MCA introduces a cartload of additional disclosures in the Financial Statements
/5 Comments/in Amendments to the Companies Act 2013, Companies Act 2013 /by Vinod Kothari Consultants-The amendments to be applicable from FY 2021-2022 onwards!
Shreya Masalia and Harsh Juneja | Executives
With the ever-increasing stringency in the regulatory framework and disclosure requirements under various provisions of law, MCA, vide notification dated March 24, 2021[1] has further prescribed a list of numerous additional disclosure required in the financial statements by amending schedule III to the Companies Act, 2013. The amendments have been brought to bring more transparency by providing for various disclosures including dealing with struck off companies, details of benami property, undisclosed income etc. which shall be applicable from FY 2021-22.
Since the amendments have been brought in Division I, II and III of Schedule III, accordingly, the same will be applicable to the companies which need to comply with the Companies (Accounting Standards) Rules, 2006 as well as the Companies (Indian Accounting Standards) Rules, 2015 including NBFCs.
This Article is an attempt to cover all the major new inclusions that the companies will have to disclose henceforth.
Disclosures to be made to the notes of the Balance sheet under various Divisions of Schedule III
- Statement on changes in equity
Prior to the amendment, the companies including NBFCs required to prepare financial statements as per IND AS were required to disclose only balance at the beginning and end of the reporting period along with changes during the current year. Post the amendments in Sch. III, disclosure shall be made regarding the changes in equity due to prior period errors and restated balance at the beginning of the reporting year and similarly disclose the same for the previous reporting period. Additionally, the details of other equity shall also be given for prior reporting period.
- Disclosure of shareholding of all promoters
Currently, only the shareholding of the shareholders holding more than 5% of the shares is required to be disclosed in the Balance Sheet. After the amendments, a company shall now be required to disclose the shareholding of all promoters. The details shall include change in shareholding taken place during the year. The meaning of the promoter has to be taken from the definition provided in the Act which is different from the definition provided in the SEBI (ICDR) Regulations, 2009. This change has been made to all companies covered under all three Divisions of schedule III.
- Loans and advances to promoters, directors, key managerial persons (KMP) & related parties
Where the company makes any loan and advances to the promoters, directors, KMPs and other related parties either jointly or severally and such loan/ advances so given are either in the nature of a loan/ advance repayable on demand or without any specific terms or period of repayment, the details of such loans shall be disclosed separately in the financial statements along with the amount of loan and % to total loans and advances. The related parties are those parties as defined under sec. 2(76) of the Act.
It is pertinent to note here that while related party disclosures are already required under applicable accounting standards, this may, to some extent, tantamount to be an overlapping of disclosures.
- Ageing Schedule of trade payables and trade receivables
Companies that failed to make payment to companies under MSME Act, 2006 or which had made any delayed payments to MSME were required to disclose the principal and interest due at the end of the FY, amount of interest paid for delay in payment in the current year, interest accrued and unpaid during the year and amount of interest further remaining to be paid in succeeding years in their balance sheet.
Companies covered under all 3 divisions will henceforth be required to provide ageing schedule for trade payables due for the periodicity of 1 year, 1-2 year, 2-3 year & more than 3 years. These include trade payables to MSMEs, disputed dues to MSMEs, and other dues and disputed dues. Similarly, disclosures shall also be made where no due date of payment is specified. Information for unbilled dues is also required to be disclosed separately.
Similarly, companies will also be required to disclose the ageing schedule of its trade receivables i.e. including undisputed and disputed trade receivables considered good and doubtful with ageing classified as less than 6 months, 6 months to 1 year, 1-2 years, 2-3 years and 3 years or more along with disclosures separate disclosure for information of unbilled dues. These undisputed and disputed trade receivables which are further categorized into good and doubtful.
- Disclosure related to funds borrowed from banks and financial institutions
Where the company has borrowings from banks or financial institutions on the basis of security of current assets, it shall disclose whether the quarterly returns or statements of current assets filed by it with the banks or financial institutions are in agreement with the books of accounts. Further, where there is any material mismatch/ discrepancies between the two, then a summary of reconciliation and reasons of material discrepancies needs to be adequately disclosed. This amendment shall be applicable to all the companies covered under the scope of three Divisions of Schedule III. It clearly states that an auditor must find the differences between these statements filed by the company with the books of accounts and if there is any difference, then a reconciliation statement needs to be prepared.
In addition to the above, where funds borrowed by a company from a bank or a financial institution for a specific purpose has not used for the same purpose, a disclosure providing details of utilisation of funds shall also be required to be provided.
- Revaluation of property
The reconciliation of gross and net carrying amount of both intangible and tangible assets at the beginning and end of the reporting period, along with other separate disclosures related to additions, disposals, acquisitions, depreciation, impairment, etc shall also disclose separately details related to the amount of change due to revaluation, where there is a change of more than 10% in aggregate of the net carrying amount of the asset.
The company is also required to disclose whether the plant, property or equipment has been revalued by a registered valuer as defined under rule 2 of Companies (Registered Valuers and Valuation) Rules, 2017.
- Disclosure of Ratios
The amendment requires the companies covered under division I and II of schedule III to disclose the following ratios:
(a) Current Ratio,
(b) Debt-Equity Ratio,
(c) Debt Service Coverage Ratio,
(d) Return on Equity Ratio,
(e) Inventory turnover ratio,
(f) Trade Receivables turnover ratio,
(g) Trade payables turnover ratio,
(h) Net capital turnover ratio,
(i) Net profit ratio,
(j) Return on Capital employed,
(k) Return on investment.
The company shall explain the items included in the numerator and denominator for computing the above ratios and an explanation shall be provided for any change in the ratio by more than 25% as compared to the preceding year. To note, amongst these, various ratios such as current ratio, debt-equity ratio, net profits ratio, etc. were required to be disclosed by equity listed entities in their Board’s report under Management Discussion and Analysis Report as per regulation 34(3) r.w. Schedule V to SEBI( Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements), 2015.
In addition to the above, NBFCs that need to comply with Ind AS covered under division III of schedule III are required to disclose the following ratios:
(a)Capital to risk-weighted assets ratio (CRAR)
(b) Tier I CRAR
(c) Tier II CRAR
(d) Liquidity Coverage Ratio
However, as per annex XVI of Master Direction – NBFC-ND-SI and NBFC-DI Directions, 20163 , all deposit taking NBFCs and NBFC – non-deposit taking having asset size of INR 500 crore are already required to disclose their CRAR, tier I CRAR and tier II CRAR as a part of their balance sheet. Similarly, NBFCs as covered under para 15B read with annex III of Master Direction – NBFC-ND-SI and NBFC-DI Directions, 2016 are already required to provide disclosures related to LCR in the prescribed format.
Though these amendments are aimed at increasing disclosure requirements, this addition seems more repetitive in nature rather than being informational.
Disclosures required in an attempt to curb money laundering
- Details of Benami Property held
Where any proceedings have been initiated or pending against the company for holding any benami property, the company shall disclose various details of the property including the reasons of not disclosing the same in the books of accounts, details of the proceedings against the company including its nature, status and the views of the company on the same. This amendment covers the companies under the scope of all three divisions of schedule III.
- Relationship with Struck off Companies
Where the company has any transaction with companies struck off under section 248 of the Act, or under section 560 of the Companies Act, 1956, it shall disclose the name of struck off company, the nature of transactions with this company, balance outstanding and relationship with the struck off the company. The transaction can be in the nature of investment in securities, receivables, payables, shareholding of the struck-off company in the company and any other outstanding balances.
- Disclosures related to conduit lending and borrowing
The amendments in the Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules, 2014 dated March 24, 2021[2] requires the management of the company to give a representation that, except as otherwise disclosed in the notes to accounts, the company has neither employed nor is itself acting as a “conduit entity” for any financial transaction. To align schedule III with the same, additional disclosures are required to be made by the company w.r.t. disbursement of funds by way of advance, loan, investment, guarantee or security by the company to any person/ entity being an ultimate beneficiary through any intermediary. Similarly, disclosure shall also be made about any receipt of funds in the aforesaid manners by the company as an intermediary for further disposal of the same to any person/ entity being ultimate beneficiary. The details shall include the date, amount, details of the intermediary and the ultimate beneficiary including a declaration to the effect that it is in compliance with the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 and Companies Act, 2013 and does not violate the provisions of Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 in respect to the aforesaid transactions.
