-Siddarth Goel (finserv@vinodkothari.com)
Abstract
The penetration of electronic retail payments has witnessed a steep surge in the overall payment volumes during the latter half of the last decade. One of the reasons accorded to this sharp rise in electronic payments is the exponential growth in online merchant acquisition space. An online merchant is involved in marketing and selling its goods and/or services through a web-based platform. The front-end transaction might seem like a simple buying-selling transaction of goods or services between a buyer (customer) and a seller (merchant). However, the essence of this buying-selling transaction lies in the payment mode or methodology of making/accepting payments adopted between the customer and the merchant. One of the most common ways of payment acceptance is that the merchant establishes its own payment integration mechanism with a bank such that customers are enabled to make payments through different payment instruments. In such cases, the banks are providing payment aggregator services, but the market is limited usually to the large merchants only. Alternatively, merchants can rely upon third-party service providers (intermediary) that facilitate payment collection from customers on behalf of the merchant and thereafter remittance services to the merchant at the subsequent stage – this is regarded as a payment aggregation business.
The first guidelines issued by the RBI governing the merchant and payment intermediary relationship was in the year 2009[1]. Over the years, the retail payment ecosystem has transformed and these intermediaries, participating in collection and remittance of payments have acquired the market-used terminology ‘Payment Aggregators’. In order to regulate the operations of such payment intermediaries, the RBI had issued detailed Guidelines on Regulation of Payment Aggregators and Payment Gateways, on March 17, 2020. (‘PA Guidelines’)
The payment aggregator business has become a forthcoming model in the online retail payments ecosystem. During an online retail payment by a customer, at the time of checkout vis-à-vis a payment aggregator, there are multiple parties involved. The contractual parties in one single payment transaction are buyer, payment aggregator, payment gateway, merchant’s bank, customer’s bank, and such other parties, depending on the payment mechanism in place. The rights and obligations amongst these parties are determined ex-ante, owing to the sensitivity of the payment transaction. Further, the participants forming part of the payment system chain are regulated owing to their systemic interconnectedness along with an element of consumer protection.
This write-up aims to discuss the intricacies of the regulatory framework under PA Guidelines adopted by the RBI to govern payment aggregators and payment gateways operating in India. The first part herein attempts to depict growth in electronic payments in India along with the turnover data by volumes of the basis of payment instruments used. The second part establishes a contrast between payment aggregator and payment gateway and gives a broad overview of a payment transaction flow vis-à-vis payment aggregator. The third part highlights the provisions of the PA Guidelines and establishes the underlying internationally accepted best principles forming the basis of the regulation. The principles are imperative to understand the scope of regulation under PA Guidelines and the contractual relationship between parties forming part of the payment chain.
Market Dynamics
The RBI in its report stated that the leverage of technology through the use of mobile/internet electronic retail payment space constituted around 61% share in terms of volume and around 75% in share in terms of value during FY 19-20.[2] The innovative payment instruments in the retail payment space, have led to this surge in electronic payments. Out of all the payment instruments, the UPI is the most innovative payment instrument and is the spine for growth in electronic payments systems in India. Chart 1 below compares some of the prominent payment instruments in terms of their volumes and overall compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) over the period of three years.
