2] https://www.sebi.gov.in/legal/regulations/jun-2009/securities-and-exchange-board-of-india-delisting-of-equity-shares-regulations-2009-last-amended-on-april-17-2020-_34625.html
[3] https://www.sebi.gov.in/legal/circulars/jun-2020/relaxation-of-time-gap-between-two-board-audit-committee-meetings-of-listed-entities-owing-to-the-covid-19-pandemic_46945.html
[4] http://www.mca.gov.in/Ministry/pdf/Circular_25032020.pdf
Other reading materials on the similar topic:
- ‘COVID-19 – Incorporated Responses | Regulatory measures in view of COVID-19’ can be viewed here
- ‘Resources on virtual AGMs’ can be viewed here
- Our other articles on various topics can be read at: http://vinodkothari.com/
Email id for further queries: corplaw@vinodkotahri.com
Our website: www.vinodkothari.com
Our YouTube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCgzB-ZviIMcuA_1uv6jATbg
Corporate Law Updates – June, 2020
/0 Comments/in Corporate Law Updates, Corporate Laws, Publications, UPDATES /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsRecent Trends in Crypto-Industry: India & Abroad
/1 Comment/in Covid-19, Financial Services, Financial services/ NBFCs/Fin-tech - Covid-19, Fintech /by Vinod Kothari Consultants-Megha Mittal
“Opportunity amidst tragedy” would likely be the most suitable phrase to summarise the journey of cryptos during the Global Pandemic- with disruption taking a toll on people and economies, and physical proximities massively restrictred, cryptos have outshone traditional assets, by virtue of its inherent features- easy liquidity, access and digitalisation.
Further, as countries around the globe attempt to stimulate their economies by opening floodgates of liquid funds, the ‘digital natives’ have and are expected to increasingly venture into adventure-some investments- think, cryptos. And while such adventurous investing may be short-lived, the results may infact have a long-lasting impact- it is this expected impact that has sets the ‘bull’ stage for cryptos in times to come.
In this brief note, we cover the recent highlights and developments in the crypto-industry, also discussing developments in the relatively new concepts of stablecoins, crypto-lending.
Limits on creeping acquisition by promoters increased during COVID-19 crises
/0 Comments/in Corporate Laws, Covid-19, SEBI, UPDATES /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsShaifali Sharma | Vinod Kothari and Company
Introduction
SEBI has been taking several proactive measures to relax fund raising norms and thereby making it easier for companies to raise capital amid the COVID-19 pandemic. With a view to further facilitate fund raising by the companies, SEBI vide its notification dated June 16, 2020[1], has relaxed the obligation for making open offer for creeping acquisition under Regulation 3(2) of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Substantial Acquisition of Shares and Takeovers) Regulations, 2011 (Takeover Code).
The relaxation allows creeping acquisition upto 10% instead of the existing 5%, for acquisition by promoters of a listed company for the financial year 2020-21. The relaxation is specific and limited to acquisition by way of a preferential issue of equity shares and therefore excludes acquisitions through transfers, block and bulk deals etc. Also recently, SEBI in its Board Meeting[2] held on June 25, 2020 has proposed to provide an additional option to the existing pricing methodology for preferential issue under which the minimum price for allotment of shares will be volume weighted average of weekly highs and low for twelve weeks or two weeks, whichever is higher.However, this new rule shall apply till December 31, 2020 with 3 years lock-in condition for allotted shares. Further, by way of the same notification, SEBI has also relaxed the provisions of voluntary open offer where an acquirer together with PAC will be eligible to make voluntary offer irrespective of any acquisition in the previous 52 weeks from the date of voluntary offer, this will promote investments into various companies in future.
This article tries to discuss on whether the relaxation given by SEBI to the promoters are as encouraging as it seems to be, when connected with the pricing norms for preferential issue under the SEBI (Issue of Capital and Disclosures Requirement) Regulations, 2018 (‘ICDR Regulations’) and how the new pricing methodology proposed by SEBI can leverage the situation.
What is Creeping Acquisition?
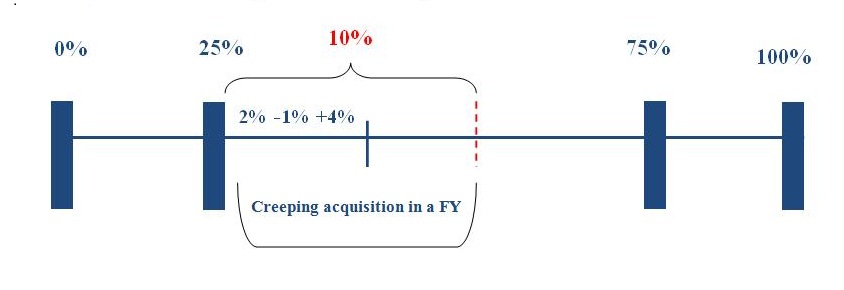
Creeping acquisition, governed by Regulation 3(2) of the Takeover Code, refers to the process through which the acquirer together with PAC holding more than 25% but less than 75%, to gradually increase their stake in the target company by buying up to 5% of the voting rights of the company in one financial year. Any acquisition of further shares or voting rights beyond 5% shall require the acquirer to make an open offer. Further, for the purpose of creeping acquisition, SEBI considers gross acquisitions only notwithstanding any intermittent fall. The same is projected in Figure 1 below. Also, in all cases, the increase in shareholding or voting rights is permitted only till the 75% non-public shareholding limit.
Figure 1: Creeping acquisition limit increased from 5% to 10%
Rationale for easing the norms of Creeping Acquisition
While the companies are currently struggling to manage their cash flows due to the financial challenges faced on account of COVID-19, the amendment will allow companies to raise funds from promoters to tide over their difficulties for the financial year 2020-21. This revision will also boost the sagging stock market and help sustain the stock prices of the company.
Promoters, on the other hand, owning 25% or more of the shares or voting rights in a company will be able to increase their shareholdings up to 10% in a year versus the previously allowed threshold limit of 5%.
Permutations and Combinations of Creeping Acquisition during FY 2020-21
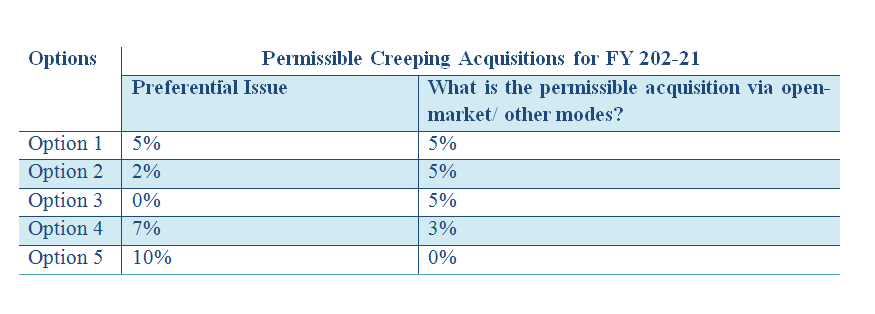
Since the enhanced 10% limit applies only in case of acquisition under preferential issue, the total acquisition of 10% may be achieved by any of the following combinations:
Option 1: Acquire upto 5% shares via open-market purchase or any other form and the remaining 5% shares can be acquired through subscribing to a preferential issue.
Option 2:Acquire 10% shares through preferential issue
Accordingly, in a block of 12 months of financial year 2020-21, if the promoterwants to acquire share through open market, bulk deals, block deals or in any other form, the 5% threshold shall remain in force and additional 5% can be acquired through preferential issue.
Identified below are the permitted acquisitions through open market, transfers or other forms in case promoter opts for preferential issue:
Whether the relaxation in open offer is actually encouraging when read with the pricing norms under ICDR Regulations?
As stated above, the relaxation can be availed only in the cases where the investments are done undera preferential issue. Regulation 164 of the SEBI (Issue of Capital and Disclosures Requirement) Regulations, 2018 (‘ICDR Regulations’) deals with the pricing norms under preferential issue. It provides that the issue price in cases where the shares have been listed for more than 26 weeks on a recognized stock exchange as on the relevant date, the issue price has to be higher of the following:
- the average of the weekly high and low of the volume weighted average price of the related equity shares quoted on the recognized stock exchange during the twenty six weeks preceding the relevant date; or
- the average of the weekly high and low of the volume weighted average prices of the related equity shares quoted on a recognized stock exchange during the two weeks preceding the relevant date.
The computation of the prices as per the above stated regulation will lead to a wide gap between the pricing at the beginning of the twenty-six week period and the current price when the company raises funds.
During this time of stock market crises, the stock prices of many companies have dropped sharply from their respective all-time high values recorded 6 months back. Further, in the cases where the market price is lower than the minimum price calculated as per ICDR Regulations for preferential issue, the promoters will be discouraged to acquire shares under preferential allotment as they will end up paying higher values.
Due to the challenges faced by the economy in view of COVID-19, the trading prices of the listed companies have gone down sharply. Accordingly, the price determined under ICDR Regulations may not be a motivating factor for the promoters to subscribe to the additional shares though, elimination of the costs involved in a public offer may compensate the same.
However, to curb the above situation, SEBI in its Board meeting held on June 25, 2020, has proposed an additional option to the existing pricing methodology for preferential issuance as under:
In case of frequently traded shares, the price of the equity shares to be allotted pursuant to the preferential issue shall be not less than higher of the following:
- the average of the weekly high and low of the volume weighted average price of the related equity shares quoted on the recognized stock exchange during the twelve weeks preceding the relevant date; or
- the average of the weekly high and low of the volume weighted average prices of the related equity shares quoted on a recognized stock exchange during the two weeks preceding the relevant date.