For an in-depth understanding of the concept and the amendment, refer our separate article[3] covering various aspects of the same.
- Wilful Defaulter
A company categorized as a wilful defaulter by any bank or financial institution will be required to disclose details regarding the date of declaration as a wilful defaulter and the amount and nature of defaults.
- Title deeds of property not held in the company’s own name
If any the title deed of any immovable property (other than in case of lease where the agreement is duly in favour of lessee) is not held in the name of the company, the details related the same is required to be disclosed in the financial statements. This disclosure shall not be required for properties held on lease where the lease agreements are duly executed. In case of joint holding of such property, the disclosure shall be made to the extent of the company’s share thereon.
The details of the disclosure includes the gross carrying value, name of the person in whose name property is held, whether such person is a promoter/ director or relative of promoter/director or an employee of the company, since when the property is held by the person and details for the same. If such property is under dispute the same shall also be disclosed.
Other miscellaneous disclosures:
- Depending upon the Total income of the company the financial statements are to be mandatorily rounded off to the nearest unit as mentioned in the schedule. Prior to the amendment, the same was to be adopted on a voluntary basis for companies preparing their financials as per Companies (Accounting Standards) Rules, 2006 and the nearest unit was based on the turnover of the company. The amendment aligns all the divisions of schedule III making it mandatory for all companies to round off their financial statements based on their total income.
- In case of revaluation of any plant, property & equipment, the disclosure w.r.t the fact that the valuation has been done by a registered valuer as defined under the Companies (Registered Valuers and Valuation) Rules, 2017.
- Disclosures related to ageing of capital work in progress (CWIP) and any other CWIP which has exceeded its originally planned cost or completion schedule. Details of projects where activity has been suspended shall be disclosed separately.
- Disclosures related to ageing of intangible assets and along with any other intangible asset which has exceeded its originally planned cost or completion schedule. Details of projects where activity has been suspended shall be disclosed separately.
- Details and reasons of pending registration of creation/ or satisfaction of charge with the Registrar of Companies beyond statutory time period.
- A company in non-compliance with the number of layers prescribed under clause (87) of section 2 of the Act read with Companies (Restriction on Number of Layers) Rules, 2017 shall disclose the same.
- A disclosure to effect that the books of accounts of the company are in accordance with the approved scheme of arrangement and accounting standards in case the competent authority has approved the same.
Disclosures to be given in the Profit and Loss statements:
- Disclosures related to CSR
Where the company is covered under section 135 of the Companies Act, 2013 (Act), the disclosures shall be made similar to the disclosures in the Board’s Report as required under then Act. In addition to that, a disclosure regarding the details of related party transactions such as, contribution to a trust controlled by the company in relation to CSR expenditure as per relevant Accounting Standards shall also be made.. Where a provision is made with respect to a liability incurred by entering into a contractual obligation, the movements in the provision during the year should be shown separately. The term “provision” shall be construed as a liability. The provision shall be estimated on the basis of past CSR events already conducted by the company.
- Details of Crypto Currency or Virtual Currency
Where the company has traded or invested in Crypto Currency or Virtual Currency during the financial year, the following needs to be disclosed:
(a) profit or loss on transactions involving Crypto currency or Virtual Currency
(b) amount of currency held as at the reporting date,
(c) deposits or advances from any person for the purpose of trading or investing in Crypto Currency/ virtual currency.
The Amendment has now mandated the companies to prepare a separate set of accounts for all their transaction involving Crypto Currency or Virtual Currency.
- Undisclosed Income
Details of any transactions not recorded in the books of accounts that has been surrendered or disclosed as income during the year in the tax assessments under the Income Tax Act, 1961, shall be disclosed unless there is immunity for disclosure under any scheme. Further, the company shall also state whether the previously unrecorded income and related assets have been properly recorded in the books of account during the year.
Conclusion
As discussed above, the intent of law seems to bring more transparency in reporting by corporates. Though certain disclosures may lead to repetition of information in various places, to avoid the same cross referencing may be done. Surely, the amendments will curb the problem of inadequacy of information in the books of accounts of the company.
[1] http://www.mca.gov.in/Ministry/pdf/ScheduleIIIAmendmentNotification_24032021.pdf
[2] http://www.mca.gov.in/Ministry/pdf/AuditAuditorsAmendmentRules_24032021.pdf
[3] http://vinodkothari.com/2021/03/changes-in-auditors-report-and-financial-statements-to-reveal-camouflaged-financial-transactions/
Changes in Auditors’ Report and Financial Statements to reveal camouflaged financial transactions
/1 Comment/in Amendments to the Companies Act 2013, Companies Act 2013, Corporate Laws, MCA /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsTeam Corplaw, Vinod Kothari & Company [corplaw@vinodkothari.com]
[This version: 25th March, 2021]
Accountants and auditors will have to grapple with a ton of new details and disclosures while preparing financial statements and audit reports, come financial year 2021-22. MCA brought, vide separate notifications dated 24th March, 2021 amendments in the Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules,2014 (“Audit Rules”), the Companies (Accounts) Rules, 2014 (“Accounts Rules”) and Schedule III of the Companies Act.
While Schedule III changes will require wide ranging disclosures [to be covered by a separate write up], the amendments in Audit Report Rules and Accounts Rules require the following new disclosures:
- Camouflaged lending or investment, that is, where out-bound or inbound loans, advances and investments are intended to be routed through a conduit entity, masking the identity of the ultimate beneficiary
- Compliance with respect to payment of dividend
- The need for accounting software to maintain an audit trail, that is, edit log, of the primary entries, possibly with a view to enable the detection of any changes in primary entries
- Gaps in valuations of securities, so as to reflect the valuations at the time of borrowing money, and at the time of OTS
We briefly discuss these.
Applicability – scope and date
- The changes as will be discussed below will be applicable on the Auditor’s Report and Board’s Report from the financial year 2021-22 and onwards.
- Since statutory audit is a mandatory requirement for all the companies, the changes in the Auditor’s Report shall be applicable on all companies.
- From the language of the amendments, it is apparent that the changes are applicable only for the annual financial statements; neither are they applicable to interim financial statements, nor to special purpose financial statements.
- An important question will remain whether the required management representation and the auditors’ check will pertain to transactions done during the financial year 2021-22 and thereafter, or does it pertain to opening balances of transactions as on 1st April, 2021. In absence of any suggestion as to retroactivity, it should be logical to assume that the required management representation and the auditors’ checking should pertain to the transactions done during the financial year.
- The changes in relation to Board Report shall be applicable on all the companies, since the Board Report is a mandatory requirement for all.
- The requirements of audit trail and edit log are applicable on companies maintaining their accounts in the electronic form. However, practically, all companies maintain accounts in electronic format, so the same can be said to be applicable on all companies.
Camouflaged lending and investment:
What is the offence?
The issue under consideration is “camouflaged investments”. By using the term camouflage investments, we mean those transactions which are undertaken by a company for some identified beneficiary. However, the transaction does not take place between the company and the ultimate beneficiary directly, but is masked by the inclusion of an intermediary acting as a conduit entity (an entity acting on the instructions of the company for channelizing the funds to any other entity identified by the company).
These transactions mask the identity of the real beneficiary. In a world where financial transactions are regularly used for carrying illicit transactions, money-laundering transactions or other suspicious activities, it is important that the trail of financial transactions is transparent. Hence, if the identification of the end beneficiary is consciously being masqueraded, there is a concern. The proposed amendments are a means to address this issue.
What is the MCA intending to do?
The MCA, vide the amendment notification, is aiming to unveil the ultimate beneficiary behind the camouflage financing. Though investment through “conduit entities” is not barred by law, the same needs to be adequately disclosed in the notes of accounts of the company. Therefore, MCA, vide its amendment notification, requires the management of the company to give a representation that, except as otherwise disclosed in the notes to accounts, the company has neither employed, nor is itself acting as a “conduit entity” for any financial transaction.
Is it illegal to have investments via conduits?
Several laws refer to indirect lending or investment –
- Sec 185 of the Act prohibits both direct and indirect loans, investments, guarantees or security to the directors and other specified entities.
- Under the FEMA Regulations, the definition of “foreign equity holder” includes those equity holders having minimum 51% of indirect equity holding
- Sec 186 (1) also refers to investment “through” one or more layers of subsidiaries, which is again a case of indirect investments.