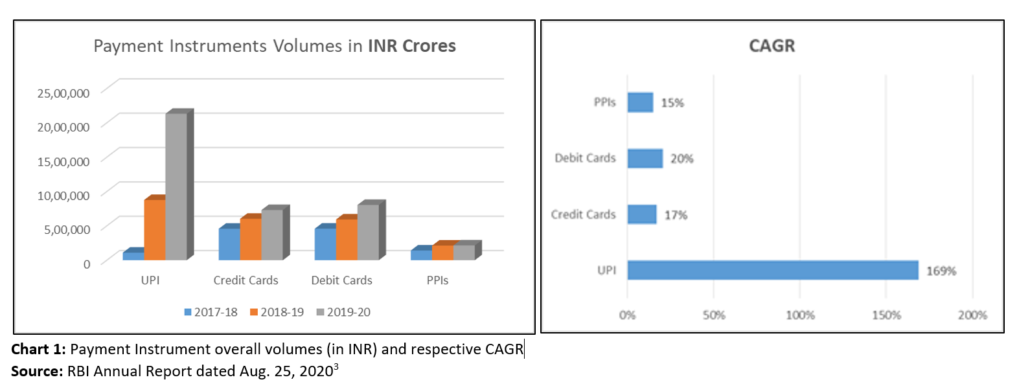
The payment system data alone does not show the complete picture. In conformity with the rise in electronic payment volumes, as per the Government estimates the overall online retail market is set to cross the $ 200 bn figure by 2026 from $ 30 bn in 2019, at an expected CAGR of 30 %.[4] India ranks No. 2 in the Global Retail Development Index (GRDI) in 2019. It would not be wrong to say, the penetration of electronic payments could be due to the presence of more innovative products, or the growth of online retail has led to this surge in electronic payments.
What are Payment Aggregators and Payment Gateways?
The terms Payment Aggregator (‘PA’) and Payment Gateways (‘PG’) are at times used interchangeably, but there are differences on the basis of the function being performed. Payment Aggregator performs merchant on-boarding process and receives/collects funds from the customers on behalf of the merchant in an escrow account. While the payment gateways are the entities that provide technology infrastructure to route and/or facilitate the processing of online payment transactions. There is no actual handling of funds by the payment gateway, unlike payment aggregators. The payment aggregator is a front-end service, while the payment gateway is the back-end technology support. These front-end and back-end services are not mutually exclusive, as some payment aggregators offer both. But in cases where the payment aggregator engages a third-party service provider, the payment gateways are the ‘outsourcing partners’ of payment aggregators. Thereby such payments are subject to RBI’s outsourcing guidelines.
PA Transaction Flow
One of the most sought-after electronic payments in the online buying-selling marketplace is the payment systems supported by PAs. The PAs are payment intermediaries that facilitate e-commerce sites and merchants in accepting various payment instruments from their customers. A payment instrument is nothing but a means through which a payment order or an instruction is sent by a payer, instructing to pay the payee (payee’s bank). The familiar payment instruments through which a payment aggregator accepts payment orders could be credit cards, debit cards/PPIs, UPI, wallets, etc.
Payment aggregators are intermediaries that act as a bridge between the payer (customer) and the payee (merchant). The PAs enable a customer to pay directly to the merchant’s bank through various payment instruments. The process flow of each payment transaction between a customer and the merchant is dependent on the instrument used for making such payment order. Figure 1 below depicts the payment transaction flow of an end-to-end non-bank PA model, by way of Unified Payment Interface (UPI) as a payment instrument.