The new option will consider the weighted average price of equity shares preceding 12 weeks instead of the preceding 26 weeks and therefore reflect the accurate price during the pandemic period. This may prove to be the solution to above crises,making fundraising through preferential issue easier for the corporates and simultaneously encouraging the promoters as well to infuse funds.
Compliances for preferential issue to promoters under PIT Regulations
Considering the fact that promoter is one of the designated person as per the SEBI (Prohibition of Insider Trading) Regulations, 2015 (‘PIT Regulations’), the companies, in addition to the procedural requirements for preferential issue prescribed under the Companies Act, 2013, ICDR Regulations and other applicable laws, shall also comply with the provisions of PIT Regulations.
Closure of trading window in case of preferential allotment
Designated persons and their immediate relatives shall not trade in securities when the trading window is closed. The trading restriction period shall apply from the end of every quarter till 48 hours after the declaration of financial results.
Further, the trading window shall also be closed when the compliance officer determines that a designated person (DP) or class of designated persons can reasonably be expected to have possession of unpublished price sensitive information (UPSI). Therefore, the trading window shall be closed and communicated to all DPs as soon as the date/notice of board meeting to approve issue of share via preferential allotment is finalized upto 2nd trading day after communication of the decision of the Board to the Stock Exchanges.
Accordingly, promoter/ class of promoters acquiring shares under preferential issue shall conduct all their dealings in the securities of the company only in a valid trading window i.e. once the trading widow is open subject to the pre-clearance norms prescribed under PIT Regulations and the Code of Conduct for prevention of insider trading of the Company.
Concluding Remarks
Given the lack of liquidity in the market, the proposed amendments maybe seen as an opportunity for target companies to raise capital from its promoters. Further, promoters can also infuse funds through equity issuance and will be able to increase their shareholding in the target company without the formalities of making the open offer.
Having said that since the market might take some time to recover, this relaxation provides a gateway for promoters to avoid open offer requirements which would otherwise have involved compliance burden on the promoter. However, the pricing factor may seem to be the only hindrance or a demotivation for actually availing this relaxation which seems to be resolved through the new pricing method proposed by SEBI in its Board meeting.
[1]To view the notification, click here
[2]https://www.sebi.gov.in/media/press-releases/jun-2020/sebi-board-meeting_46929.html
Other reading materials on the similar topic:
- ‘SEBI revisits Takeover Code’ can be viewed here
- ‘Takeover Code 2011’ can be viewed here
- ‘Decoding Takeover Code’ can be viewed here
- Our other articles on various topics can be read at: http://vinodkothari.com/
Email id for further queries: corplaw@vinodkothari.com
Our website: www.vinodkothari.com
Our Youtube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCgzB-ZviIMcuA_1uv6jATbg
A Guide to Disclosure on COVID-19 related impacts
/2 Comments/in Corporate Laws, Corporate Laws - Covid-19, Covid-19, SEBI, UPDATES /by Vinod Kothari Consultants| SEBI seeks transparency from listed entities in times of COVID crises
Shaifali Sharma | Vinod Kothari and Company
Introduction
The impact of COVID-19 on companies is evolving rapidly not only in India but all over the world. In times of increased volatility and uncertainty in the capital market, detailed information regarding any material impact on the company’s business will not only assist the investors in making informed investment decisions but will also be fundamental formarket integrity and functioning.
Pursuant to the requirements of Listing Regulations, many listed entities have made disclosures, primarily intimating shutdown of operations owing to the pandemic and the resultant lockdowns. However, such probable information may be relatively less relevant and investors are more interested to know where these companies stand today, what are their estimated future impacts, strategiesadopted by these companies for addressing the effects of COVID-19, etc.
Given the information gaps in the market, SEBI, highlighting the importance of timely and adequate disclosures to investors and other stakeholders, issued an advisory[1]on May 20, 2020 (‘Advisory’), asking all the listed entities to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on their business, performance and financials, both qualitatively and quantitatively, and disseminated the same to the stock exchange.
This article discuss in detail the disclosure requirements under Listing Regulations and provides a quick guide for the listed entities in evaluating and disclosing impact of pandemic on their business.
Existing disclosure norms under Listing Regulations on impact of COVID-19
The existing requirements prescribed under Listing Regulations in relation to the disclosure of impact of COVID-19 on listed entities are summarized below.The same is applicable to the following entities:
- companies listed with specified securities i.e. equity shares and convertible securities
- companies listed with Non-convertible Debt Securities (NCDs) and/or Non-Convertible Redeemable Preference Shares (NCRPSs)
| Entities having specified securities listed | Entities having NCDs/NCRPS listed |
| What is the disclosure requirements prescribed under Listing Regulations? | |
| The events can be divided into two broad categories a. Deemed Material Events and b. Material Events based on application of materiality criteria as provided in Regulation 30(4).
In the first category, the events specified in Para A of Part A of Schedule III get covered and requires mandatorily disclosure on the occurrence and in the second category, events under Para B are disclosed based on the application of the guidelines for materiality prescribed under sub-regulation (4) of Regulation 30. |
Unlike Regulation 30, Regulation 51 does not provide for any test of materiality.
Part B of Schedule III requires disclosure of all information either,
|
| Whether disclosure on COVID impact required by Listing Regulations? | |
| Yes.
Disclosure w.r.t. disruption of operations of any one or more units or division of a listed entity due to natural calamity (earthquake, flood, fire etc.), force majeure or events such as strikes, lockouts etc. falls under second category. Therefore, disruption of operations due to COVID-19 is required only if the same is considered material after applying the materiality guidelines. |
Yes.
Since disruption caused by COVID may be said to have the aforesaid effects. |
| What are the actionables as per Listing Regulations? | |
| In terms of sub- regulation (5) of Regulation 30, the Board of Directors (BoD) is required to authorize one or more KMPs for the purpose of determining materiality. Therefore, such authorized KMP(s) shall determine if the impact of COVID on company’s operations is material based on the criteria prescribed under sub-regulation (4) and the policy framed by company for said purpose.
On determination of the materiality, the same shall be disclosed to stock exchange and also host the disclosure on company’s website. |
For this category of companies, the law does not provide for the similar requirements as provided for companieshaving specified securities listed eg. framing of policy, determination of materiality by Board authorized person etc. Therefore, the disruption caused by COVID-19 shall be intimated to the stock exchanges(s) as per Regulation 51 of the Listing Regulations.
In this case, disclosure on website is not mandatory; however, company may do so for better reach of information to investors and stakeholders. |
| When is the disclosure required? | |
| Regulation 30 provides for disclosure as soon as reasonably possible, but not later than 24 hours from the occurrence of the event. The guidance on when an event is said to have occurred has been provided in SEBI Circular[2] dated September 09, 2015. In terms of the said Circular, the same would depend upon the timing when the listed entity became aware of the event/information or as soon as, an officer of the entity has, or ought to have reasonably come into possession of the information in the course of the performance of his duties. | Regulation 51 provides for prompt dissemination i.e. as soon as practically possible and without any delay and that the information shall be given first to the stock exchange(s) before providing the same to any third party. |
| What all disclosures have been suggested by SEBI vide its Circular dated September 09, 2015? | |
| As per SEBI circular dated September 09, 2015, companies shall disclose:
At the time of occurrence of disruption:
Regularly, till complete normalcy is restored
|
Though the said Circular refers to only Regulation 30, however, the same requirements should apply to this category of companies also which should additionally disclose the impact on servicing of interest/ dividend/ redemption etc. |
Similar disclosure requirement are prescribed for entities which has listed its Indian Depository Receipts, Securitized Debt Instruments and Security Receipts where all information which is price sensitive or having bearing on the performance/ operation of the listed entity and other material event as prescribed under Chapter VII, VIII, VIIIA read with Schedule III of the Listing Regulations shall be disclosed
Disclosure requirements as per SEBI Advisory
As mentioned earlier, SEBI Advisory is an addition to the above requirements of Listing Regulations. Though, one may argue that the Advisory is recommendatory in nature and it does not mandate the companies to make the disclosure, however, in our view, the same is not a mere recommendation. Keeping this in mind, the probable questions that one can have with respect to SEBI Advisory have been captured below:
What is the intention of the SEBI behind issuing such Advisory?
As mentioned in the SEBI Advisory, the outbreak of COVID-19 pandemic and the consequent nationwide lockdown has lead to distortions in the market due to the gaps in information available about the operations of a listed entity and therefore, it is important for a listed entity to ensure that all available information about the impact of pandemic on the company and its operations is communicated in a timely and cogent manner to its investors and stakeholders.
These disclosures ensure transparency and will provide investors an opportunity to make an accurate assessment of the company. So, the idea behind the disclosures is to give an equal access to the information to all the stakeholders at large.
Which all entities are covered by SEBI Advisory?
Due to the COVID-19, a global pandemic, all kinds of businesses are impacted in one way or another. Unlike the Listing Regulations, SEBI Advisory does not differentiate the disclosure requirements for the companies listed with specified securities and companies listed with NCDs/NCRPS, and the Advisory is applicable to all the listed entities.
Whether the requirements of Advisory are mandatory for listed entities?
Considering the purpose of making fair and timely disclosure of any material impact on the companies, the disclosures as mentioned in the Advisory shall be treated as mandatory in nature.