- In many commercial transactions, it is understood that the recipient is acting as a conduit – for example, lending through a fintech platform
- Special purpose vehicles, which are well allowed to operate under various laws, are intended to be conduits only
- Use of conduits is commonplace practice in many commercial transactions
Hence, while it is not illegal on the face of it, the use of a masquerading entity camouflages the real nature of the financial transaction. It acts as a subterfuge and hence, creates opacity. In the context of PMLA, these transactions may also be hiding the real identity of the real beneficiary.
Hence, it is important to ensure that the identity of the real beneficiary, if so targeted by the lender or investor, is disclosed.
What sort of transactions will be covered?
There are several elements in the camouflage rule that need to be understood:
There are 3 legs of the transaction: a source transaction, a conduit or intermediary transaction, and an ultimate beneficiary transaction.
The source transaction may be
- Investments,
- Advances, or
- Loans
At the source stage, the money has come as a result of any borrowing, issue of shares or share premium or any other source or kind of funds. Since these expressions are wide enough, it does not matter what the source of the funds at the source level is.
The intermediary transaction may be by way of
- Loan or advance
- Investment
- Provision of any guarantee or security
The ultimate beneficiary is the end beneficiary of the source transaction.
The following points may be noted about the scope of the Camouflage rule:
- Commercial transactions are not covered: Notably, the transactions covered by the rule are financial transactions, in the nature of loans, advances or investments. Real sector transactions such as sales, purchases, services, including payment and collection services, etc., are not covered by the rule.
- Non-discretionary transactions as regards the intermediary: In order to attract the offence of the camouflage rule,the source must have identified the ultimate beneficiary. This is clear from the words: “identified in any manner whatsoever by or on behalf of the company”. Thus, if the intermediary had the discretion in identifying the beneficiary, this rule is not attracted. Hence, the identification of the beneficiary is done by the source, and without any discretion on the part of the intermediary.
- Pre-contemplated transfer to the ultimate beneficiary: Next important element is the existence of an understanding with the intermediary that the funds passing through the intermediary are intended by the ultimate beneficiary. This is clear from the words “with the understanding, whether recorded in writing or otherwise”. The form of the understanding or the formal nature of the understanding also doesn’t matter, but the understanding must have been there.
- Direct nexus: This suggests that the flow of funds from the source of the intermediary, and from intermediary to the ultimate beneficiary must be part of the same transaction, showing a clear nexus.
- The intent of camouflaging the chain financial transaction is present: It is only when the real nature of the transaction is sought to be garbed, and the transaction purports to be a financial transaction with the intermediary, whereas the real intent is to provide funding to the ultimate beneficiary. For example, if a special purpose vehicle collects money from the investors, it is evident on the face of the transaction that the money is intended to go to another beneficiary. There is no garbing of the identity of the end beneficiary. These transactions are explicit and transparent transactions. The whole intent of the camouflage rule is to eliminate opacity. If the transaction was itself transparent, the rule has no relevance at all.
There are several interconnected financial transactions that abound in the world of finance. Hence, it will remain a matter of intrigue as to what all transactions may be regarded as falling under the offence of the camouflage rule. There are several questions that arise in this respect:
- Does a time gap matter?
For instance, the transaction by the source to the intermediary happens on 1st of 1st month, and the transaction by the intermediary to the beneficiary happens on 1st of 4th month. There may be a suggestion as to the existence of an understanding between the parties, but the very fact that there is a gap of time between the two legs of the transactions helps to create some opacity. It may be noted that the whole purpose of the camouflage disclosures is to pierce through the opacity and create transparency. Hence, if the gap in timing is merely a device to create opacity, it should not matter.
- Does a change in nature of the instrument at the intermediary level matter?
For example, the transaction from the source to the intermediary may be by way of loans. The transaction from the intermediary to the ultimate beneficiary may be by way of investment in shares. The terms of the two investments obviously differ. The first may have a limited tenure. The second one may be perennial. The entire approach has to be driven by substance over form – if the substantive view of the transaction suggests the two inter-connected transactions being part of the same chain, it will be wise to disclose the same.
- Does the infusion of some extent of funds by the intermediary matter?
For example, the source may have contributed Rs 1000. The intermediary may add another Rs 100 of its own, and transfer Rs 1100. To the extent of Rs 1000, there may still be a chain financial transaction requiring disclosure, while the remaining Rs 100 may be an independent transaction by the intermediary.
- Does the existence of a trust or fiduciary or agency relationship matter?
There are numerous transactions where a servicing agent, collecting agent, paying agent, etc acts merely as a conduit. This is the explicit nature of the transaction itself. Same goes with fiduciary transactions where the trustee or fiduciary discloses on the face of it that the trustee is merely a stop-over. However, trusts with undisclosed principals, while doing financial transactions, may be hit by the rule.
Duty of the auditor
The provisions are not just casting a responsibility on the directors, but the auditors are also required to substantiate the statement of the directors by applying their audit procedures. While the auditors can have ways and means to identify the instances of “outward” surrogate lending well, how the auditors can assure there are no instances of “inward” surrogate lending will require some new auditing methods.
Reasons of such reporting requirement
The amendments can be looked upon as a way to ensure that the companies do not use masquerades for the purpose of distinguishing the identity of the ultimate beneficiary of the funds. These might be to also check the instances of money laundering and terrorism financing.
Impact of the change
Though no specific punishments have been specified, on a conjoint reading of Sections 447 and 448 of the Act, it seems that the directors may be liable for fraud in cases of active concealment of material information or making mis-statements deliberately.
Since the Auditors are required to substantiate that there are no material mis-statements made by the directors as aforesaid, where the auditor fails to prove his innocence, he might also be penalised in cases of material misstatement.
Other additional disclosures required to be made in the Auditor’s Report
Compliance of Section 123 of the Act with respect to declaration/payment of dividend
The amended Audit Rules require the auditor to report on compliance with Section 123 of the Act by the company where it has declared/paid dividend. This has been done to ensure that the companies pay dividend on the basis of their profits and satisfies all the necessary conditions, and not when the companies may be suffering losses and it is practically impossible to pay dividend to its members.
Proper maintenance of audit trail at all times during the financial year
The auditors are also required to report on the maintenance of the audit trails and edit logs by the companies who opt to maintain their books of accounts in electronic mode. A discussion of the same is given in the later part of the write-up.
Accounting in electronic form – maintenance of audit trail
With effect from 1st April, 2021 the companies that maintain their accounts electronically by means of accounting software shall be required to ensure that the software is capable of maintaining audit trail and edit logs, and the same is not disabled at any point of time. The auditors are also required to report on the proper maintenance of such systems as discussed earlier.
Impact of the change
The compulsory maintenance of audit trail is a way to ensure the fabrication of books and any subsequent overwriting in the books of accounts. Through the audit trails, any person scrutinising the books of accounts can very easily track what changes have been made to the accounts and can require the company to explain the reasons thereof.
Additional disclosures in the Board’s Report
Applications/proceedings under IBC
Vide the amendments, the directors will be required to report the applications initiated or proceedings pending under IBC. Though the language of the law is not very clear on this, the understanding is that the directors will be required to report on the applications initiated or the proceedings pending against the company. Where such an application or proceedings are pending, the Board’s Report is also required to contain the status of the same as at the end of the year.
Impact of the change
The aforesaid amendment may be said to be an additional reporting requirement to keep the members, the real owners of the company as well as other stakeholders of the company updated about the current status of the company. The “insolvency” is a serious matter and shall not come as a shock to the stakeholders of a company, when the same is announced publicly at a later point of time.
Diabolical valuations of assets
Another very interesting insertion in the Board’s report is the details including the reason for the differences between the valuations of the company done at the time of one-time settlement and that at the time of taking loans from banks or other financial institutions. This is with a motive to ensure why there is a difference in valuation of the assets of the company at the time of one-time settlements v/s at the time of borrowing funds from the banks and financial institutions.
Reason of the change
The change is to ensure that the company has not inflated the value of their books at the time of seeking loans from the banks and financial institutions, nor has it deflated the same at the time of proposing one-time settlement.
We understand that there may be various reasons for the differential valuation, like difference in time period and resultant depreciation, amortization etc, or due to varying market forces. Whatever be the reasons, the same needs to be adequately captured in the Board’s Report for the company.
[The version above is a work in progress and we will continue to develop it further. Please do come back to this page. Please feel free to post your comments/questions in the space below.]