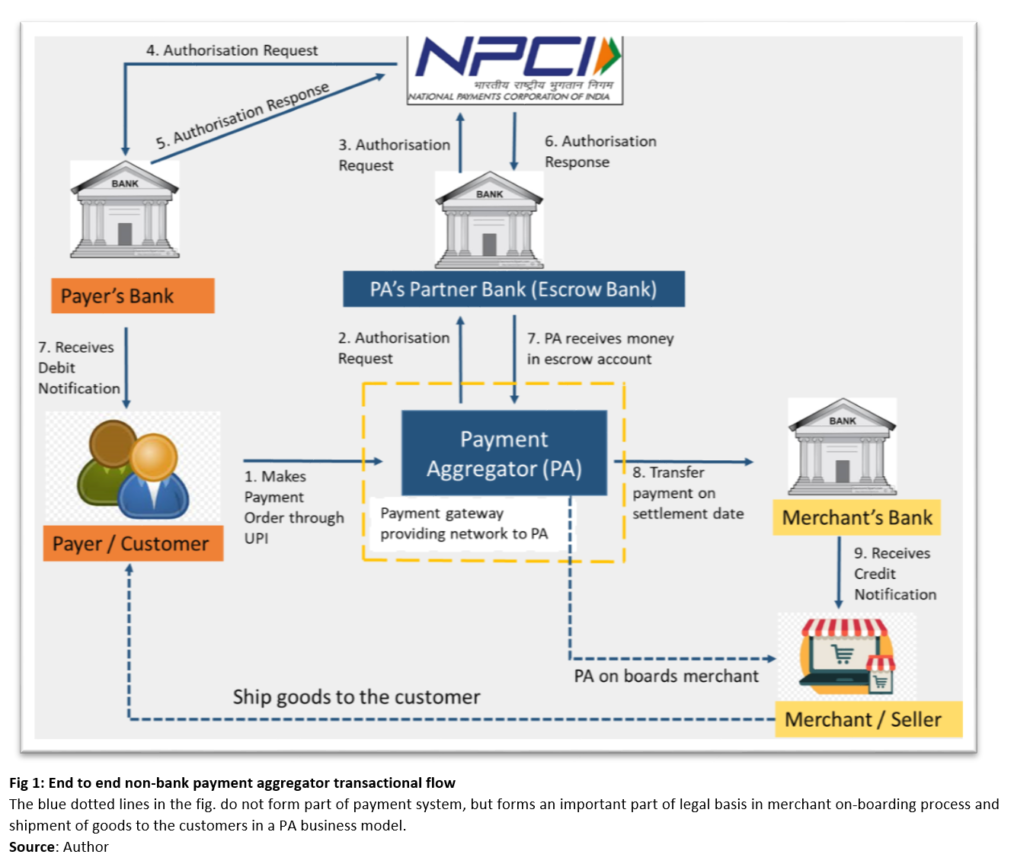
In an end-to-end model, the PA uses the clearing and settlement network of its partner bank. The clearing and settlement of the transaction are dependent on the payment instrument being used. The UPI is the product of the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), therefore the payment system established by NPCI is also quintessential in the transaction. The NPCI provides a clearing and settlement facility to the partner bank and payer’s bank through the deferred settlement process. Clearing of a payment order is transaction authorisation i.e., fund verification in the customer’s bank account with the payer’s bank. The customer/payer bank debits the customer’s account instantaneously, and PA’s bank transfers the funds to the PA’s account after receiving authorisation from NPCI. The PA intimates the merchant on receipt of payment and the merchant ships the goods to the customer. The inter-bank settlement (payer’s bank and PA’s partner bank) happens at a later stage via deferred net-settlement basis facility provided by the NPCI.
The first leg of the payment transaction is settled between the customer and PA once the PA receives the confirmation as to the availability of funds in the customer’s bank account. The partner bank of PA transfers the funds by debiting the account of PA maintained with it. The PA holds the exposure from its partner bank, and the merchant holds the exposure from the PA. This explains the logic of PA Guidelines, stressing on PAs to put in place an escrow mechanism and maintenance of ‘Core Portion’ with escrow bank. It is to safeguard the interest of the merchants onboarded by the PA. Nevertheless, in the second leg of the transaction, the merchant has its right to receive funds against the PA as per the pre-defined settlement cycle.