Whether disclosure required if the thresholds as set out in company’s materiality policy are not met?
The materiality of an event is generally measured in terms of thresholds laid down by the companies in their ‘policy for determination of materiality’ however, such criteria should not be considered as an absolute test to determine the materiality of an event like COVID pandemic
In times of the ongoing crises, investors would be interested to know all the inside information about the impact of pandemic on the company’s business operations, financial results, future strategies, etc. i.e. every qualitative or quantitative factors.
Since every person is doing an assessment of the impact of the crisis, it is intuitive to say that the management of the companies must also have done some assessment. Considering that the idea is to provide general and equal access to the information to all the stakeholders at large, the management must disclose every positive/negative/neutral impact of the crises on the company, irrespective of the fact that it qualifies the prescribed materiality threshold or not.
What if there no impact on the business caused by the pandemic? Whether the same is also required to be disclosed?
In our view, not getting affected by the pandemic at the time when the entire world is otherwise getting affected is also material. Therefore, the disclosure shall have to be made.
Further, it is not always necessary that the pandemic will have to have a negative impact e.g. decrease in sales volume. For example, companies in pharmaceutical sector or in the sector of manufacturing of essential items such as, mask, sanitizer etc. will have a boost in sales, thereby carrying a positive impact on them.
Whether Board meeting is required to be conducted in this regard? Or will the company be required to wait till the Board decision to make the disclosure?
While an internal assessment is required at the management level, however, a Board meeting is not mandatory to be conducted. Yes, the estimates already made may be changed at a later stage which may be disclosed at that stage again.
Is it ok to say for the management to take a position that they have not analyzed the impact of the crisis?
Considering the current risk and challenges as a result of COVID-19, it is very unlikely to say that companies have not done any internal assessment to determine the current and potential impact on the company’s financial and business operations.
What are the steps involved in making the disclosure?
Step 1: Evaluate the impact of the pandemic on the business, performance and financial
Before making any disclosure to the stock exchange(s), the management of the company must properly assess the impact of COVID-19 on its business, performance and financials, both qualitative and quantitative impact.
Step 2: Dissemination of impact of pandemic to stock exchange
The following information shall be disseminated to the stock exchange:
- Impact of the pandemic on the business;
- Ability to maintain operations including factories/ units/ office spaces functioning and closed down;
- Schedule, if any for restarting the operations;
- Steps taken to ensure smooth functioning of the operations;
- Estimation of future impact on the operations;
- Details of impact on the listed entity’s
- capital and financial resources;
- profitability;
- liquidity position;
- ability to service debt and other financing arrangements;
- assets;
- internal financial reporting and control;
- supply chain
- demand for its products/services;
- Existing contracts/agreements where non-fulfilment of the obligations byany party will have significant impact on the listed entity’s business;
- Any other information as the entity may determine to be relevant and material;
While making the above disclosure to stock exchanges, entities shall also adopt the principle of disclosure and transparency prescribed under Regulation 4(2)(e) of the Listing Regulations.
Who is responsible to evaluate and make disclosures to the stock exchange(s)? What is the role of the Board in the process of assessment and/or disclosure?
- Responsibility of KMP(s) as per Listing Regulations
Pursuant to Regulation 30 of the Listing Regulations, the KMP(s), as may be authorized by the Board, is responsible to determine the materiality of the impact of pandemic on the company based on the on the guidelines for materiality and the materiality policy of the company and disclose the same to the stock exchange
- Role of Board in the assessment of other material qualitative and quantitative impacts
Considering the language of the Advisory issued by SEBI, in addition to the KMPs authorized to test the materiality, the Board will also have a role in determining the COVID impact as the same requires disclosure in which management intervention may be necessary, e.g. future plans for business continuity, capability of running the business smoothly, material changes expected during the year, impact of the financial position etc.
However, as discussed above, a Board level discussion is not a prerequisite of making the disclosure.
Is there any timeline prescribed for making disclosers to the stock exchange(s)?
There is no specific timeline provided in the Advisory for making disclosures, however, in the present situation, the disclosure is required to be made as soon as an assessment is done on the probable impact by the management.
Whether the disclosures a one-time requirement for the listed entities?
Since the operations of the company will recommence soon, question arises if the companies should continue with its assessment and disclosure process. As stated in Advisory, to have continuous information about the impact of COVID-19, listed entities may provide regularupdates, as and when there are material developments. Further, since the disclosures will be made based on estimates, any changein those estimates or the actual position shall also be disclosed in regular intervals.
Therefore, disclosure is required not only at the time of occurrence but also on a continuous basis till the normalcy of the situation.
Whether impact on an unlisted subsidiary company shall also be disclosed?
To get an overall view of company’s performance, we always evaluate consolidated figures. Sometimes, company’s standalone performance is strong as compared to its performance at consolidated level. Accordingly, if the pandemic’s impact on unlisted subsidiary is such that it is having a material impact at the group level, the same shall be disclosed to the stock exchange.
Whether effects of COVID-19 be also reported in Financial Results?
In the coming days, companies will be disclosing their quarterly and yearly financial results. This time, however, investors will be interested inknowing the impact of COVID-19 on the company’s financial positions. Therefore, while submitting financial statements under Regulation 33 of the Listing Regulations, companies should mention about the impact of the CoVID-19 pandemic on their financial statements.
What will be the consequences for not complying with the SEBI Advisory?
Since no separate penal provisions are prescribed under the Advisory, non- compliance of the same may not lead to any penal consequences.
What is the global position as regards disclosure of COVID impact?
Market regulators worldwide have taken various steps to ensure transparency related to the impacts of the pandemic on the listed companies. In United States, the Securities Exchange Commission has issued guidance[3] regarding disclosure and other securities law obligations that companies should consider w.r.t the COVID-19 and related business and market disruptions. Similarly, for listed companies and auditors in Hong Kong, the Securities and Futures Commission and the Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited issued a joint press release[4] in relation to the disclosure requirements in response to the COVID-19 outbreak
Our write-up giving an insightful analysis on the said SEBI advisory drawing an inference from the global perspective can be viewed here
What kind of information be disclosed to the stock exchange?
The table below is a quick guide for the listed entities in determining and disclosing the impact of COVID-19 on their businesses:
| Sr. No. | Subject of Assessment and Disclosure | Broad Contents (Illustrative list)
|
| I. | Current status (both financial and operating status)
|
|
| II. | Steps taken to address effects of COVID | Steps taken to:
|
| III. | Future operational and financial status (estimates) |
|
| IV. | Company Specific | Focusing on the sectors in which the company deals in, the impact of crises varies from company to company and shall be assessed accordingly. For example:
|
The above list is illustrative but not exhaustive and each company will need to carefully assess COVID-19’s impact and related material disclosure obligations.
Concluding Remarks
In light of the effects and uncertainties created by COVID-19, disclosure about shutdowns and safety measures against COVID will not help the investors in making an informed assessment about the company’s financial position. Timely and adequate information about company’s current operational and financial status with future plans to address the effects of COVID-19 will better equip the investors to make an investment decision. Therefore, the Advisory should not be considered as a mere recommendation of SEBI as a transparent communication by the companies will allow the investors and other stakeholders to evaluate current and expected impact of COVID-19 on company’s businesses, financial and operating conditions and future estimated performance.
[1]https://www.sebi.gov.in/legal/circulars/may-2020/advisory-on-disclosure-of-material-impact-of-covid-19-pandemic-on-listed-entities-under-sebi-listing-obligations-and-disclosure-requirements-regulations-2015_46688.html
[2]https://www.sebi.gov.in/legal/circulars/sep-2015/continuous-disclosure-requirements-for-listed-entities-regulation-30-of-securities-and-exchange-board-of-india-listing-obligations-and-disclosure-requirements-regulations-2015_30634.html
[3] https://www.sec.gov/corpfin/coronavirus-covid-19
[4] https://www.hkex.com.hk/-/media/HKEX-Market/Listing/Rules-and-Guidance/Other-Resources/Listed-Issuers/Joint-Statement-with-SFC/20200204news.pdf
Other reading materials on the similar topic:
- ‘Listed company disclosures of impact of the Covid Crisis: Learning from global experience’ can be viewed here
- ‘Resources on virtual AGMs’ can be viewed here
- ‘COVID-19 – Incorporated Responses | Regulatory measures in view of COVID-19’ can be viewed here
- Our other articles on various topics can be read at: http://vinodkothari.com/
Email id for further queries: corplaw@vinodkothari.com
Our website: www.vinodkothari.com
Our Youtube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCgzB-ZviIMcuA_1uv6jATbg
Corporate Law Updates – May, 2020
/0 Comments/in Corporate Law Updates, Corporate Laws, Publications, UPDATES /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsIMPACT OF COVID-19 ON FINANCIAL CONTRACTS
/0 Comments/in Covid-19, Financial Services, Leasing and Asset Financing /by Vinod Kothari Consultants-Richa Saraf
With the outbreak of COVID pandemic, there have been several instances wherein parties are running to court for various reliefs, whether to obtain injunction from invocation of bank guarantee or to seek extension of letter of credit, but mostly to seek declaration that COVID is a force majeure event and therefore, there is an impossibility of performance of the obligations. While some regulatory relief has been provided by regulators such as RBI, by allowing moratorium on loan repayments/ asset deterioration[1], and SEBI has provided relaxation on disclosure requirements[2], for other matters, the judiciary has been quite proactive in delivering judgments. Below we discuss the impact of COVID-19 on financial contracts.