FAQs on Minimum Remuneration to NEDs and IDs
/5 Comments/in Amendments to the Companies Act 2013, Companies Act 2013, Corporate Laws, MCA /by Vinod Kothari Consultants
Remunerating in a lean year: Statutory amendments for minimum remuneration to independent directors now effective
/0 Comments/in Amendments to the Companies Act 2013, Companies Act 2013, Corporate Laws, MCA /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsPayal Agarwal | Executive (payal@vinodkothari.com)
Highlights
Introduction
Independent directors (IDs) are a crucial part of corporate governance structure; however, their remuneration is currently solely by way of sitting fees and a “profit-linked” commission[1]. Profit is something which is completely dependent on business models, a whole matrix of internal and external factors, and something like a Covid-crisis will evidently leave a whole lot of companies in India and elsewhere into the red. In these circumstances, how do companies remunerate independent directors, to reward them for the time they spend and the responsibilities they shoulder.
To resolve this difficulty, amendments were made vide the Companies (Amendment) Act, 2020.While most of the sections of the Amendment Act were made effective on 28th September 2020, the sections relating to remuneration of NEDs and IDs were not been made applicable since the same was required to be adequately supplemented by corresponding amendments in Schedule V of the Act as well. However, just before the Covid-ravished FY 2021 was to end, MCA has put into effect the amended sections 149(9) and Section 197(3) and simultaneously brought amendments in Schedule V of the Act.
Effects of the amendments
These amendments will enable companies to adequately remunerate their NEDs and IDs for their efforts. Contrary to the rigidity in the erstwhile provisions, which had a complete bar on payment of remuneration to NEDs and IDs in absence of profits, these amendments enable companies to pay minimum remuneration to NEDs and IDs even at times of losses/ inadequate profits. Note that there always was a provision for minimum remuneration in case of EDs.
Applicability
- Private companies are not covered by the ceilings of managerial remuneration. Hence, private companies are completely outside the purview of the restriction.
- Public companies, both listed and unlisted, will be covered by the amendment.
- The amendment is of enabling nature. It does not mandate companies to remunerate their NEDs and IDs. So, companies may, if they so desire, remunerate their IDs and NEDs in the year of inadequate profits, or losses.
- The amendment applies to all NEDs and IDs.
- The amendment pertains to the “profit-linked” commission. That does not mean the commission as originally proposed had to be profit-linked. Even if the commission was a fixed amount, it will still be covered by the ceiling given in second proviso to sec. 197 (1). Hence, any commission is necessarily profit-linked.
- The amendment is effective immediately. That means companies may make use of the amended provisions for FY 2020-21.
- The amendment does not lead to an automatic variation in the remuneration policy or shareholders’ resolution. In essence, the amendments are of enabling nature: within the ambit of the amended provisions, companies may take corporate action to remunerate their NEDs and IDs. The actions have to be taken by the companies in question, which may include remuneration policy, appropriate shareholder resolutions, etc.
Amendments to Schedule V – maximum limits on remuneration of “other directors” specified
Part II of Schedule V of the Act deals with the remuneration of “managerial personnel”. In this connection, please note that “managerial personnel” refers to managing director, manager and whole-time director of the company. Now, with the present amendment to the Schedule, part II has become applicable on the “other directors” as well. The term “other directors” has been clarified in the amendment notification itself by way of an explanation which states,
“For the purposes of Section I, II and III (relevant parts that have been amended) the term “or other director” shall mean a non-executive director or an independent director.”
Section II of Part II of the Schedule specifies maximum remuneration that can be paid to a director, be it a managerial personnel or otherwise. For directors other than the managerial personnel, the remuneration has been specified at an amount almost 1/5th of that permissible to the managerial personnel.
The result of bringing IDs within the scope of Schedule V is that whereas the IDs would have been receiving very low remuneration in comparison to their roles and responsibilities in an organisation due to inadequacy of profits, the IDs will have a chance of getting a fair remuneration.
Questions relevant to the amendments
Various questions arise out of the amendments, such as –
- Will the amendments require modification in existing remuneration policy?
- Can the NEDs and IDs be paid remuneration in excess of those specified in Schedule V?
- Whether a single approval can suffice for the remuneration of all NEDs and IDs or such resolutions will have to be approved separately for the individual directors?
- Whether NRC will be eligible to recommend remuneration payable to IDs?
- Whether a prior approval of shareholders will be required or whether post facto approval may be obtained?
Answers to these and other relevant questions revolving around the aforesaid amendments has been dealt with in our detailed FAQs and can be accessed here.
Conclusion
The role of non-executive and IDs is very crucial to a company. The professional expertise of NEDs in their specific fields brings requisite value to a company. Considering the role played by IDs in effectively balancing the conflicting interest of the company and its stakeholders and bringing independent judgement to the Board’s decisions, it would be unfair if they are not paid adequately for the efforts put by them in the effective conduct of business.
Further, in the present scenario, amidst the economic breakdown worldwide, many companies may not be able to earn the profits as expected, or might be facing losses as well. In such circumstances, the aforesaid amendments were a necessity.