Regulatory approach towards PAs and PGs
The international standards and best practices on regulating Financial Market Infrastructure (FMI) are set out in CPSS-IOSCO principles of FMI (PFMI).[5] A Financial Market Infrastructure (FMI) is a multilateral system among participating institutions, including the operator of the system. The consumer protection aspects emerging from the payment aggregation business model, are regulated by these principles. Based on CPSS-IOSCO principles of (PFMI), the RBI has described designated FMIs, and released a policy document on regulation and supervision of FMIs in India under its regulation on FMIs in 2013.[6] The PFMI stipulates public policy objectives, scope, and key risks in financial market infrastructures such as systemic risk, legal risk, credit risk, general business risks, and operational risk. The Important Retail Payment Systems (IRPS) are identified on the basis of the respective share of the participants in the payment landscape. The RBI has further sub-categorised retail payments FMIs into Other Retail Payment Systems (ORPS). The IRPS are subjected to 12 PFMI while the ORPS have to comply with 7 PFMIs. The PAs and PGs fall into the category of ORPS, regulatory principles governing them are classified as follows:
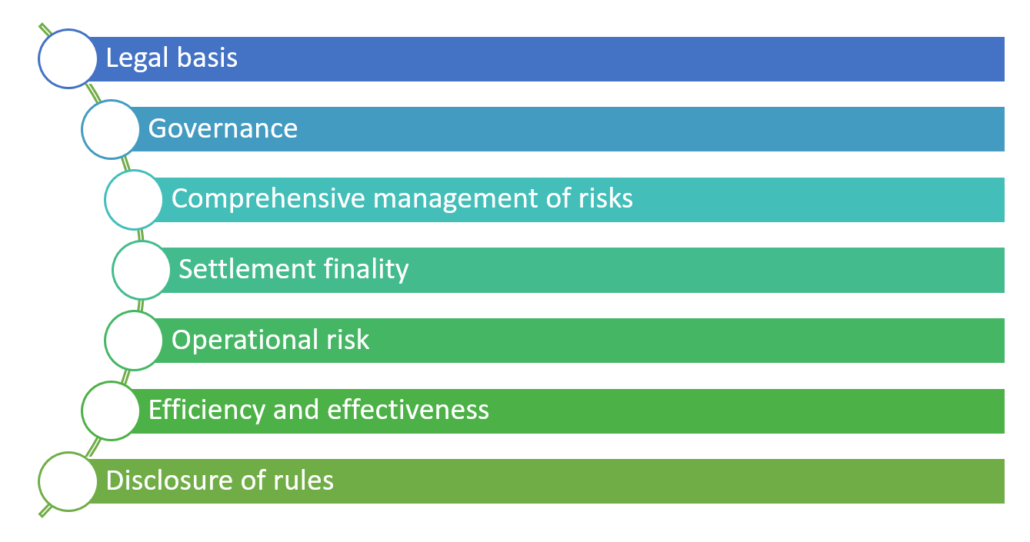
These principles of regulation are neither exclusive nor can said to be having a clear distinction amongst them, rather they are integrated and interconnected with one another. The next part discusses the broad intention of the principles above and the supporting regulatory clauses in PA Guidelines covering the same.
Legal Basis and Governance framework
The legal basis principle lays the foundation for relevant parties, to define the rights and obligations of the financial market institutions, their participants, and other relevant parties such as customers, custodians, settlement banks, and service providers. Clause 3 of PA Guidelines provides that authorisation criteria are based primarily on the role of the intermediary in the handling of funds. PA shall be a company incorporated in India under the Companies Act, 1956 / 2013, and the Memorandum of Association (MoA) of the applicant entity must cover the proposed activity of operating as a PA forms the legal basis. Henceforth, it is quintessential that agreements between PA, merchants, acquiring banks (PA’s Partners Bank), and all other stakeholders to the payment chain, clearly delineate the roles and responsibilities of the parties involved. The agreement should define the rights and obligations of the parties involved, (especially the nodal/escrow agreement between partner bank and payment aggregator). Additionally, the agreements between the merchant and payment aggregator as discussed later herein are fundamental to payment aggregator business. The PA’s business rests on clear articulation of the legal basis of the activities being performed by the payment aggregator with respect to other participants in the payment system, such as a merchant, escrow banks, in a clear and understandable way.