Guaranteed Emergency Line of Credit: Understanding and FAQs
/23 Comments/in Financial services/ NBFCs/Fin-tech - Covid-19, Housing finance, NBFCs /by Vinod Kothari Consultants-Financial Services Division (finserv@vinodkothari.com)
-Updated as on June 08, 2021
The Finance Minister has, in the month of May, 2020, announced a slew of measures as a part of the economic stimulus package for self-reliant India. Among various schemes introduced in the package, one was the Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS, ‘Scheme’), which intends to enable the flow of funds to MSMEs. This is the so-called Rs 300000 crore scheme. The scheme was further amended on 4th August 2020 for widening the scope of the said scheme.
Under this Scheme the GoI, through a trust, will guarantee loans provided by banks and Financial Institutions (FIs) to Individuals MSMEs and MUDRA borrowers. The Scheme aims to extend additional funding of Rs. 3 lakh crores to eligible borrowers in order to help them through the liquidity crunch faced by them due to the crisis.
Based on the information provided by the Finance Minister about this Scheme, the press release issued in this regard and the operating guidelines scheme documents issued subsequently, we have prepared the below set of FAQs. There is also a set of FAQs prepared by NCGTC – we have relied upon these as well.
In brief, the Guaranteed Emergency Line of Credit [GECL] is a scheme whereby a lender [referred to as Member Lending Institution or MLI in the Scheme] gives a top-up loan of 20% of the outstanding facility as on 29th February, 2020. This top up facility is entirely guaranteed by NCGTC. NCGTC is a special purpose vehicle formed in 2014 for the purpose of acting as a common trustee company to manage and operate various credit guarantee trust funds.
[Vinod Kothari had earlier recommended a “wrap loan” for restarting economic activity – http://vinodkothari.com/2020/04/loan-products-for-tough-times/. The GECL is very close to the idea of the wrap loan.]
Essentially, the GECL will allow lenders to provide additional funding to business entities and individual businessman. The additional funding will run as a separate parallel facility, along with the main facility. The GECL loan will have its own term, moratorium, EMIs, and may be rate of interest as well. Of course, the GECL will share the security interest with the original facility, and will rank second charge, with the main facility, both in terms of cashflows as in terms of security interest.
The major questions pertaining to the GECL are going to be about the eligible borrowers to whom GECL may be extended, and the allocation of cashflows and collateral with the main facility. Operationally, issues may also centre round the turnaround time, after disbursement, for getting the guarantee cover, and whether the guarantee cover shall be in batch-processed, or processed loan-by-loan. Similarly, there may be lots of questions about how to encash claims on NCGTC.
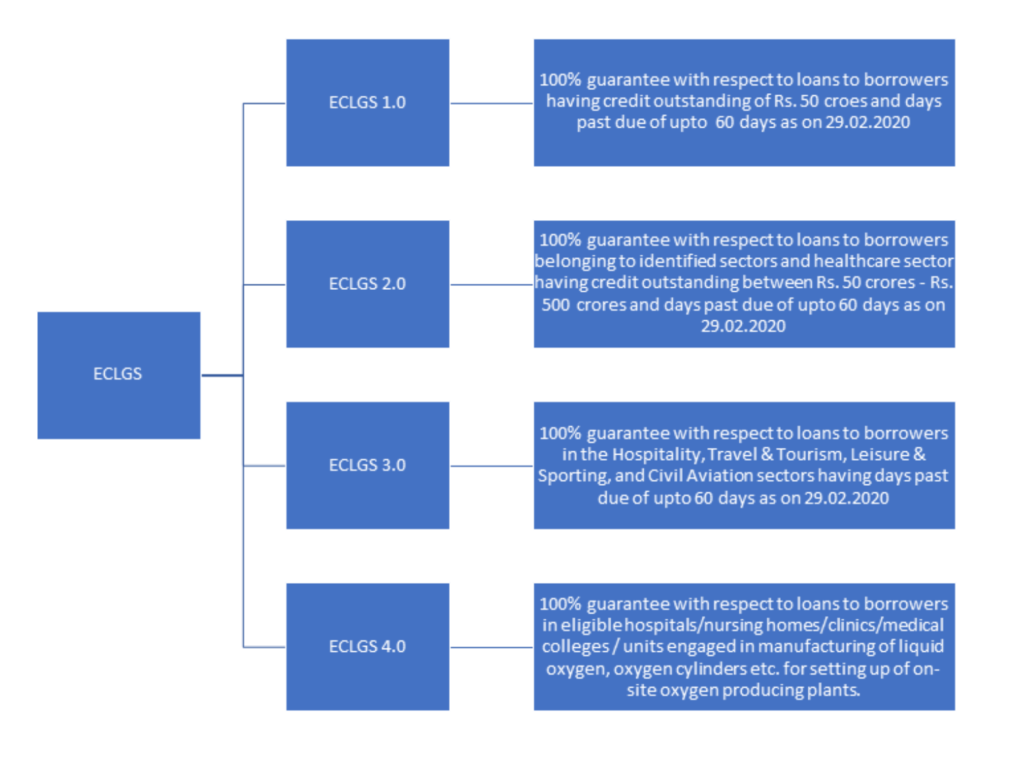
On account of nationwide disruption due to COVID-19 pandemic second wave, the Government has further enlarged the scope of the Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) via updated ECLGS operation guidelines dated June 07, 2021(‘ECLGS 4.0’). Additionally, FAQs pertaining to scheme operational guidelines were also updated via notification dated June 07, 2021.
The following chart depicts the various parts of ECLGS as per updated operational guidelines on June 07, 2021.
Eligible Lenders and eligible borrowers
- What is the nature of GECL (ECLGS 1.0)?
The GECL shall be an additional working capital term loan (in case of banks and FIs), and additional term loan (in case of NBFCs) provided by the MLIs to Eligible Borrowers. The GECL facility may run upto 20% of the loan outstanding on 29th February, 2020.
The meaning of “working capital term loan” is that the amount borrowed may be used for general business purposes by the borrower.
1A. What are the key differences between ECLGS 1.0, ECLGS 2.0, ECLGS, 3.0 and ECLGS 4.0?
Refer to the comparative table at the end of the FAQs.
- Who are the MLIs/eligible lenders under the Scheme?
For the purpose of the Scheme MLIs/eligible lenders include:
- All Scheduled Commercial Banks. Other banks such as RRBs, co-operative banks etc. shall not be eligible lenders.
- Financial Institutions (FIs), defined under section 45-I(c) of the RBI Act, 1934. The term all-India Financial Institutions” now includes Exim Bank, NABARD, SIDBI and NHB, none of which are extending primary loans. Hence, the term “financial institutions” as per sec. 45I (c) of the RBI Act will essentially refer to NBFCs, covered below..
III. Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), registered with the RBI and which have been in operation for a period of 2 years as on 29th February, 2020.
- What is the meaning of NBFC having been in operation for 2 years? Are we referring to 2 years from the date of incorporation of the Company, or 2 years from the date of getting registration with the RBI as an NBFC, or 2 financial years?
The language of the scheme indicates that the NBFC must be in operation for 2 years (and not financial years) as on 29th February, 2020. Thus, the period of 2 years shall be counted from the starting of operations after getting registration as an NBFC.
Usually, the RBI while granting registration requires the NBFC to start operations within a period of six months of getting registration. It also requires the NBFC to intimate to RBI that it has commenced operations. Logically, the 2 years’ time for starting of operations should be read from the date of commencement of operations
- Does the NBFC have to be a systemically important company? Or any NBFC, whether SI or not, will qualify?
The asset size of the NBFC would not matter. The NBFC must only hold a valid certificate of registration issued by RBI in order to be eligible under the scheme (and in operation for 2 years). Thus, whether SI or not, any NBFC will qualify.
- Is it necessary that the NBFC must be registered with the RBI?
Yes, the eligibility criteria specifically requires the NBFC to be registered.
- Will the following qualify as MLIs?
- HFCs: HFCs fall under the definition of financial institutions provided under the eligibility criteria for lenders. While HFCs essentially grant home loans, HFCs are permitted to have other types of loans within a limit of 50% of their assets. Hence, if the HFC has facilities that qualify for the purpose of the Scheme, an HFC will also qualify as MLI. This is further clarified in the FAQs 44 as well.
- MFIs: MFIs are a class of NBFCs and thus, eligible as MLIs. However, it is to be seen if the nature of loans granted by the MFI will be eligible for the purpose of the Scheme.
- CICs: CICs again are a class of NBFCs and thus, eligible as MLIs. However, they can grant loans to their group companies only.
- Companies giving fin-tech credit to consumers: The nature of the loan will mostly be by way of personal loans or consumer credit. While the lender may qualify, but the facility itself may not.
- Gold loan companies: Mostly, the loan is a personal loan and does not relate to a business purpose. Hence, the loan will not qualify.
- Is it possible for a bank to join as co-lender in case of a loan given by an NBFC? To be more precise, the primary loan is on the books of the NBFC. Now, the NBFC wants to give the GECL facility along with a bank as a co-lender. Is that possible?
In our view, that should certainly be possible. However, in our view, in that case, the rate of interest charged to the borrower should be the blended rate considering the interest rate caps for the bank [9.25%] and the NBFC [14%].
- Who are the eligible borrowers (Eligible Borrower or Borrower) under ECLGS 1.0?