However, the erstwhile provisions had no scope of payment of remuneration to them in case of loss. With the aforesaid amendments coming into force, the companies will be able to compensate their non-executive and IDs well, even in case of no/inadequate profits.
Our other articles on the related topics can be read here –
[4] http://vinodkothari.com/2020/03/remunerating-neds-ids-in-low-profit-yrs/
[5] http://vinodkothari.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/Manangerial-Remuneration_IMTB-_26.08.pdf
[1] SEBI has recently in its consultation paper on review of regulatory framework applicable to IDs suggested that profit-linked commissions should be barred and shall be substituted by higher sitting fees or issue of stock options. Please refer to our article for broader understanding of the same.
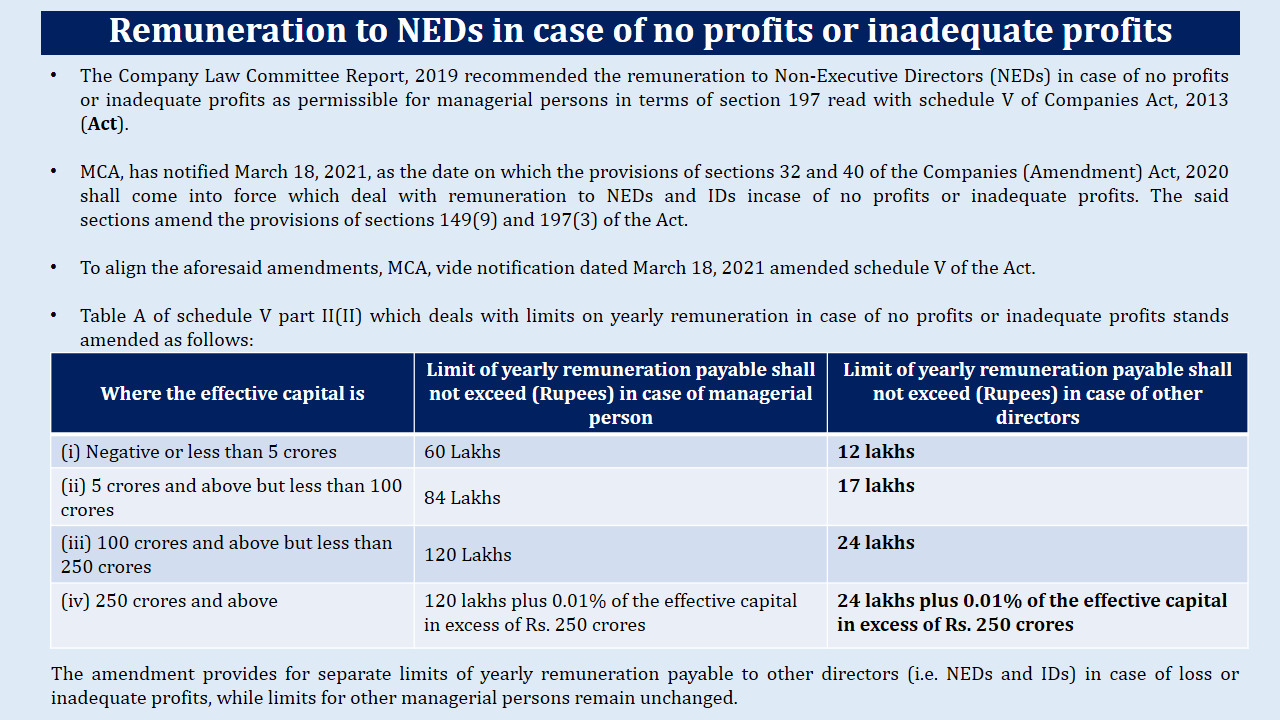
Remuneration to NEDs in case of no/inadequate profits – snippet
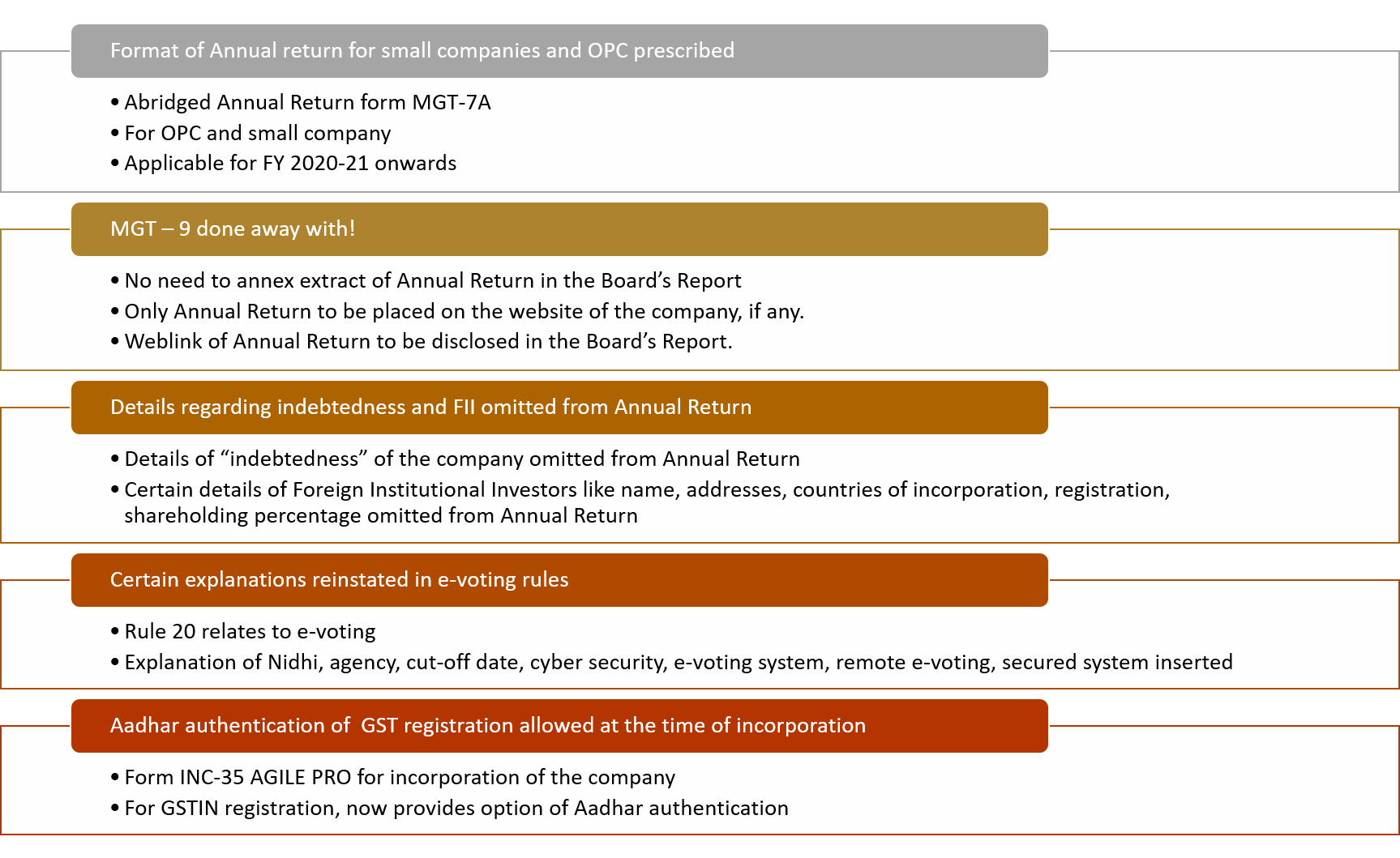
/0 Comments/in Amendments to the Companies Act 2013, Companies Act 2013, Corporate Laws, MCA /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsMCA notifies abridged annual return for small companies after 4 years
/2 Comments/in Amendments to the Companies Act 2013, Companies Act 2013, Corporate Laws /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsCarries out corrective changes in MGT Rules
By CS Aisha Begum Ansari, Assistant Manager, Vinod Kothari & Company
Introduction
Four years after proposing amendment in Section 92 (1) of Companies Act, 2013 (‘Act’), Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) notified the amendment in Companies (Amendment) Act, 2017[1] with effect from March 5, 2021.
The aforesaid amendment provided for following under Section 92 (1) & (3):
- Empowering Central Government to prescribe an abridged form of annual return for One Person Company (OPC) and Small Companies[2];
- Deletion of requirement to furnish details of indebtedness in the annual return;
- Deletion of requirement to furnish details indicating names, addresses, countries of incorporation, registration and percentage of shareholding of Foreign Institutional Investors;
- Doing away with the requirement of annexing extract of annual return to the Board’s report and mandating companies to place a copy of annual return on their website and provide the link of the same in the Board’ report.
While the amendment in relation to point 4. above was already notified with effect from August 28, 2020; MCA notified amendment in Companies (Management and Administration) Rules, 2014[3] (‘MGT Rules’) giving companies the option to annex extract of annual return in case of inability to place a copy of annual return on the website. Section 92 (3) of the Act post amendment did not provide any specific power to prescribe rules, however, MCA had amended Rule 12 of MGT Rules.
Further, in 2016 while amending MGT rules[4] in relation to voting by electronic means, MCA inadvertently deleted the explanations provided in sub-2 of Rule 20 that defined terms viz, agency, cut-off date, remote e-voting etc.
Corrective amendments in MGT Rules
MCA, on 5th March, 2021[5] notified amendments in MGT Rules to carry out corrective changes and to insert format of abridged annual return subsequent to notification of amendment in Section 92 (1) of the Act. The synopsis of the amendments are as mentioned below:
Insertion of abridged annual return in Form MGT-7A and revision of Form MGT-7
Rule 11(1) of MGT Rules have been substituted prescribing separate format of annual return for OPC and small companies which shall be filed in Form No. MGT-7A from the financial year 2020-21 onwards. Other companies to continue to file annual return in Form MGT-7.
MCA has also revised the format of Form MGT-7 for filing the annual return by companies other than OPC and small companies.
Form MGT-7 v/s Revised Form MGT-7
| Sr. No. | Para & Field No. | Information required in revised Form MGT-7 which was not required under erstwhile Form MGT-7
(For Companies other than OPC & Small Companies) |
| 1. | Para IV Field (i) (d) | 1. Bifurcation of shares held in demat and physical form.
2. Requirement of mentioning ISIN of equity shares of the Company; |
| 2. | Para IV Field (iv) | Following rows are deleted:
1. Secured Loans (including interest outstanding/accrued but not due for payment) excluding deposits; 2. Unsecured Loans (including interest outstanding/accrued but not due for payment) excluding deposits; 3. Deposit. |
| 3. | Certification part | Following new certification are required to be confirmed, (seems relevant only for private companies).
1. The company has not, since the date of the closure of the last financial year with reference to which the last return was submitted or in the case of a first return since the date of incorporation of the company, issued any invitation to the public to subscribe for any securities of the company. 2. Where the annual return discloses the fact that the number of members, (except in case of one person company), of the company exceeds two hundred, the excess consists wholly of persons who under second proviso to clause (ii) of sub-section (68) of section 2 of the Act are not to be included in reckoning the number of two hundred. |
Revised Form MGT-7 and Form MGT-7A
| Sr. No | Para & Field No. | Information required to be provided in Form MGT-7A which was not required under Form MGT-7
(For OPC & Small Companies) |
| 1. | Para I Field vi | Whether Form is filed for OPC or Small Co. [New Insertion]
|
| 2. | Para III | Particulars of associate companies including joint ventures. (not applicable for OPC) [Substituted by deleting holding and subsidiary Companies] |
| 3. | Para IV (ii) | Details of shares/Debentures Transfer since closure date of last financial year (or in the case of the first return at any time since the incorporation of the Company) (not applicable for OPC-Newly Inserted) |
| 4. | Para IV (iv) | Securities (other than shares and debentures) (not applicable to OPC-Newly Inserted) |
| 5. | Para VIII Field A | Members/Class/Requisitioned/CLB/NCLT/Court Convened Meetings (not applicable to OPC-Newly Inserted) |
| 6. | Para VIII Field B | Board Meetings (not applicable for OPC-Newly Inserted) |
| 7. | Para VIII Field C | Attendance of Directors (not applicable for OPC-Newly Inserted) |
| 8. | New attachment | List of Directors [Newly Inserted] |
| 9. | Certification part | Following new certification are required to be confirmed.