Comprehensive Management of Risk
The framework for the comprehensive management of risks provides for integrated and comprehensive view of risks. Therefore, this principle broadly entails comprehensive risk policies, procedures/controls, and participants to have robust information and control systems. Another connecting aspect of this principle is operational risk, arising from internal processes, information systems and disruption caused due to IT systems failure. Thus there is a need for payment aggregator to have robust systems, policies to identify, monitor and manage operational risks. Further to ensure efficiency and effectiveness, the principle entails to maintain appropriate standards of safety and security while meeting the requirements of participants involved in the payment chain. Efficiency is resources required by such payment system participants (PAs/PGs herein) to perform its functions. The efficiency includes designs to meet needs of participants with respect to choice of clearing and settlement transactions and establishing mechanisms to review efficiency and effectiveness. The operational risk are comprehensively covered under Annex 2 (Baseline Technology-related Recommendation) of the PA Guidelines. The Annex 2, inter alia includes, security standards, cyber security audit reports security controls during merchant on-boarding. These recommendations and compliances under the PA Guidelines stipulates standard norms and compliances for managing operational risk, that an entity is exposed to while performing functions linked to financial markets.
KYC and Merchant On-boarding Process
An important aspect of payment aggregator business covers merchant on-boarding policies and anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CFT) compliance. The BIS-CPSS principles do not govern within its ambits certain aspects like AML/CFT, customer data privacy. However, this has a direct impact on the businesses of the merchants, and customer protection. Additionally, other areas of regulation being data privacy, promotion of competition policy, and specific types of investor and consumer protections, can also play important roles while designing the payment aggregator business model. Nevertheless, the PA Guidelines provide for PAs to undertake KYC / AML / CFT compliance issued by RBI, as per the “Master Direction – Know Your Customer (KYC) Directions” and compliance with provisions of PML Act and Rules. The archetypal procedure of document verification while customer on-boarding process could include:
- PA’s to have Board approved policy for merchant on-boarding process that shall, inter-alia, provide for collection of incorporation certificates, constitutional document (MoA/AoA), PAN and financial statements, tax returns and other KYC documents from the merchant.
- PA’s should take background and antecedent checks of the merchants, to ensure that such merchants do not have any malafide intention of duping customers, do not sell fake/counterfeit/prohibited products, etc.
PAs shall ensure that the merchant’s site shall not save customer’s sensitive personal data, like card data and such related data. Agreement with merchant shall have provision for security/privacy of customer data.
Settlement and Escrow
The other critical facet of PA business is the settlement cycle of the PA with the merchants and the escrow mechanism of the PA with its partner bank. Para 8 of PA Guidelines provide for non-bank PAs to have an escrow mechanism with a scheduled bank and also to have settlement finality. Before understanding the settlement finality, it is important to understand the relevance of such escrow mechanisms in the payment aggregator business.
Escrow Account
Surely there is a bankruptcy risk faced by the merchants owing to the default by the PA service provider. This default risk arises post completion of the first leg of the payment transaction. That is, after the receipt of funds by the PA from the customer into its bank account. There is an ultimate risk of default by PA till the time there is final settlement of amount with the merchant. Hence, there is a requirement to maintain the amount collected by PA in an escrow account with any scheduled commercial bank. All the amounts received from customers in partner bank’s account, are to be remitted to escrow account on the same day or within one day, from the date amount is debited from the customer’s account (Tp+0/Tp+1). Here Tp is the date on which funds are debited from the customer’s bank account. At end of the day, the amount in escrow of the PA shall not be less than the amount already collected from customer as per date of debit/charge to the customer’s account and/ or the amount due to the merchant. The same rules shall apply to the non-bank entities where wallets are used as a payment instrument.[7] This essentially means that PA entities should remit the funds from the PPIs and wallets service provider within same day or within one day in their respective escrow accounts. The escrow banks have obligation to ensure that payments are made only to eligible merchants / purposes and not to allow loans on such escrow amounts. This ensures ring fencing of funds collected by the PAs, and act as a deterrent for PAs from syphoning/diverting the funds collected on behalf of merchants. The escrow agreement function is essentially to provide bankruptcy remoteness to the funds collected by PA’s on behalf of merchants.