The Eligible Borrowers shall be entities/individuals fulfilling each of the following features :
- Nature of the activity/facility: Our understanding is that Scheme is meant only for business loans. Hence, the nature of activity carried by the entity must be a business, and the facility must be for the purpose of the business.
- Scale of business: Business enterprises /MSMEs. The term MSME has a wide definition and we are of the view that it is not necessary for the borrower to be registered for the purpose of MSME Development Act. Please see our detailed resources on the meaning of MSMEs here: http://vinodkothari.com/2020/05/resources-on-msme/.In addition, the word “business enterprises” is also a wide term – see below.
- Existing customer of the MLI: The borrower must be an existing customer of the MLI as on 29th Feb., 2020. That is, there must be an existing facility with the borrower.
- Size of the existing facility: The size of the existing facility, that is, the POS, as on 29th Feb. 2020, should be upto Rs 50 crores.
- Turnover for FY 2019-20: The turnover of the Eligible Borrower, for financial year 2019-20, should be upto Rs 250 crores. In most cases, the financial statements for FY 2019-20 would not have been ready at the time of sanctioning the GECL. In that case, the MLI may proceed ahead based on a borrower’s declaration of turnover.
- GST registration: Wherever GST registration is mandatory, the entity must have GST registration.
- Performance of the loan: As on 29th Feb., 2020, the existing facility must not be more than 59 DPD.
- Further, Business Enterprises / MSMEs/Individuals would include loans covered under Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana extended on or before 29.2.2020, and reported on the MUDRA portal. All eligibility conditions including the condition related to Days past due would also apply to PMMY loans.
8A. Can the beneficiary under one scheme avail benefits under other schemes?
The guaranteed extended credit line (GECL) is borrower-specific and sector-specific relief. The additional credit line under ECLGS 1.0 and ECLGS 2.0 are mutually exclusive. Whereas, in cases where an additional credit line has been extended under ECLGS 1.0 and the borrower is also covered ECLGS 3.0, such accounts are eligible for additional funding up to 40% of the outstanding amount as on Feb 29. 2020. The additional funding up to 2 crores under ELGS 4.0 is allowed to all the eligible borrowers under ECLGS 4.0, irrespective of whether the funding has been availed under ECLGS 1.0, ECLGS 2.0, ECLGS 3.0.
- Who are eligible Mudra borrowers?
Mudra borrowers are micro-finance units who have availed of loans from Banks/NBFCs/MFIs under the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojna (PMMY) scheme.
- Do Eligible Borrowers have to have any particular organisational form, for example, company, firm, proprietorship, etc?
No. There is no particular organisational form for the Eligible Borrower. It may be a company, firm, LLP, proprietorship, etc.
Note that the Scheme initially used the expression: “all Business Enterprises / MSME institution borrower accounts”. From the use of the words “business enterprises” or “institution borrower account”, it was contended that individuals are excluded. In Para 7 of the Operational Guidelines on the website of NCGTC, it mentioned that “Loans provided in individual capacity are not covered under the Scheme”. However, the very same para also permitted a business run as a proprietorship as an eligible case of business enterprise.
Hence, there was a confusion between a business owned/run by an individual, and a loan taken in individual capacity. The latter will presumably mean a loan for personal purposes, such as a home loan, loan against consumer durables, car loan or personal loan. As opposed to that, a loan taken by a business, even though owned by an individual and not having a distinctive name than the individual himself, cannot be regarded as a “loan provided in individual capacity”.
For instance, many SRTOs, local area retail shops, etc are run in the name of the proprietor. There is no reason to disregard or disqualify such businesses. It is purpose and usage of the loan for business purposes that matters.
To ensure clarity, the revised operational guidelines include business loans taken by individuals for their own businesses in the ambit of scheme, Further, individual would be required to fulfil eligibility criteria for the borrower.
- What is the meaning of the term “business enterprise” which is defined as one of the Eligible Borrowers?
The term “ business enterprise” has been used repetitively in the Scheme, and is undefined. In our view, its meaning should be the plain business meaning– enterprises which are engaged in any business activity. The word “business activity” should be taken broadly, so as to give an extensive and purposive interpretation to fulfil the intent of the Scheme. Clearly, the Scheme is intended to encourage small businesses which are the backbone of the economy and which may help create “self reliant” India.
Having said this, it should be clear that the idea of the Scheme is not to give loans for consumer durables, personal use vehicles, consumer loans, personal loans, etc. While taking the benefit of the Scheme, the MLI should bear in mind that the intent of the lending is to spur economic activity. There must be a direct nexus between the granting of the facility and economic/business activity to be carried by the Eligible Borrower.
- One of the Eligible Borrowers is an MSME. Is it necessary that the entity is registered i.e. has a valid Udyog Aadhaar Number, as required under the MSMED Act?
The eligibility criteria for borrowers does not specifically require the MSMEs to be registered under the MSMED Act. Thus, an unregistered MSME may also be an Eligible Borrower under the scheme.
- For the borrowers to give a self-declaration of turnover for FY 2019-20, is there a particular form of declaration?
There is no particular form. However, we suggest something as simple as this:
To whomsoever it may concern
Sub: Declaration of Turnover
I/ We………………………………….. (Name of Authorized Signatory), being ……………………..(Designation) of …………………………………………………. (Legal Name as per PAN) do hereby state that while the financial statements for the FY 2019-20 have not still been prepared or finalised, based on our records, the turnover of the abovementioned entity/unit during the FY 2019-2 will be within the value of Rs 250 crores.
Signed …………. Date:…………………
Note: The turnover applicability under ECLGS 1.0 has been removed.
- One of the important conditions under ECLGS 1.0, ECLGS 2.0 and ECLGS 3.0 for the Eligible Borrower is that the Borrower must not be an NPA, or SMA 2 borrower. For finding the DPD status of the existing facility, how do we determine the same in the following cases?
- My EMIs are due on 10th of each month. On 10th Feb., 2020, the borrower had two missing EMIs, viz., the one due on 10th Jan. 2020 and the one due on 10th Feb., 2020. Is the Borrower an Eligible Borrower on 29th Feb., 2020?
The manner of counting DPD is – we need to see the oldest of the instalments/ principal/interest due on the reckoning date. Here, the reckoning date is 29th Feb. On that date, the oldest overdue instalment is that of 10th Jan. This is less than 59 DPD. Hence, the borrower is eligible.
- My EMIs are due on the 1st of each month. The borrower has not paid the EMIs due on 1st Jan. and 1st Feb., 2020. Is the Borrower an Eligible Borrower on 29th Feb., 2020?
On the reckoning date, the oldest instalment is that of 1st Jan. 2020. Since the reckoning date is 29th Feb., we will be counting only one two dates – 1st Jan and 29th Feb. The time lag between the two adds to exactly 59 days. The borrower becomes ineligible if the DPD status is more than 59 days. Hence, the borrower is eligible.
- Is the Scheme restrictive as to the nature of the existing facility? Can the GECL be different from the existing facility?
It does not seem relevant that the GECL should be of the same nature/type or purpose as the primary facility. We have earlier mentioned that the purpose of the GECL is to support the business/economic activity of the borrower.
However, there may be issues where the existing facility itself would not have been eligible for the Scheme. For instance, if the existing facility was a car loan to a business entity (say, an MSME), can the GECL be eligible if the same is granted for working capital purposes? Intuitively, this does not seem to be covered by the Scheme. Once again, the intent of the Scheme is to provide “further” or additional funding to a business. Usually, the so-called further or additional funding for a business may come from a lender who had facilitated business activity by the primary facility.
Hence, in our view, the primary as well as the GECL facility should be for business purposes.
- Is there a relevance of the residual tenure of the primary facility? For example, if the primary facility is maturing within the next 6 months, is it okay for the MLI to grant a GECL (ECLGS 1.0) for 4 years?
There does not seem to be a correlation between the residual term of the primary facility and the tenure of the GECL facility. The GECL seems to be having a term of 4 years, irrespective of the original or residual term of the primary facility.
Of course, the above should be read with our comments above about the primary facility as well as the GECL to be for business purposes.
- A LAP loan was granted to a business entity/Individual. The loan was granted against a self-owned house, but the purpose of the loan was working capital for the retail trade business carried by the borrower. Will this facility be eligible for GECL (ECLGS 1.0)?
Here, the purpose of the loan, and the nature of collateral supporting the loan, are different, but what matters is the end-use or purpose of the loan. The collateral is a self-occupied house. But that does not change the purpose of the loan, which is admittedly working capital for the retail trade activity.
Hence, in our view, the facility will be eligible for GECL (ECLGS1.0), subject to other conditions being satisfied.
- I have an existing borrower B, who is a single borrower as on 29th Feb 2020. I now want to grant the GECL loan to C, who would avail the loan as a co-borrower with B. Can I lend to B and C as co-borrowers?
It seems that even loans extended to co-obligors or co-applicants also qualify.
We may envisage the following situations:
- The primary facility was granted to B and C. B is an Eligible Borrower. The GECL is now being granted to B and C. This is a good case for GECL funding, provided B remains the primary applicant. In co-applications, the co-borrowers have a joint and several obligations, and the loan documentation may not make a distinction between primary and secondary borrower. However, one needs to see the borrower who has utilised the funding.
- The primary facility was granted to B who is an Eligible Borrower. The GECL is now being granted to B and C. This is a good case for GECL funding if B is the primary applicant. See above for the meaning of “primary” applicant.