1. The company has not, since the date of the closure of the last financial year with reference to which the last return was submitted or in the case of a first return since the date of incorporation of the company, issued any invitation to the public to subscribe for any securities of the company. 2. Where the annual return discloses the fact that the number of members, (except in case of one person company), of the company exceeds two hundred, the excess consists wholly of persons who under second proviso to clause (ii) of sub-section (68) of section 2 of the Act are not to be included in reckoning the number of two hundred (seems relevant only for small companies). |
| 10. | Information not required to be provided in Form MGT-7A which was required in Form MGT-7 | 1. Whether shares listed on recognized Stock Exchange(s);
2. CIN of the Registrar and Transfer Agent; 3. Details of stock split/consolidation during the year (for each class of shares); 4. Secured Loans (including interest outstanding/accrued but not due for payment) excluding deposits; 5. Unsecured Loans (including interest outstanding/accrued but not due for payment) excluding deposits; 6. Deposit; 7. Details of directors and key managerial personnel; 8. Committee Meetings; 9. Number of CEO, CFO and Company secretary whose remuneration details to be entered |
Deletion of extract of annual return
Realizing that amended Section 92(3) of the Act did not provide any prescriptive power to MCA, Rule 12 has been substituted to provide that Annual Return is required to be filed with the Registrar upon payment of specified fees. While, the requirement to file Annual Return with the Registrar along with timelines has been provided in Section 92 (4), Rule 12 still provides a generic statement.
So, the positions stands clarified that companies will be required to upload the annual return on the website, if any, and provide the link thereof in the Board’s report.
Explanations relating to e-voting restored
Rule 20 of MGT Rules deals with voting through electronic means wherein it mandates the companies whose equity shares are listed on recognized stock exchange and who have not less than 1000 members to provide the facility of e-voting to the members in the general meeting. It exempted Nidhi companies from the requirement of providing e-voting facility to its members.
The original text of Rule 20 explained the following terms:
- Agency
- Cut-off date
- Cyber security
- Electronic voting system
- Remote e-voting
- Secured system
- Voting by electronic means
The above terms were omitted vide Companies (Management and Administration) Amendment Rules, 2016[6]. MCA has restored the same with the present amendment. Accordingly, the cut-off date will be not earlier than seven days before the date of general meeting, which was previously specified in the Rules.
Conclusion
The present amendment brings clarity and settles all questions relating to annual return and e-voting. Annexing extract of annual return is past. Whole of the annual return in Form MGT-7 or Form MGT – 7A as applicable, is required to be uploaded on the website of the company and web-link of the same to be provided in the Board’s Report.
[1]http://ebook.mca.gov.in/notificationdetail.aspx?acturl=TTbtgoimZaEriqvC1uq63cVI1aUKrmySF7pn3LWSIhRnwlDT+xFtqSRh8eE9YDYmTZpXWl/g6A+Dx/OT8agtKUclWEhfgK03TlnWLOuiGw6K1VTDhD8p3mpQTiLgy2ewBHNyAHD0wK1NTYvNTxvKE72myo++ycxQaipOFSzBIY4coKGinwHEcAFWj2Fn6hr6
[2] “small company” means a company, other than a public company whose paid-up share capital does not exceed two crore rupees and turnover as per profit and loss account for the immediately preceding financial year does not exceed twenty crore rupees
[3]http://ebook.mca.gov.in/notificationdetail.aspx?acturl=6CoJDC4uKVUR7C9Fl4rZdatyDbeJTqg3z9mihm9CxHHzu82fmWlMKzy8jPS04vbR
[4]http://ebook.mca.gov.in/notificationdetail.aspx?acturl=6CoJDC4uKVUR7C9Fl4rZdatyDbeJTqg3DZ3eKuS27Ryli2KQpdUJBX7LNlkBrkXwnB0Mo6W4iI/tFsp4nH5DYuXMxD09O4auZIWA0g9jbZU=
[5] https://www.mca.gov.in/Ministry/pdf/CompaniesMgmtAdminAmndtRules_05032021.pdf
[6]http://ebook.mca.gov.in/notificationdetail.aspx?acturl=6CoJDC4uKVUR7C9Fl4rZdatyDbeJTqg3DZ3eKuS27Ryli2KQpdUJBX7LNlkBrkXwnB0Mo6W4iI/tFsp4nH5DYuXMxD09O4auZIWA0g9jbZU=
Our other videos and write-ups may be accessed below:
Relating to above topics:
YouTube:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCgzB-ZviIMcuA_1uv6jATbg
Other write-up relating to corporate laws:
http://vinodkothari.com/category/corporate-laws/
MCA updates brings changes to the Annual Return
/0 Comments/in Amendments to the Companies Act 2013, Companies Act 2013, Corporate Laws, MCA, Uncategorized /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsEase of doing business: Debt listed companies slide down to unlisted companies
/11 Comments/in Amendments to the Companies Act 2013, Companies Act 2013, Corporate Laws, MCA /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsCompanies with listed but privately placed debt paper not to be regulated as ‘listed company’.
FCS Vinita Nair | Senior Partner, Vinod Kothari & Company
With an intent to promote listing of securities and bond market, Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) in consultation with Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), intended to exclude certain class of companies from the definition of ‘listed company’ as defined under Section 2 (52) of Companies Act, 2013 (CA, 2013). The existing provisions of CA, 2013 applicable to a listed company did not distinguish between private companies and public companies. As a result, private companies were unintendedly subject to similar compliance as a public company. A browse through the list of companies with listed privately placed debentures, shows private companies abound in the list[1]. On the other hand, public companies that listed debt securities on a private placement basis, were subject to similar compliances as a public company issuing debt securities to public.
Accordingly, one of major amendments proposed in Companies (Amendment) Act, 2020 (CAA, 2020) was to revisit definition of listed company and provide a suitable carve out to certain class of companies to be determined in consultation with SEBI.
The rationale behind the carve out, as explained in the Report of the Company Law Committee of November, 2019[2] was that private companies listing its debt securities on any recognized stock exchange were subject to more stringent regulations compared to unlisted private companies viz. appointment of auditors, independent directors, woman directors, constitution of board committees etc. that were dis-incentivizing private companies from seeking listing of their debt securities. This was also discussed in the Report of Company Law Committee in 2016[3] wherein the Committee, while acknowledging the anomaly in the definition of listed company, felt that while the definition of the term ‘listed company’ need not be modified, the thresholds prescribed for private companies for corporate governance requirements may be reviewed. Further, the Committee proposed that specific exemptions under Section 464 of CA, 2013 could also be given to listed companies, other than equity listed companies, from certain corporate governance requirements prescribed in the Act.
Currently, companies issuing non- convertible debt securities (NCDS) or non-convertible redeemable preference shares (NCRPS) on a private placement basis, list the same under SEBI (Issue and Listing of Debt Securities Regulations, 2008 (SEBI ILDS) and SEBI (Issue and Listing of Non-Convertible Redeemable Preference Shares) Regulations, 2013 (SEBI ILNCRPS) respectively and are regarded as ‘listed company’ for the provisions of CA, 2013.