Settlement Finality
Settlement finality is the end-goal of every payment transaction. Settlement in general terms, is a discharge of an obligation with reference of the underlying obligation (whatever parties agrees to pay, in PA business it is usually INR). The first leg of the transaction involves collection of funds by the PA from the customer’s bank (originating bank) to the PA escrow account. Settlement of the payment transaction between the PA and merchant, is the second leg of the same payment transaction and commences once funds are received in escrow account set up by the PA (second leg of the transaction).
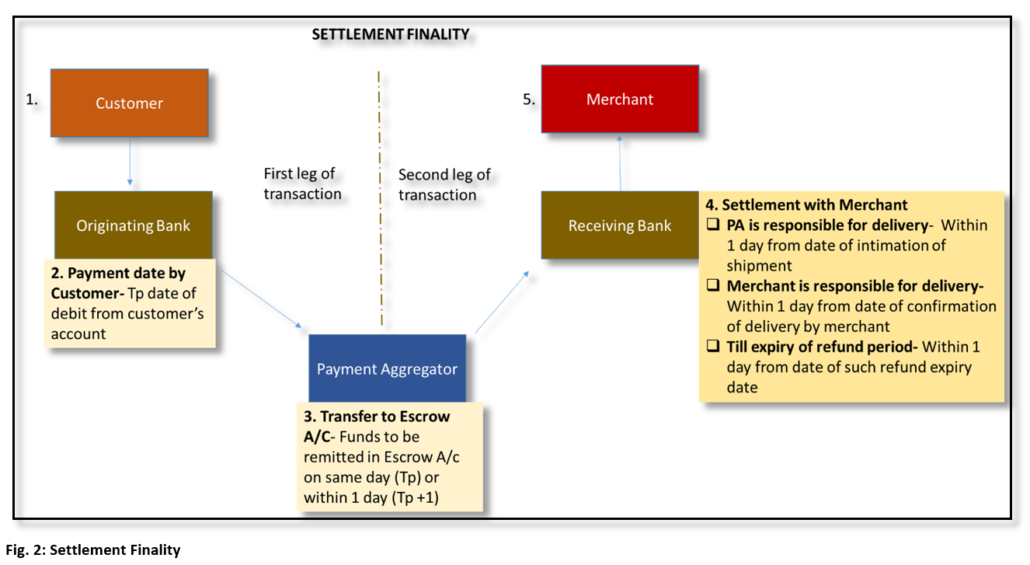
Settlement finality is the final settlement of payment instruction, i.e. from the customer via PA to the merchant. Final settlement is where a transfer is irrevocable and unconditional. It is a legally defined moment, hence there shall be clear rules and procedures defining the point of settlement between the merchant and PA.
For the second leg of the transaction, the PA Guidelines provide for different settlement cycles:
- Payment Aggregator is responsible for the delivery of goods/service– The settlement cycle with the merchant shall not be later than one day from the date of intimation to PA of shipment of goods by the merchant.
- Merchant is responsible for delivery– The settlement cycle shall not be later than 1 day from the date of confirmation by the merchant to PA about delivery of goods to the customer.
- Keeping the amount by the PA till the expiry of refund period– The settlement cycle shall not be later than 1 day from the date of expiry of the refund period.
These settlement cycles are mutually exclusive and the PA business models and settlement structure cycle with the merchants could be developed by PAs on the basis of market dynamics in online selling space. Since the end-transaction between merchant and PA is settled on a contractually determined date, there is a deferred settlement, between PA and the merchant. Owing to the rules and nature of the relationship (deferred settlement) is the primary differentiator from the merchants proving the Delivery vs. Payment (DvP) settlement process for goods and services.