- The primary facility was granted to B, who is a director of a company, where C, the company, joined as a co-applicant. C is an Eligible Borrower. The GECL is now being granted to C. This is a good case for GECL funding since the GECL funding is to C and C is an Eligible Borrower.
- When can GECL be sanctioned? Is there a time within which the GECL should be sanctioned? –Updated as on June 08, 2021
The GECL under ECLGS 1.0, ELCGS, 2.0, ECLGS 3.0, and ECLGS 4.0 shall be sanctioned latest by Spetember 30, 2021 or till an amount of Rs. 3 lakh crore is sanctioned under GECL, whichever is earlier.
19A. Is there a sunset clause for the guarantees to be extended under the ECLGS schemes?
For fund-based (ECLGS 1.0, ECLGS 2.0, ECLGS 3.0, and ECLGS 4.0) and non-fund-based (ECLGS 2.0 and ECLGS 4.0) as may be applicable, facilities under all the Schemes to be sanctioned latest by September 30, 2021.
While the disbursement or utilisation (as the case may be) of such sanctioned additional credit facility shall be done latest by December 31, 2021.
- How can an MLI keep track of how much is the total amount of facilities guaranteed by NCGTC?
Understandably, there may be mechanisms of either dissemination of the information by NCGTC, or some sort of a pre-approval of a limit by NCGTC.
- Whether the threshold limit of outstanding credit of Rs. 50 crores under ECLGS 1.0, will have to be seen across all the lenders, the borrower is currently dealing with, or with one single lender?
The Scheme specifically mentions that the limit of Rs. 50 crores shall be ascertained considering the borrower accounts of the business enterprises/MSMEs with combined outstanding loans across all MLIs. For the purpose of determining whether the combined exposure of all MLIs is Rs 50 crores or not, the willing MLI may seek information about other loans obtained by the borrower.
- For ECLGS 1.0 the threshold limit of outstanding credit of Rs. 50 crores, are we capturing only eligible borrowings of the borrower, or all debt obligations?
Logically, all business loans, that is, loans/working capital facilities or other funded facilities availed for business purposes should be aggregated. For instance:
- Unfunded facilities, say, L/Cs or guarantees, do not have to be included.
- Non-business loans, say, car loans, obtained by the entity do not have to be included as the same are not for business purposes.
- What is the meaning of MSME? Is it necessary that the Eligible Borrower should be meeting the definition of MSME as per the Act?
The Scheme uses the term MSME, but nowhere has the Scheme made reference to the definition of MSME under the MSMED Act, 2006. Therefore, it does not seem necessary for the Eligible Borrower to have registration under the MSMED Act. Further, even if the entity in question is not meeting the criteria of MSME under the Act, it may still be satisfying the criteria of “business enterprise” with reference to turnover and borrowing facilities. Hence, the reference to the MSMED Act seems unimportant.
However, for the purpose of ease of reference, we are giving below the meaning of MSME as per the definition of MSMEs provided in the MSMED Act, 2006 (‘Act’):
| Enterprise | Manufacturing sector [Investment in plant and machinery (Rs.)] | Service sector [Investment in equipment (Rs.)] |
| Small | Not exceeding 25 lakhs | Not exceeding 10 lakhs |
| Micro | Exceeding 25 lakhs but does not exceed 5 crores | Exceeding 10 lakhs but does not exceed 2 crores |
| Medium | Exceeding 5 crores but not exceeding 10 crores | Exceeding 2 crores but does not exceed 5 crores |
The above definition has been amended by issue of a notification dated June 1, 2020. As per the amendment such revised definition shall be applicable with effect from July 01, 2020. Accordingly, w.e.f. such date, following shall be the definition of MSMEs:
| Enterprise | Investment in plant and machinery or equipment (in Rs.) | Turnover (in Rs.) |
| Micro | Upto 1 crore | Upto 5 crores |
| Small | Upto 10 crores | Upto 50 crores |
| Medium | Upto 50 crores | Upto 250 crores |
- The existing schemes laid down by the CGTMSE, CGS-I and CGS-II, cover the loans extended to MSE retail traders. Will the retail traders be eligible borrowers for this additional facility?
The Scheme states that a borrower is eligible if the borrower has –
(i) total credit outstanding of Rs. 50 Crore or less as on 29th Feb 2020;
(ii) turnover for 2019-20 was upto Rs. 250 Cr; (Turnover limit omitted by way of updated operational guidelines)
(iii) The borrower has a GST registration where mandatory.
Udyog Aadhar Number (UAN) or recognition as MSME is not required under this Scheme.
Hence, even retail traders fulfilling the eligibility criteria above would be eligible under the scheme.
- If the borrower does not have any existing credit facility as on 29th February, 2020, will it still be able to avail fresh facility(ies) under this Scheme?
Looking at the clear language of the Scheme, it seems that existence of an outstanding facility is a prerequisite to avail credit facility under the Scheme. The intent of the Scheme is to provide additional credit facility to existing borrowers.
25 A. What if the borrower satisfies the conditions with respect to DPDs on the respective cut-off dates under various ECLGS schemes, but subsequently is downgraded to NPA – will the borrower still be eligible for additional finance under the schemes?
The borrower account otherwise eligible under the scheme should not be an NPA as on the date of sanction / disbursement.
- I have a borrower to whom I have provided a sanction before 29th February, 2020; however, no disbursement could actually take place within that date. Will such a borrower qualify for the Scheme?
Since the amount of GECL is related to the POS as on 29th Feb., 2020, there is no question of such a borrower qualifying.
- The Scheme seems to refer to the facility as a “working capital term loan” in case of banks/FIs and “additional term loan” in case of NBFCs. Does that mean the MLIs cannot put any end-use restrictions on utilisation of the facility by the Eligible Borrowers?
It is counter-intuitive to think that the MLI cannot put end-use restrictions. Ensuring that the funds lent by the MLI are used for the purpose for which the facility has been extended is an essential prudential safeguard for a lender. It should be clear that the additional facility has been granted for restarting business, following the disruption caused by the COVID crisis. There is no question of the lender permitting the borrower to use the facility for extraneous or irrelevant purposes.
Terms of the GECL Facility
- What are the major terms of the GECL Facility (ECLGS 1.o)?
The major terms are as follows:
- Amount of the Facility: Up to 20% of the POS as on 29th Feb., 2020. Note that the expression “upto” implies that the MLI/borrower has discretion in determining the actual amount of top up funding, which may go upto 20%.
- Tenure of the Facility: 4 years. See below about whether the parties have a discretion as to tenure.
- Moratorium: 12 months. During the moratorium, both interest and principal will not be payable. Hence, the first payment due under the top up facility will be on the anniversary of the facility.
- Amortisation/repayment term: 36 months.
- Mode of repayment: While the Scheme says that the principal shall be payable in 36 installments, it should not mean 36 equal instalments of principal. The usual EMI, wherein the instalment inclusive of interest is equated, works well in the financial sector. Hence, EMI structure may be adopted. However, if the parties prefer equated repayment of principal, and the interest on declining balances, the same will also be possible. Note that in such case, the principal at the end of 12 months will have the accreted interest component for 12 months’ moratorium period as well.
- Collateral: The Scheme says that no additional collateral shall be asked for the purposes of the GECL. In fact, given the sovereign guarantee, it may appear that no additional collateral is actually required. [However, see comment below on dilution of the collateral as a result of the top-up funding].
- Rate of interest: The rate of interest is capped as follows – In case of banks/ – Base lending rate + 100 bps, subject to cap of 9.25% p.a. In case of NBFCs, 14% p.a.
- Processing/upfront fees: None
- As regards the interest rate, is it possible that the MLI has the benefit under any interest rate subvention scheme as well?
Yes. This scheme may operate in conjunction with any interest rate subvention scheme as well.
- Is the tenure of the GECL facility non-negotiably fixed at 4 years or do the parties have discretion with respect to the same? For example, if the borrower agrees to a term of 3 years, is that possible?
It seems that the Scheme has a non-negotiable tenure of 4 years. Of course, the Scheme document does say the parties may agree to a prepayment option, without any prepayment penalty. However, in view of the purpose of the Scheme, that is, to restart business activity in the post-COVID scenario, it does not seem as if the purpose of the Scheme will be accomplished by a shorter loan tenure.
- Is it possible for MLI to lend more than 20%, but include only 20% for the benefit of the guarantee?
Minus the Scheme, nothing stopped a lender from giving a top-up lending facility on a loan. Therefore, the wrapped portion of the GECL facility is 20% of the loan, but if the lender so wishes to give further loan, there is nothing that should restrain the lender from doing so.
- The Scheme document provides that the collateral for the primary loan shall be shared pari passu with the GECL facility. What does the sharing of the collateral on pari passu basis mean?- Updated -The collateral under ECLGS scheme will rank second in terms of collateral and cashflows to the primary credit facility.
Para 11 of the Scheme document says: “…facility granted under GECL shall rank pari passu with the existing credit facilities in terms of cash flows and security”. The concept of pari passu sharing of the security, that is, the collateral, may create substantial difficulties in actual operation, since the terms of repayment of the primary facility and the GECL facility are quite divergent.
To understand the basic meaning of pari passu sharing, assume there is a loan of Rs 100 as on 29th Feb., 2020, and the MLI grants an additional loan of Rs 20 on 1st June, 2020. Assume that the value of the collateral backing the primary loan is Rs 125. As and when the GECL is granted, the value of this collateral will serve the benefit of the primary loan as well as the GECL facility. In that sense, there is a dilution in the value of the security for the primary loan. This, again, is illogical since the primary does not have a sovereign wrap, while the GECL facility has.