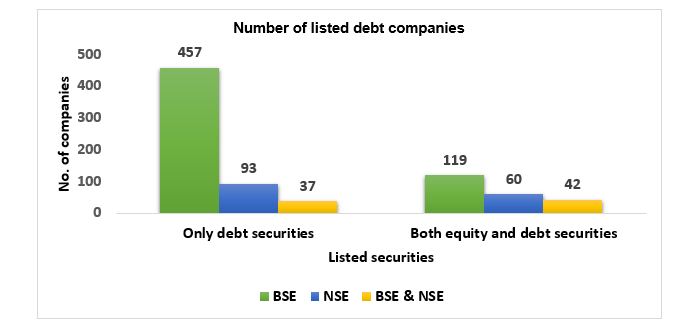
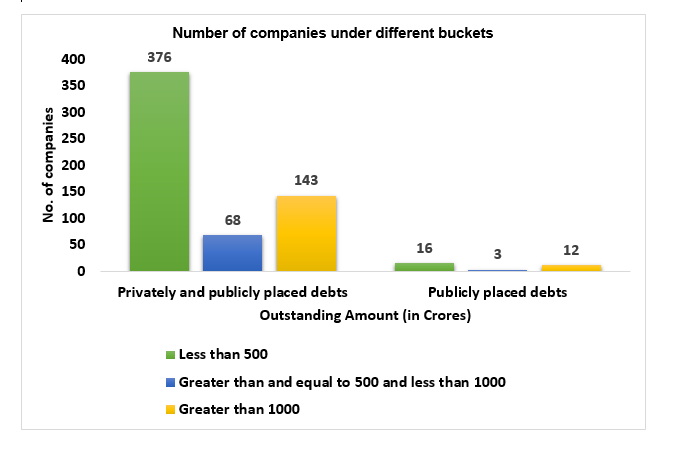
Total number of companies with listed debt
Number of companies, which come under different buckets as per the outstanding value of listed Debt Securities (as per face value) as on December 31, 2020
Present amendment
While the amendment made in Section 2 (52) in the definition of ‘listed company’ was notified with effect from January 22, 2021[4], the class of companies were pending to be prescribed. Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) on February 19, 2021[5] notified Companies (Specification of Definition Details) Second Amendment Rules, 2021 effective from April 1, 2021 to insert Rule 2A excluding following class of companies from the definition of ‘listed company’ under CA, 2013
- Public companies with listed NCDS issued on private placement basis in terms of SEBI ILDS;
- Public companies with listed NCRPS issued on private placement basis in terms of SEBI ILNCRPS;
- Public companies with listed NCDS and NCRPRS issued on private placement basis in terms of SEBI ILDS and SEBI ILNCRPS respectively;
- Private companies with listed NCDS in terms of SEBI ILDS.
- Public companies with equity shares exclusively listed on stock exchanges in permissible foreign jurisdictions under Section 23 (3) of CA, 2013.
Point to note here is that companies with listed commercial papers were anyways outside the purview of listed companies as commercial papers are excluded from the definition of debentures.
Listed company post amendment
Post amendment, the definition of listed company will mainly comprise of public companies offering securities to public i.e. having listed equity shares in India (with or without ADR/GDR listed overseas), listed debt securities pursuant to public issue or listed NCRPS pursuant to public issue.
Compliances for listed company under CA, 2013
A listed company is required to ensure following additional compliances under CA, 2013:
| Amount in Rs/ Other specification | Section No. | Rule No. | Brief of the provision | Other thresholds under CA, 2013 |
| 1. Provisions/ exemptions applicable to all listed companies | ||||
| Exemption for creation of Debenture Redemption Reserve (DRR) | 71 | 18 (7) (b) (iii) (B) of SHA Rules | Listed NBFCs need not create DRR for privately placed and public issue of debentures. | Refer discussion below |
| Creation of Debenture Redemption Fund (DRF) | 71(4) | Rule 18(7)(b)(v) of SHA Rules as amended. | No requirement for creation of DRF by listed companies issuing debenture on private placement basis. | Refer discussion below |
| Annual return | 92 | 11 of MGT Rules
|
Company to file Annual Return certified by a PCS in Form MGT-8 | Applicable to Company with
|
| Records in electronic form | 120 | 27 of MGT Rules | Company may maintain records in electronic form.
Note: Whether companies other than those specified have the option to maintain in electronic form, is not clear. |
Company having not less than 1000 shareholders, debenture holders and other security holders. |
| Investigation by NFRA
|
132 | Rule 3(1)(b) of NFRA Rules | NFRA shall undertake investigation or conduct quality review of audit. |
|
| Statement in Board report indicating manner of Board evaluation | 134(3) | 8 (4) of AOC Rules
|
A statement indicating manner in which formal evaluation of Board, committee and individual directors has been done by Board needs to be included in Board’s report. | Public company having a paid up share capital of Rs. 25 crore or more calculated at the end of the preceding financial year. |
| Financial statements in electronic form | 136 | 11
of AOC Rules |
Financial statements may be sent in electronic format. | Public companies which have
|
| Internal auditor | 138 | 13
of AOC Rules |
Appointment of internal auditor or a firm of internal auditors to conduct internal audit. |
|
| Appt/ re-appt of Auditor | 139
(2) |
5 of ADT Rules
|
Restriction on term of appointment or reappointment of auditor. Rotation of Statutory Auditors mandatory. |
|
| Woman Director | 149
(1) |
3 of DIR Rules
|
Appointment of a Woman Director on the Board.
Any intermittent vacancy of a woman director shall be filled-up by the Board at the earliest but not later than immediate next Board meeting or three months from the date of such vacancy whichever is later. |
Public company having –
|
| Small shareholder director | 151 | 7 of DIR Rules
|
May appoint a small shareholder director suo moto or upon notice from shareholder. | – |
| Vigil mechanism | 177 | 7 of MBP Rules
|
Company to establish vigil mechanism for their directors and employees to report genuine concerns. |
|
| Disclosure in Board’s Report | 197
(12) |
5 of MR Rules
|
Disclosure in Board’s report regarding ratio of the remuneration of each director to the median employee’s remuneration and such other details as prescribed in the Rules. | – |
| Appointment of KMP | 203 | 8 of MR Rules | Appointment of whole-time key managerial personnel.
|
|
| Secretarial Audit Report | 204 | 9(2) of MR Rules
|
Shall annex with its Board’s report a secretarial audit report, given by a company secretary in practice |
|
| 2. Provisions applicable only to a listed public company | ||||
| Report on Annual General meeting | 121 | 31 of MGT Rules
|
Report on AGM to be filed with the Registrar in eForm MGT-15. | – |
| Independent Director | 149
(4) |
4 of DIR Rules
|
Atleast 1/3rd of total number of Board members shall be independent directors. |
|
| Constitution of certain committees | 177 & 178 | 6 of MBP Rules
|
Constitution of Audit Committee and Nomination and Remuneration Committee. |
|
With the present amendment, the class of companies provided above will not be required to ensure aforesaid compliances unless it meets other criteria/ thresholds prescribed for respective compliance.
As evident from the table above, a public company will hardly have any exemptions if it meets any of the thresholds specified. While the intent of exempting class of companies is benign, it will be of some benefit to public companies only if the other thresholds are also revised. While, the holy wish is for ease of doing business, static thresholds prescribed in 2013 needs to be revisited to assess the adequacy and the intent to regulate such class of companies. For e.g. public companies having paid up capital of 10 crore or borrowing of Rs. 50 crore is a very common phenomena.
Additionally, in case the sectoral regulator prescribes composition of committee or induction of independent directors or other corporate governance requirement, those will override the exemptions.
Applicability of DRR and DRF[6]
Section 71(4) read with Rule 18(1)(c) of the Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Rules, 2014 (SHA Rules) requires every company issuing debentures to create a Debenture Redemption Reserve (DRR) of 10% (as the case maybe) of outstanding value of debentures for the purpose of redemption of such debentures.
Some class of companies as prescribed, has to either deposit, before April 30th each year, in a scheduled bank account, a sum of at least 15% of the amount of its debentures maturing during the year ending on 31st March of next year or invest in one or more securities enlisted in Rule 18(1)(c) of SHA (DRF).
Pursuant to the present amendment, it is important to ascertain applicability of creation of DRR and DRF in terms of CA, 2013. The exemption in relation to DRR and DRF was applicable to listed companies in case of private placement. While NBFCs continue to enjoy exemption even in case of unlisted companies, pursuant to the present amendment Non-NBFCs listing NCDS will not be eligible to avail the benefit of the said exemption and will be required to maintain DRR and DRF.
The intent of MCA at the time of amending Rule 18 of Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Rules, 2014 was to extend the exemption to all listed companies i.e. companies having securities listed on stock exchange, in case of privately placed debentures, from maintenance of DRR and DRF.
The intent behind amending the definition of ‘listed company’ under 2 (52) was to reduce the compliance burden of debt listed entities that were regarded as listed entities merely by virtue of listing the privately placed debentures.