Market Concerns
Banks operating as PAs do not need any authorisation, as they are already part of the the payment eco-system, and are also heavily regulated by RBI. However, owing to the sensitivity of payment business and consumer protection aspect non-bank PA’s have to seek RBI’s authorisation. This explains the logic of minimum net-worth requirement, and separation of payment aggregator business from e-commerce business, i.e. ring-fencing of assets, in cases where e-commerce players are also performing PA function. Non-bank entities are the ones that are involved in retail payment services and whose main business is not related to taking deposits from the public and using these deposits to make loans (See. Fn. 7 above).
However, one could always question the prudence of the short timelines given by the regulator to existing as well as new payment intermediaries in achieving the required capital limits for PA business. There might be a trade-off between innovations that fintech could bring to the table in PA space over the stringent absolute capital requirements. While for the completely new non-bank entity the higher capital requirement (irrespective of the size of business operations of PA entity) might itself pose a challenge. Whereas, for the other non-bank entities with existing business activities such as NBFCs, e-commerce platforms, and others, achieving ring-fencing of assets in itself would be cumbersome and could be in confrontation with the regulatory intention. It is unclear whether financial institutions carrying financial activities as defined under section 45 of the RBI Act, would be permitted by the regulator to carry out payment aggregator activities. However, in doing so, certain additional measures could be applicable to such financial entities.
Conclusion
The payment aggregator business models in India are typically based on front-end services, i.e. the non-bank entitles are aggressively entering into retail payment businesses by way of providing direct services to merchants. The ability of non-bank entitles to penetrate into merchant onboarding processes, has far overreaching growth potential than merchant on-boarding processes of traditional banks. While the market is at the developmental stage, nevertheless there has to be a clear definitive ex-ante system in place that shall provide certainty to the payment transactions. The CPSS-IOSCO, governing principles for FMIs lays down a good principle-based governing framework for lawyers/regulators and system participants to understand the regulatory landscape and objective behind the regulation of payment systems. PA Guidelines establishes a clear, definitive framework of rights between the participants in the payment system, and relies strongly on board policies and contractual arrangements amongst payment aggregators and other participants. Therefore, adequate care is necessitated while drafting escrow agreements, merchant-on boarding policies, and customer grievance redressal policies to abide by the global best practices and meet the objective of underlying regulation. In hindsight, it will be discovered only in time to come whether the one-size-fits-all approach in terms of capital requirement would prove to be beneficial for the overall growth of PA business or will cause a detrimental effect to the business space itself.
[1] RBI, Directions for opening and operation of Accounts and settlement of payments for electronic payment transactions involving intermediaries, November 24, 2009. https://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/NotificationUser.aspx?Mode=0&Id=5379
[2] Payment Systems in India – Booklet (rbi.org.in)
[3] https://m.rbi.org.in/Scripts/AnnualReportPublications.aspx?Id=1293
[4] https://www.investindia.gov.in/sector/retail-e-commerce
[5] The Bank for International Settlements (BIS), Committee on Payment and Settlement Systems (CPSS) and International Organisation of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) published 24 principles for financial market infrastructures and and responsibilities of central banks, market regulators and other authorities. April 2012 <https://www.bis.org/cpmi/publ/d101a.pdf>
[6]Regulation and Supervision of Financial Market Infrastructures, June 26, 2013 https://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/bs_viewcontent.aspx?Id=2705
[7] CPMI defines non-banks as “any entity involved in the provision of retail payment services whose main business is not related to taking deposits from the public and using these deposits to make loans” See, CPMI, ‘Non-banks in retail Payments’, September 2014, available at <https://www.bis.org/cpmi/publ/d118.pdf>
Our other related articles:
Overview of Regulatory Framework of Payment and Settlement Systems in India by Anita Baid – Vinod Kothari Consultants
RBI to regulate operation of payment intermediaries – Vinod Kothari Consultants
Major recommendations of the Committee on Payment Systems on Payment and Settlement System Bill, 2018 – Vinod Kothari Consultants