What makes the situation even worse is that due to amortizing nature of the primary loan, and the accreting nature of the GECL facility during the moratorium period, the POS of the primary facility will keep going down, while the POS of the GECL facility will keep going up. It may also be common that the primary facility will run down completely in a few months (say 2 years), while the GECL facility is not even half run-down. In such a situation, the benefit of the collateral will serve the GECL loan, in proportion to the amount outstanding of the respective facilities. Obviously, when the primary facility is fully paid down, the collateral serves the benefit of the GECL facility only.
The ECLGS scheme initially provided for parri-passu charge over collateral, but by way of subsequent amendment, the anomaly discussed above was removed by the Government. Therefore, in the example above, there will be no dilution in the value of the security for the primary loan. Since the proceeds from the collateral will be used, firstly to recover dues of the primary loan facility, and secondly the remaining amount from realisation of collateral (if any) will be used to satisfy loan under GECL Facility.
- The Scheme provides that the primary facility and the GECL facility shall rank pari passu, in terms of cash flows. What is the meaning of pari passu sharing of cashflow? Updated -The cashflows under ECLGS scheme will rank second to the primary credit facility.
The sharing of cashflows on pari passu basis should mean, if there are unappropriated payments made by the borrower, the payment made by the borrower should be split between the primary facility and the GECL facility on proportionate basis, proportional to the respective amounts falling/fallen due.
For instance, in our example taken in Q 15 above, assume the borrower makes a payment in the month of July 2020. The entire payment will be taken to the credit of the primary loan since the GECL loan is still in moratorium.
Say, in the month of July 2021, an aggregate payment is made by the borrower, but not sufficient to discharge the full obligation under the primary facility and the GECL facility. In this case, the payment made by the borrower will be appropriated, in proportion to the respective due amounts (that is, due for the month or past overdues) for the primary facility and the GECL facility.
Refer to updated FAQ 32.
- Given the fact that the payments for the GECL are still being collected by the MLI, who also has a running primary facility with the same borrower, is there any obligation on the part of the MLI to properly appropriate the payments received from the borrower between the primary and the GECL facility?
Indeed there is. The difficulty arises because there are two facilities with the borrower, one is naked, and the other one wrapped. The pari passu sharing of cashflows will raise numerous challenges of appropriation. Since the claim is against the sovereign, there may be a CAG audit of the claims settled by the NCGTC.
- The Scheme document says that the charge over the collateral has to be created within 3 months from the date of disbursal. What is the meaning of this?
If the existing loan has a charge securing the loan, and if the same security interest is now serving the benefit of the GECL facility as well, it will be necessary to modify the charge, such that charge now covers the GECL facility as well. As per Companies Act, the time for registration of a modification is thirty days, and there is an additional time of ninety days.
- Say the primary loan is a working capital loan given to a business and has a residual tenure of 24 months. The loan is secured by a mortgage of immovable property. Now, GECL (ECLGS 1.0) facility is granted, and the same has a tenure of 48 months. After 24 months, when the primary loan is fully discharged, can the borrower claim the release of the collateral, that is, the mortgage?
Not at all. The grant of the GECL facility is a grant of an additional facility, with the same collateral. Therefore, until the GECL loan is fully repaid, there is no question of the borrower getting a release of the collateral.
- Should there be a cross default clause between the primary loan and the GECL loan?
In our view, the collateral is shared by both the facilities on pari passu basis. Hence, there is no need for a cross default clause.
- What are the considerations that should prevail with the borrower/MLI while considering the quantum of the GECL facility?
The fact that the GECL facility is 100% guaranteed by the sovereign may encourage MLIs to consider the GECL facility as risk free, and go aggressively pushing lending to their existing borrowers.
For the borrower as well, the borrower eventually has to pay back the loan. In case of NBFCs, the loan is not coming cheap – it is coming at a cost of 14%. While for the lender, the risk may be covered by the sovereign guarantee, the risk of credit history impairment for the borrower is still the same.
Hence, we suggest both the parties to take a considered call. For the lender, the consideration should still be the value of the collateral, considering the amount of the top up facility. In essence, the top up facility does not mechanically have to be 20% -the amount may be carefully worked out.
- Does the disbursal of the GECL facility have to be all in cash, or can it be adjusted partly against the borrower’s obligations, say for any existing overdues? Can it be partly given to MLI as a security deposit?
While the disbursal should appropriately be made by the MLI upfront, if the borrower uses the money to settle existing obligations with the MLI, that should be perfectly alright.
- In case the borrower has multiple loan accounts with multiple eligible lenders, how will such borrower avail facility under GECL?
It is clarified that a borrower having multiple loan accounts with multiple lenders can avail GECL. The GECL will have to be availed either through one lender or each of the current lenders in proportion depending upon the agreement between the borrower and the MLI.
Further, In case the borrower wishes to take from any lender an amount more than the proportional 20% of the outstanding credit that the borrower has with that particular lender, a No Objection Certificate (NOC) would be required from the lender whose share of ECLGS loan is proposed to be extended by a specific lender. Further, it would be necessary for the specific lender to agree to provide ECLGS facility on behalf of such of the lenders.
Lender-Borrower documentation
- The Scheme has consistently talked about an opt-out facility for the GECL scheme. What exactly is the meaning of the opt-out facility?
In our understanding, the meaning is, except for those borrowers who opt out of the facility, the lender shall consider the remaining borrowers as opting for the facility. However, there cannot be a case of automatic lending, as a loan, after all, is a mutual obligation of the borrower towards the lender. Hence, there has to be explicit agreement on the part of the borrower with the lender.
Of course, a wise borrower may also want to negotiate a rate of interest with the lender.
- What documentation are we envisaging as between the MLI and the borrower?
At least the following:
- Additional loan facility documentation, whether by a separate agreement, or annexure to the master facility agreement executed already by the borrower.
- Modification of charge.
Income recognition, NPA recognition, risk weighting and ECL computation
- During the period of the moratorium on the GECL facility, will income be recognised?
Of course, yes. In case of lenders following IndAS 109, the income will be recognised at the effective interest rate. In case of others too, there will be accrual of income.
- Once we give a GECL loan, we will have two parallel facilities to the borrower – the primary loan and the GECL loan. Can it be that one of these may become an NPA?
The GECL loan will have a moratorium of 12 months – hence, nothing is payable for the first 12 months. The primary facility may actually be having upto 59 DPD overdues at the very start of the scheme itself. Hence, it is quite possible that the primary facility slips into an NPA status.
As a rule, if a facility granted to a borrower has become an NPA, then all facilities granted to the same borrower will also be characterised as NPAs.
Therefore, despite the 100% sovereign guarantee, the facility may still be treated as an NPA, unless there is any separate dispensation from the RBI.
- If the GECL facility becomes an NPA, whether by virtue of being tainted due to the primary loan or otherwise, does it mean the MLI will have to create a provision?
As regards the GECL facility, any provision is for meeting the anticipated losses/shortfalls on a delinquent loan. As the GECL is fully guaranteed, in our view, there will be no case for creating a provision.
- Will there be any expected credit loss [ECL] for the GECL facility?
In view of the 100% sovereign guarantee, this becomes a case of risk mitigation. In our view, this is not a case for providing for any ECL.
- Will the 40 bps general loss provision for standard assets have to be created for the GECL loans too?
Here again, our view is that the facility is fully sovereign-guaranteed. Hence, there is no question of a prudential build up of a general loss provision as well. The RBI should come out with specific carve out for GECL loans.
- Will capital adequacy have to be created against GECL assets?
The RBI issued a notification on June 22, 2020 stating that since the facilities provided under the Scheme are backed by guarantee from GoI, the same shall be assigned 0% risk weight, in the books of MLIs.
Guarantor and the guarantee
- Who is the guarantor under the Scheme?
The Guaranteed Emergency Credit Line (GECL) or the guarantee under the Scheme shall be extended by National Credit Guarantee Trustee Company Limited (NCGTC, ‘Trust’).
- What is National Credit Guarantee Trustee Company Ltd (NCGTC)?
NCGTC is a trust set up by the Department of Financial Services, Ministry of Finance to act as a common trustee company to manage and operate various credit guarantee trust funds. It is a company incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956.
- What is the role of NCGTC?
The role of NCGTC is to serve as a single umbrella organization which handles multiple guarantee programmes of the GoI covering different cross-sections and segments of the economy like students, micro entrepreneurs, women entrepreneurs, SMEs, skill and vocational training needs, etc.
Presently, NCGTC manages 5 credit guarantee schemes that deal with educational loans, skill development, factoring, micro units etc.
- To what extent will the guarantee be extended?
The guarantee shall cover 100% of the eligible credit facility.
- Whether the guarantee will cover both principal and interest components of the credit facility?
Yes, the Scheme shall cover both the interest as well as the principal amount of the loan.
- What will be the guarantee fee?
The NCGTC shall charge no guarantee fee from the Member Lending Institutions (MLIs) in respect of guarantee extended against the loans extended under the Scheme.
- Are eligible lenders required to be registered with the NCGTC to become MLIs?
Usually, eligible lenders under such schemes are required to enter into an agreement with the trust extending the guarantee, to become their members. In this scheme, the eligible lenders are required to provide an undertaking to the NCGTC, in the prescribed format, in order to become MLIs.