The amendment to the definition of ‘listed company’ was subsequent and the same has resulted in an anomaly as corresponding amendment has not been carried out in Rule 18 of SHA Rules. The intent behind mandating DRR and DRF requirement, in case of private placement, was for unlisted companies with unlisted debt and not for unlisted companies with listed debt.
This is surely a matter of representation to be made to MCA as the gap seems inadvertent and not intentional.
Applicability of Rule 9A of PAS Rules
Section 29 of CA, 2013 read with Rule 9A of Companies (Prospectus and Allotment of Securities) Rules, 2014 (PAS Rules)[7] effective from October 2, 2018 mandates unlisted public companies to issue the securities only in dematerialised form and facilitate dematerialisation of all its existing securities. Physical transfer of securities is prohibited for unlisted public companies. Compliance with the said provisions are exempt only in case of a Nidhi, Government company and wholly owned subsidiary.
Pursuant to amendment in the definition of listed company, public companies that were originally exempted from the requirements by virtue of being a listed company, will now be required to comply with Section 29 and Rule 9A.
Status under Listing Regulations and SEBI ILDS
‘Listed entity’ as defined under Reg. 2 (p) of SEBI (Listing Obligations and Disclosures Requirements) Regulations, 2015 (Listing Regulations) means an entity which has listed, on a recognised stock exchange(s), the designated securities issued by it or designated securities issued under schemes managed by it, in accordance with the listing agreement entered into between the entity and the recognised stock exchange(s).
The present carve out under CA, 2013 will not result in any carve out for compliances under Listing Regulations as Listing Regulations anyways provides separate set of compliances equity listed companies (Chapter IV) and only NCDS/NCRPS listed companies ( Chapter V) and those with equity and debt listed (Chapter VI).
Further, SEBI Circulars issued from time to time under SEBI ILDS are addressed to all listed entities who have listed their debt securities or issuers who propose to list their debt securities.
Status under PIT Regulations
SEBI (Prohibition of Insider Trading) Regulations, 2015 (PIT Regulations) does not define the term ‘listed company’, however, applies to listed company and securities of an unlisted company proposed to be listed. The definition of ‘proposed to be listed’ is as hereunder:
“proposed to be listed” shall include securities of an unlisted company:
(i) if such unlisted company has filed offer documents or other documents, as the case may be, with the Board, stock exchange(s) or registrar of companies in connection with the listing; or
(ii) if such unlisted company is getting listed pursuant to any merger or amalgamation and has filed a copy of such scheme of merger or amalgamation under the Companies Act, 2013.”
The term ‘listed company’ is not being defined under PIT Regulations and therefore, the definition under CA, 2013 should be referred pursuant to Reg. 2 (2) of PIT Regulations[8]. In that case, PIT Regulations will apply only in case of securities issued by a listed company or a company that is proposed to become a ‘listed company’. Accordingly, only debt/ NCRPS listed companies need not comply with requirements of PIT Regulations. SEBI should consider furnishing a clarification in this regard.
However, that is not the intent of law. If a security is listed, its price is subject to change and be impacted by price sensitive information. Accordingly, such exclusively debt/ NCRPS listed companies, on account of private placement of securities, should continue to comply with the requirements of PIT Regulations. SEBI may also consider furnishing a clarification in this regard.
Conclusion
While, the present amendment expands the originally envisaged carve out for private companies to public companies as well, given the other static thresholds prescribed under CA, 2013 public companies have little reason to rejoice. Exemption to comply with PIT Regulations may be a huge relief, however, there is a need for SEBI to clarify the position given the intent of law.
Further, it is very crucial that MCA revisits DRR and DRF related provision for privately placed NCDS and consider to relax the same especially for the benefit of Non-NBFCs. Lastly, suitability of the exemption in case of companies exclusively listed in foreign jurisdiction will be required to be evaluated after a certain lapse of time as the provisions have been recently inserted in CA, 2013.
Our other videos and write-ups may be accessed below:
YouTube:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCgzB-ZviIMcuA_1uv6jATbg
Other write-up relating to corporate laws:
http://vinodkothari.com/category/corporate-laws/
Our our Book on Law and Practice Relating to Corporate Bonds and Debentures, authored by Ms. Vinita Nair Dedhia, Senior Partner and Mr. Abhirup Ghosh, Partner can be ordered though the below link:
[1] https://www.bseindia.com/markets/debt/debt_instruments.aspx?curpage=4&select_alp=all&select_ord=1
[2] Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India, ‘Report of the Companies Law Committee’
(November 2019) para 2.
[3] Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India, ‘Report of the Companies Law Committee’
(February 2016) para 1.13.
[4] http://www.mca.gov.in/Ministry/pdf/CommencementNotification_23012021.pdf
[5] http://egazette.nic.in/WriteReadData/2021/225287.pdf
[6] Refer our write up ‘Easing of DRF’ and ‘Provisions relating to DVR & DRR- stands amended’ by CS Smriti Wadehra.
[7] Discussed in our write up ‘Physical to Demat: A move from opacity to transparency’.
[8] Words and expressions used and not defined in these regulations but defined in the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992 (15 of 1992), the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956 (42 of 1956), the Depositories Act, 1996 (22 of 1996) or the Companies Act, 2013 (18 of 2013) and rules and regulations made thereunder shall have the meanings respectively assigned to them in those legislation.
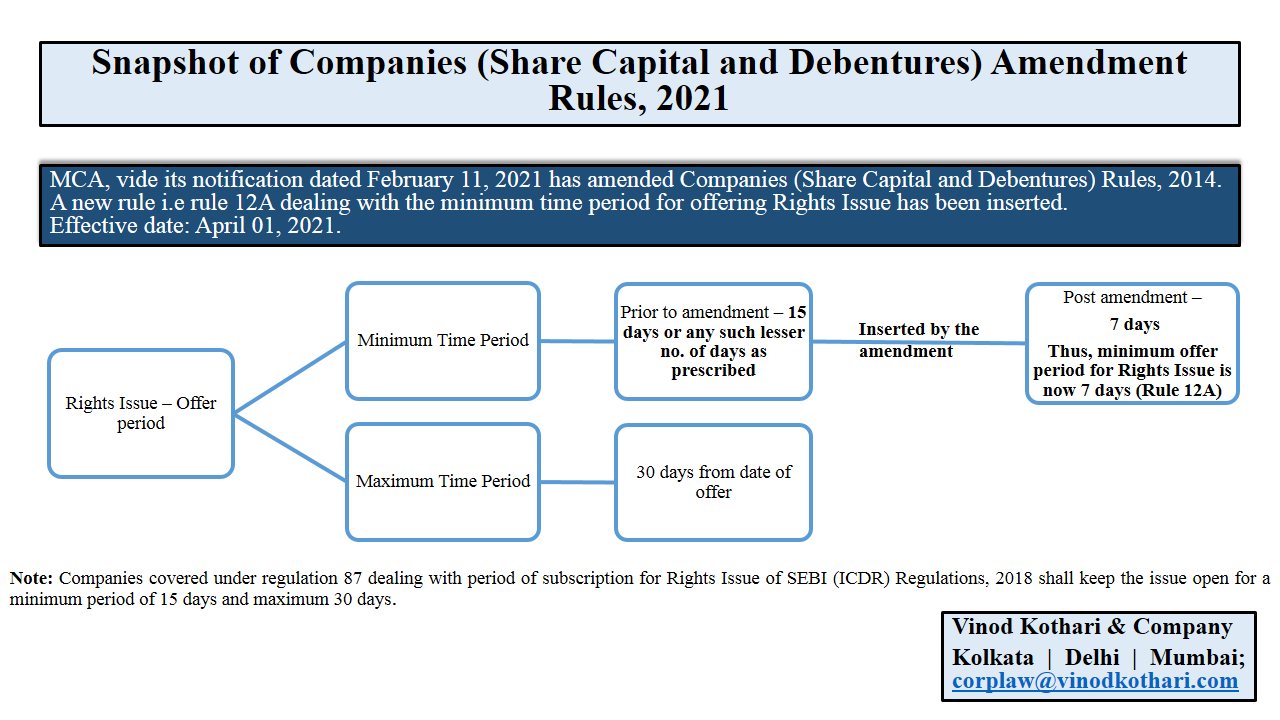
Snapshot of Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Amendment Rules, 2021
/0 Comments/in Amendments to the Companies Act 2013, Companies Act 2013, Corporate Laws /by Vinod Kothari ConsultantsVinod Kothari & Company
Below is a short snippet on Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Amendment Rules, 2021.