- What is the procedure for obtaining the benefit of guarantee under the Scheme?
The MLI shall, within 90 days from a borrower account under the scheme turning NPA, inform the date on which such account turned NPA. On such intimation, NCGTC shall pay 75% of the guaranteed amount to the MLI i.e. 75% of the default amount.
The rest 25% shall be paid on conclusion of recovery proceedings or when the decree gets time barred, whichever is earlier.
Securitisation, direct assignment and co-lending
- The loan, originated by the NBFC, has been securitised. Is it possible for the NBFC to give a GECL facility based on the POS of the securitised loan?
On the face of it, there is nothing that stops a lender from giving a further facility, in addition to the one that has been securitised. However, in the present case, there will be modification of the existing charge document, whereby the charge will be extended to the top up GECL loan as well. This amounts to a dilution of the security available for the primary loan. In our view, this will require specific consent of the PTC investors, through the trustee.
Note that FAQ 35 by NCGTC seems to be talking about off-balance sheet facility. Many securitisation transactions are actually on the balance sheet. Further, even if the original facility has gone off the balance sheet, the additional funding being given by the originator-servicer will be on-the-balance sheet.
Any interpretation of the guarantee scheme has to serve the purpose for which the scheme was envisaged – which is, clearly, to provide additional liquidity to borrowers affected by the disruption. There can be no suggestion that borrowers whose loans have been securitised will not need additional liquidity. Hence, the Scheme intends to wrap all additional lendings done by the lender, within the limits of 20%.
- The loan, originated by the NBFC, has been assigned to the extent of 90% to a bank. Is it possible for the NBFC to give a GECL facility based on the POS of the partly-assigned loan?
Same reasoning as above. Here again, FAQ 40 by NCGTC is talking about the entity on whose books the loan currently is. NCGTC’s view about the loan being on the books of a lender is seemingly overshadowed by accounting concepts which have drastically changed over time. For example, a loan which has been a matter of a DA transaction is actually partly on the books of the original lender, and partly on the books of the assignee. One cannot expect the assignee to be giving the additional line of credit, as the assignee is, practically speaking, a mere passive investor. The assignee does not have the franchise/relation with the borrower, which the originator has. To contend that the assignee bank should extend the additional facility is actually to deny the facility to the borrower completely, for no fault of the borrower and for no gain for the system. Since it is the original lender who maintains the relation with the borrower, it is original lender only who may extend the facility.
- Is it possible for the NBFC to originate the GECL facility, and securitise/assign the same? Will the assignee have the benefit of the GoI guarantee?
There is nothing in the Scheme for assignment of the benefit of guarantee. Typically, unless the guarantee agreement says to the contrary, the benefit of a security or guarantee is assignable along with the underlying loan. However, the guarantee agreement between NCGTC and the lender will be critical in determining this.
60. Can a borrower who availed facility under ECLGS 1.0, restructure the same, and to what extent?
Borrowers who have availed assistance under ECLGS 1.0 and are eligible for restructuring as per RBI guidelines of May 05, 2021, are permitted to avail of the same. However, the restructuring can involve granting of moratorium on payments, and granting of additional assistance upto 10% of the POS as on 29.02.2020 or 40% of the POS as on 29.02.2020 if borrower satisfies the conditions under ECLGS 3.0. In case, a moratorium is granted, the restructured repayment tenure can be extended upto 5 years, i.e, period upto 24 months during which only interest shall be payable and the principal instalments shall be payable thereafter in 36 monthly instalments.
61. Can the borrowers whose existing ECLGS facilities have been restructured become eligible for additional facilities under any of the ECLGS schemes?
In case the borrower has availed funding under ECLGS 1.0, the loan can be restructured and borrower can avail either of the following
1. ECLGS 3.0- 40% (incremental only), provided the borrower is an eligible borrower under ECLGS 3.0
OR
2. 10% additional facility
The borrower accounts covered under the RBI’s resolution framework would be eligible for additional assistance of 10% or additional assistance under ECLGS 3.0, but not both
62. Can the borrowers who have availed additional finance from the lender as a part of the RBI’s restructuring framework also avail additional finance under the ECLGS framework?
The borrower will have the following options
- ECLGS 1.0- 20%
- ECLGS 3.0- 40%
The only difference between the additional funding under the RBI framework and the ECLGS Scheme would be that the former is not guaranteed whereas the latter is 100% guaranteed.
63. Can the borrowers who have availed the restructuring facility for other loans avail the ECLGS facility post restructuring?
In case the borrower has not availed additional facilities under any of the ECLGS schemes previously, and gets its existing facilities restructured, it will have the option of availing additional facilities under any of the ECLGS schemes, subject to the fulfillment of the conditions provided thereunder.
64. To what extent can moratorium be granted (on the loans extended under the ECLGS scheme?
| Scheme | Total repayment period including moratorium | Moratorium period on principal repayment |
| ECLGS 1.0 | 4 years * | 1 year |
| ECLGS 2.0 | 5 years | 1 year |
| ECLGS 3.0 | 6 years | 2 year |
| ECLGS 4.0 | 5 years | 6 months |
The aforementioned indicates the maximum period of moratorium, the lenders shall have the discretion to provide shorter moratorium periods as well. Further, it is important to note that during the moratorium period, the interest will have to be serviced by the borrower – therefore, unlike the moratorium period under the COVID 19 relief package provided by the RBI which provided for complete moratorium on EMI payments, this will not be a complete moratorium, and at least the interest will have to be serviced during this period.
* Provided there is no restructuring under Restructuring Framework 2.0.
65. What is the tenure and moratorium period allowed for non-fund based facilities?
Under ECLGS 2.0 and 4.0, no tenor has been prescribed for non-fund based facility, but the guarantee cover on the non-fund based facility shall expire on completion of 5 years from the date of first disbursement/first utilization under fund based or non-fund based facility.
66. A borrower has availed 20% additional credit line under ECLGS 1.0. What incremental funding can be availed by such borrower if it qualifies as an eligible borrower under ECLGS 3.0?
The borrower who has availed 20% GECL under ECLGS 1.0, and the same borrower is also eligible under ECLGS 3.0, in such a case the borrower shall only be eligible for incremental funding amount. Incremental funding amount can be calculated as follows:
Let POS as on Feb 29 be Rs. 200
1. Eligible funding under ECLGS 3.0 (40% of POS as on Feb 29, 2020) = Rs. 80
2. Funding availed under ECLGS 1.0 (20% of POS as on Feb 29, 2020) = Rs. 40
3. Eligible incremental funding: 1-2 = Rs. 40
67. Will there be a provisioning requirement for additional 10% funding extended to loans under ECLGS 1.0, as part of RBI 05 May 2021 Restructuring Framework 2.0?
The initial top up GECL facility was zero rated (notification on June 22, 2020), therefore additional finance extended by the lender as part of restructuring of GECL under RBI Restructuring Framework 2.0 shall also be risk free. Hence there is no provisioning requirement for such additional 10% finance extended to GECL loan under Restructuring Framework 2.0.
Comparative table of ECLGS schemes :
| ECLGS 1.0 | ECLGS 2.0 | ECLGS 3.0 | ECLGS 4.0 | |
| Nature of support | Opt Out (Pre approved)- Extended Credit Guarantee Line upto 20% of Outstanding loan as on 29.02.2020 | Opt In Extended Credit Guarantee Line (fund based or non-fund based) upto 20% of Outstanding loan as on 29.02.2020 | Opt In Extended Credit Guarantee line (fund based) upto 40% of Outstanding loan as on 29.02.2020 | Opt In Extended Credit line for assistance upto 2 crores. |
| Fund based support or non-fund based support |
|
|
|
|
| Extent of additional finance permitted |
|
|
|
|
| Eligible borrowers | Business Enterprises / MSMEs/individuals who have availed loan for business purposes
|
26 key sectors identified by Kamath committee report and healthcare sector
|
Hospitality, Travel & Tourism, Leisure & Sporting sectors, scheduled and non-scheduled airlines, chartered
flight operators, air ambulances and airports
|
Existing Hospitals/nursing
homes/clinics/medical colleges / units engaged in manufacturing of liquid oxygen, oxygen cylinders etc
|
| Eligible lenders |
|
|
|
|
| Interest rate on facilities (Max cap) |
|
|
|
7.5% |
| Tenor of facilities |
|
|
|
|
| Moratorium on repayment of facilities |
|
|
|
|
| Principal repayment tenor in case moratorium has to be granted |
|
|
|
|
| Whether eligible for restructuring |
|
|
|
|
| Security |
No security for Rs.25 lakh (outstanding as on |
No security for Rs.25 lakh (outstanding as on |
No security for Rs.25 lakh (outstanding as on |
No security for Rs.25 lakh (outstanding as on February 29, 2020 plus loan sanctioned under GECL |
| Guarantee fee |
|
|
|
|
[1] https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1625306
[2] http://www.dcmsme.gov.in/publications/circulars/cate-12-6.pdf
[3] https://udyogaadhaar.gov.in/Web/doc/Activities_NIC_CodesNotAllowed.PDF
[4] The scheme earlier required the MSMEs to obtain UAN (i.e. get registered) in order to avail benefit under the same. However the same was recently done away with through a notification issued on February 5, 2020. Link to the notification- https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/NotificationUser.aspx?Id=11803&Mode=0
[5] https://www.cgtmse.in/files/CGS-I.pdf
Our related write-ups may be referred here: